|
|
Mesenteric Ischemia
Submitted by Jonathon Dorff, MD
- Acute interruption of blood flow to
small or large intestine
- Causes:
- Arterial embolism
- Superior mesenteric artery most
commonly involved
- Arterial thrombosis
- Nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia
- Low cardiac output state with
diffuse mesenteric vasoconstriction
- Mesenteric venous thrombosis
- Risk Factors
- Atrial fibrillation/flutter
- Recent acute MI
- Ventricular aneurysm
- Cardiomyopathies
- Valvular disease
- Hypovolemia or hypotension (sepsis)
- Coagulation disorders or malignancy
- Pancreatitis
- Portal hypertension/cirrhosis
- Medications
- Vasopressor medications
- Beta-blockers
- Digoxin
- Diuretics
- Clinical signs and symptoms
- Severe abdominal pain out of
proportion to physical exam
- Pain initially of a visceral nature
and poorly localized
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- GI bleeding may be present
- Imaging
- Plain abdominal radiographs
(abnormal in 20-60% of cases)
- Thumbprinting
- Non-specific finding indicating
intestinal wall edema with hemorrhage in the setting
of acute mesenteric ischemia
- Pneumatosis
- Portal venous gas
- Pneumoperitoneum
- All are indicative of infarcted bowel
- CT
- Bowel wall thickening from
edema or hemorrhage
- Lack of enhancement indicates
infarction
- Pneumatosis, portal venous gas,
pneumoperitoneum
- Intraluminal thrombus in involved
vessel
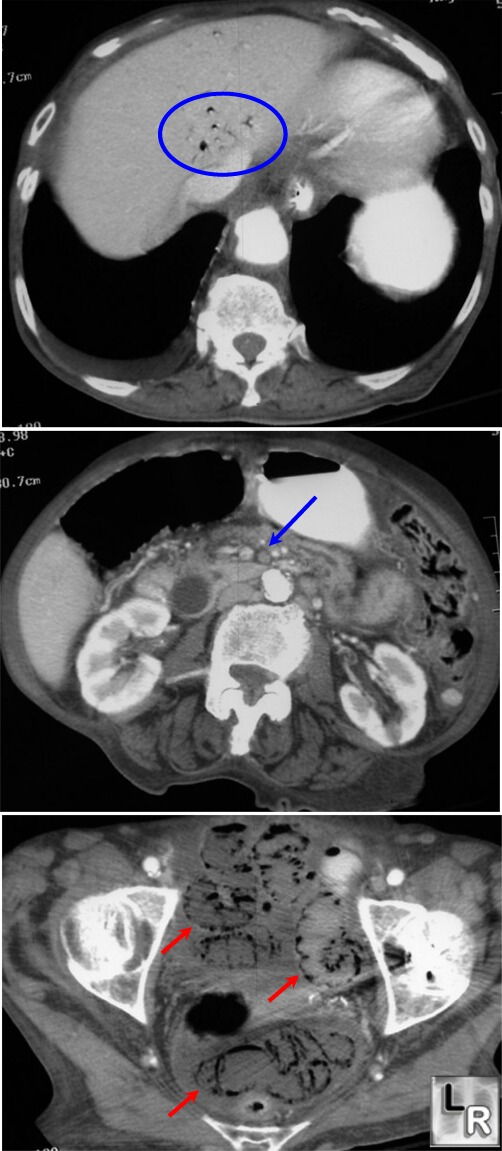
Mesenteric Vascular Ischemia. Top CT image shows gas in portal venous system (blue circle);
center image shows absence of contrast
in superior mesenteric artery due to thrombosis of this vessel (blue arrow)
[The patient also has a markedly dilated common duct, not related to
mesenteric ischemia]; lower image shows extensive pneumatosis intestinalis
(red arrows)
- Mesenteric angiogram
- Can distinguish between arterial
embolic and thrombotic causes of acute mesenteric ischemia
- Treatment
- Mesenteric angiogram
- Vasodilator therapy
- Thrombectomy/Embolectomy
- Surgery
- Thrombectomy/Embolectomy
- Arterial bypass
- Resection of necrotic bowel
- Complications
- Sepsis/septic shock
- Multiple system organ failure
- Death
- Mortality
- 70-90% overall
- From arterial embolism: 60-80%
- From arterial thrombosis: 70-100%
- From nonocclusive mesenteric ischemia: 40%
- From mesenteric venous thrombosis:
25-30%
|
|
|