|
|
Pseudomyxoma Peritonei
Submitted by Paurush Shah, MSIV
General Considerations
- Diffuse collections of gelatinous material in the abdomen and pelvis and mucinous implants on the peritoneal surfaces
- In almost all cases, it is from a ruptured mucinous tumor of the appendix
- Spectrum from more benign to more malignant findings
- Other causes may include tumors of the large and small bowel, lung, breast, pancreas, stomach, bile ducts, gallbladder, and fallopian tubes/ovary
- More common in females
- Results in mass effect on organs
- Also known as “Jelly Belly”
Clinical Findings
- Indolent course
- Most common finding in both males and females is increasing abdominal girth (40%)
- Next most common in males is inguinal hernia (25%)
- Next most common in females are bilateral or unilateral ovarian masses
Imaging Findings
- On CT scan, mucinous material has similar density to fat and appears heterogeneous.
- Scalloped surface of the liver, spleen, and mesentery
- Rim-like calcifications are common
- Undersurface of the diaphragm may be thickened by large cystic masses of mucinous tumor
- Peripheral location of tumor within the abdomen with central displacement of the small bowel and mesentery
- Narrowing, but usually not obstruction, of lumen of GI tract at
- Ileocecal valve
- Pouch of Douglas
- Usually spares the small bowel
- Ultrasound may show large, immobile ascites with septations and increased echogenicity
Differential Diagnosis
- Peritoneal mucinous carcinomatosis
- Produces picture similar to pseudomyxoma peritonei
- Implanted (signet-ring) cells are malignant
- Extensive small bowel implantation
- Worse prognosis
Treatment
- Repeated surgical debulking to decrease abdominal pressure and remove mucinous material build-up
- Heated intraperitoneal chemotherapy is controversial and is being investigated currently
Complications
- Mucous buildup, increased abdominal pressure, bowel obstruction, renal failure, death
Prognosis
- Median survival of 2 years has been reported although newer treatments are improving survival
- 25% mortality due to intestinal obstruction and renal failure
 
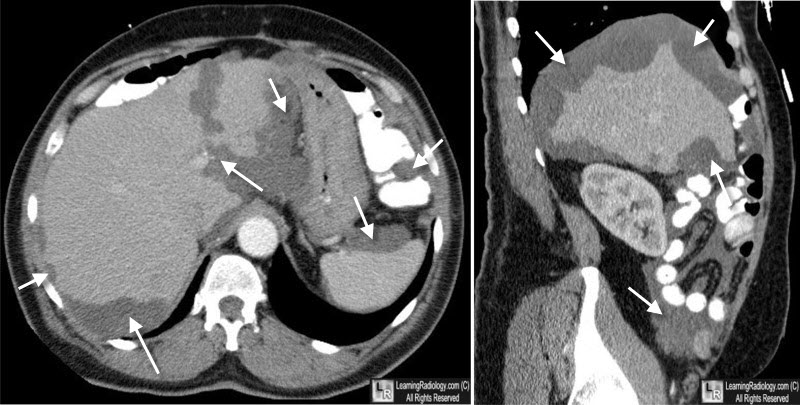
Pseudomyxoma peritonei. Axial contrast-enhanced CT images of the abdomen and pelvis
demonstrate lobulated, low-attenuation soft tissue masses scalloping the borders of the liver, spleen and along mesentery. The cause was a mucin-producing tumor of the appendix.
For more information, click on the link if you see this icon 
For this same photo without the annotations, click here and here
Swanson, Richard et al. “Cancer of the appendix and pseudomyxoma peritonei.” Jan 13, 2009 uptodate.com
MedScape Radiology
|
|
|