|
|
Large Bowel Obstruction
General Considerations
- In this case, we are talking about mechanical obstruction of the colon
- Causes include
- Carcinoma (60%)
- Diverticulitis (20%)
- Volvulus
- Strictures, such as from Crohn disease
- Fecal impaction
- Hernia
- Imperforate anus or meconium ileus in pediatric population
- Increases in prevalence with age
Clinical Findings
- Abdominal distension
- Nausea and vomiting
- Crampy abdominal pain
- Constipation, diarrhea, change in bowel habits
Imaging Findings
- Air in dilated colon, usually to the point of obstruction
- Dilated cecum
- Small bowel is not dilated unless ileo-cecal valve becomes incompetent and air flows backwards from colon to small bowel
- CT is imaging study of choice
Differential Diagnosis
- Generalized ileus – air in dilated large and small bowel down to and including rectosigmoid
- Ogilvie Syndrome (pseudo-obstruction) – absent or reduced bowel sounds, usually associated with other co-morbidities
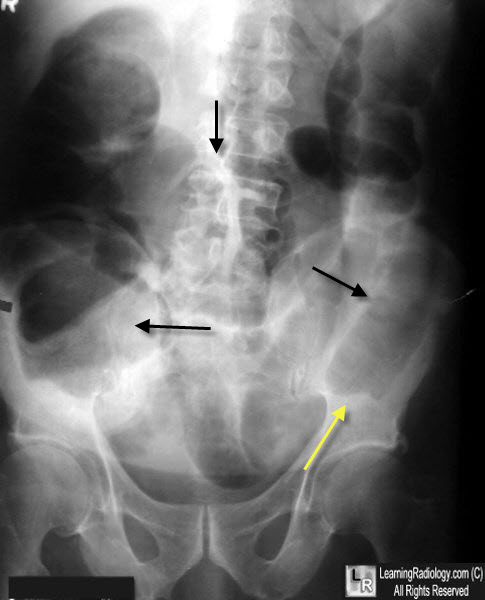
Large Bowel Obstruction. The ascending, transverse and proximal descending colon (black arrows) are all dilated. There is an abrupt cut-ff of the air column in the distal descending colon (red arrow). This was the site of a colonic carcinoma, which was removed..
|
|
|