|
|
Treated Hodgkin Lymphoma
General Considerations
- In the chest, Hodgkin lymphoma most often involves the mediastinum, especially the anterior mediastinal nodes
- External beam radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy are common treatments for the disease
- Calcification of mediastinal nodes previously involved with Hodgkin lymphoma occurs in 2-8% of those treated with either previous radiation therapy or chemotherapy
- It usually occurs at least 8 months after treatment, but has been reported later
- Most reported patients with calcification in Hodgkin's lymphoma had the nodular sclerosing type
- It is presumed the calcification is a result of cellular necrosis, hemorrhage and fibrosis in degenerating tumor
Imaging Findings
- It is very rare for lymph nodes to be calcified pre-treatment in Hodgkin lymphoma
- Calcification can either be punctate or become coalescent and dense
Differential Diagnosis
- TB
- Silicosis
- Histoplasmosis
- Coccidioidomycosis
Prognosis
- There is a suggestion that post-treatment nodal calcification is associated with a better prognosis
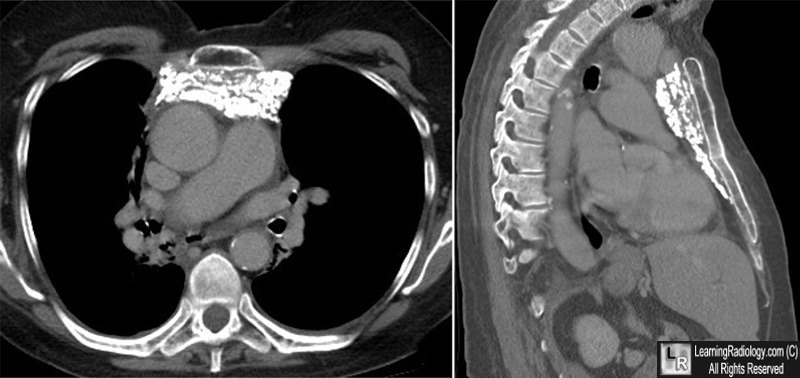
Hodgkin Lymphoma, treated. Unenhanced axial and sagittal images of a chest CT scan show numerous, punctate calcifications in the anterior mediastinum representing calcified, lymph nodes in a patient treated with radiation therapy for Hodgkin Disease 6 years earlier.
Calcification in Lymphoma Occurring Before Therapy: CT Features and Clinical Correlation. S Apter, A Avigdor, G Gayer, O Portnoy, R Zissin and M Hertz. AJR, April 2002, Vol. 178, Number 4.
Lymph Node Calcification in Hodgkin’s Disease after Chemotherapy. M Bertrand, JTT Chen and HI Libshitz. AJR. 129: 1108-1110, Dec 1977.
|
|
|