|
|
Corkscrew Esophagus
Rosary Bead Esophagus, Diffuse Esophageal Spasm
General Considerations
- One of a group of spastic esophageal motility disorders including achalasia, nutcracker esophagus and scleroderma esophagus
- Representing uncoordinated tertiary contractions of the esophagus, corkscrew esophagus is associated with diffuse esophageal spasm
- Diffuse esophageal spasm (DES) may be present, however, without the appearance of a corkscrew esophagus
- Usually occurs over the age of 50
- Normal esophageal manometry is present, at least intermittently
Clinical Findings
- Chest pain is the hallmark
- Dysphagia
- Heartburn
- Regurgitation
Imaging Findings
- Most barium swallows will be abnormal
- The classical but uncommon finding is the corkscrew appearance, especially of the distal esophagus
- The lower esophageal sphincter, unlike in achalasia, will relax normally
- Pseudodiverticula may be present
Differential Diagnosis
- Hypercontracting esophagus (nutcracker esophagus) has normal peristalsis but high manometric intra-esophageal pressures
- Barium esophagram will be normal or show dysmotility
Treatment
- Proton pump inhibitors, nitroglycerin, calcium channel blockers and botulinum toxin have been used to treat
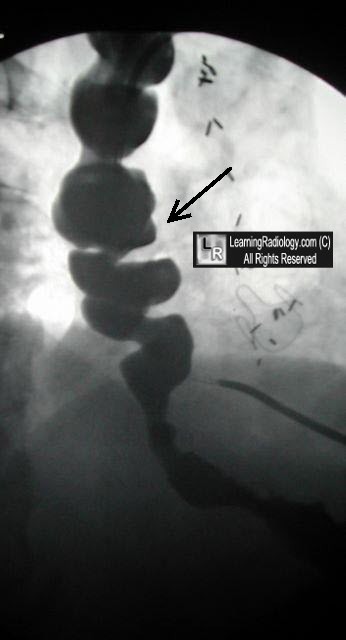
Corkscrew Esophagus, Diffuse Esophageal Spasm. There are multiple tertiary contractions in the distal esophagus (black arrow) on this barium esophagram. Barium passes through the lower esophageal sphincter into the stomach.
Esophageal Motility Disorders Treatment & Management. Eric A Gaumnitz, and Abdullah Fayyad. eMedicine
|
|
|