|
|
Retropharyngeal Air
Perforated Pharynx
- Causes
- Trauma to esophagus or trachea
- Penetrating injuries from weapons
- Perforation from within
- Mediastinal emphysema which tracks up into neck
- Retropharyngeal abscess from gas-forming organism
- Clinical findings
- Dysphagia
- Odynophagia
- Neck tenderness
- Crepitus
- Hematemesis
- Imaging findings
- Streaks of air in the soft tissues of the neck
- Anterior displacement of the pharynx
- Associated pneumothorax possible
- Cervical or mediastinal air is seen in 60% of cases of ruptured esophagus
- Treatment
- If hemodynamically stable, watch
- If hemodynamically unstable, emergent surgery
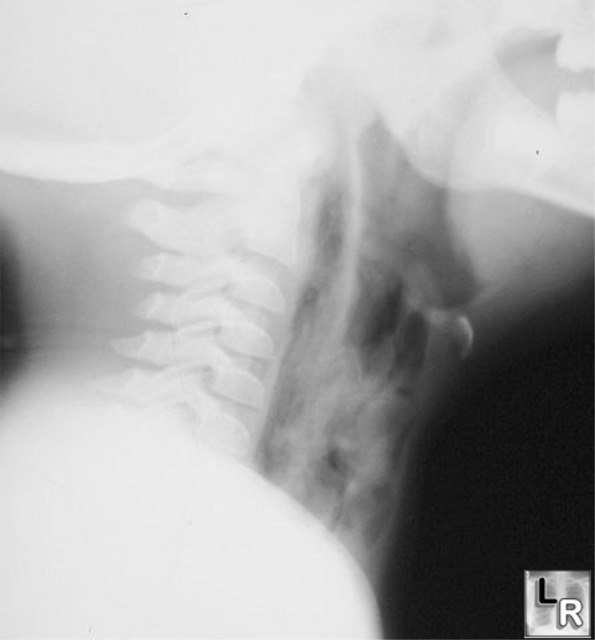
Perforated Pharynx. Streaky lucencies seen behind the airway represents
retropharyngeal air which in this case was secondary to
perforation of the cervical esophagus by a chicken bone.
|
|
|