|
|
Perivesical (Prevesical) Fluid Collection
Molar Tooth Sign
General Considerations
- Extraperitoneal pelvic fluid collections have been characterized as “molar-tooth” in appearance
- The “crown” lies anterior to the urinary bladder between the umbilicovesical fascia and the transversalis fascia of the anterior abdominal wall
- The bladder is displaced posteriorly
- The “root” of the “tooth” extends posteriorly the fascia and the perineum or parietal pelvic fascia inferiorly
- The bladder is frequently displaced from the midline, since the “roots” of the collection are usually asymmetrical
- This compartment is continuous with the infrarenal extraperitoneal compartment
- The prevesical space is also continuous with the rectus sheath, presacral space and the femoral sheath
Differential Diagnosis
- Molar tooth sign is also applied to the appearance of the midbrain on axial CT with elongated superior cerebellar peduncles
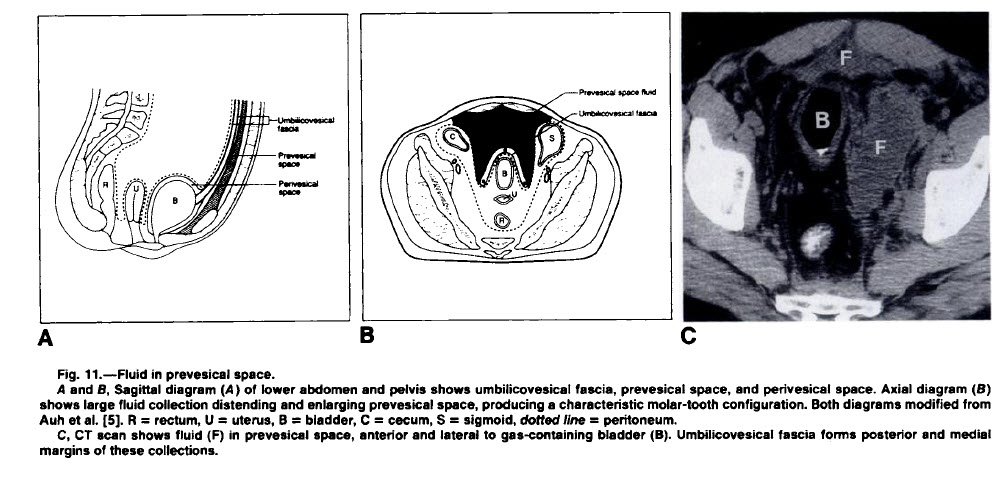
From CT of Extraperitoneal Space: Normal Anatomy and Fluid Collections. Radiology, 1992
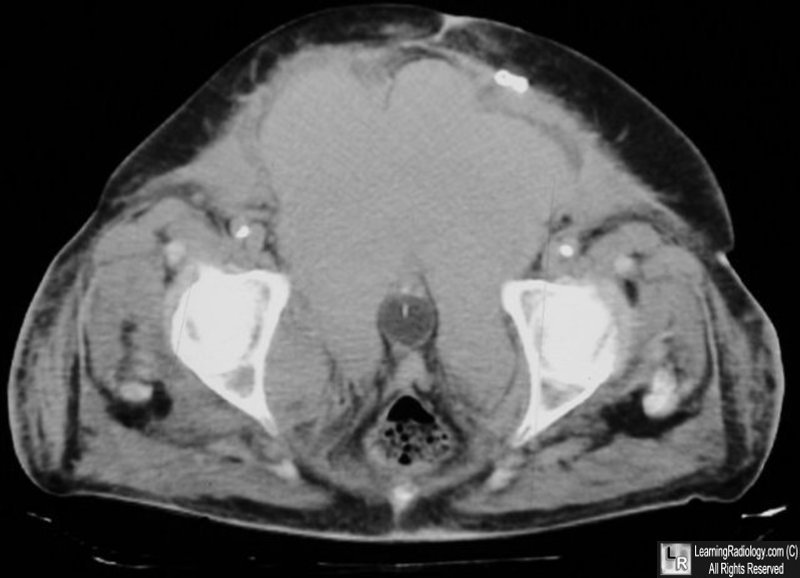
Large prevesical fluid collection. "Molar tooth sign." There is a Foley catheter in a collapsed urinary bladder which is displaced posteriorly and compressed lateral by a large prevesical fluid collection.
CT of Extraperitoneal Space: Normal Anatomy and Fluid Collections. M Korbkin; P Silverman, LE Quint and IR Francis.AJR 159:933-941, November 1992.
Extraperitoneal Paravesical Spaces: CT Delineation and US Correlation. YH Auh, WA Rubenstein, M Scneider, JM Reckler, JP Whalen and E Kazam. Radiology 1986: 159: 319-328.
|
|
|