|
|
Glioblastoma Multiforme
GBM
Gliomas of the brain
- Most common primary supratentorial, intraaxial mass in adult
- Gliomas account for 35-45% of all intracranial tumors and glioblastoma multiforme accounts for more than half of them, astrocytomas about 20% and the remainder split between ependymomas, medulloblastoma, oligodendroglioma
- Glioblastoma multiforme has the worst prognosis of all gliomas
- Occurs more commonly in males between 65-75 years of age, especially in the frontal and temporal lobes
- Recognizing glioblastoma multiforme
- As the most aggressive of tumors, glioblastoma multiforme frequently demonstrates necrosis within the tumor
- The tumor infiltrates the surrounding brain tissue, frequently crossing the white matter tracts of the corpus callosum to the opposite cerebral hemisphere producing a pattern called a butterfly glioma
- It tends to produce considerable vasogenic edema and mass effect and contrast enhances, at least in part
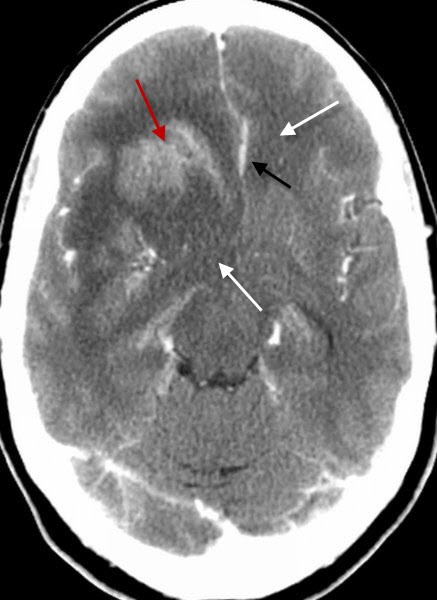
Glioblastoma Multiforme. There is a large contrast-enhancing mass in the right frontal region (red arrow) with a large amount of surrounding vasogenic edema (white arrows) and shift of the falx to the left from mass effect (black arrow).
|
|
|