|
Carcinoma of the Esophagus
• Predisposing factors
• Men>women
• Achalasia (polypoid mass in middle or distal third)
• Asbestosis
• Plummer-Vinson syndrome (iron deficiency anemia, webs)
• Barrett esophagus (columnar metaplasia of the distal esophagus 2°
chronic GE reflux)
• Celiac disease
• Lye stricture
• Alcoholism
• Smoking
• Prior radiation
• Oral/pharyngeal cancer
• Tylosis palmaris-hyperkeratosi of the palms and the soles
Histology
• Squamous cell ca (95%)
• Adenocarcinoma arising
from heterotopic gastric mucosa or columnar-lined epithelium (Barrett’s)
• Carcinosarcoma=spindle-cell
carcinoma
• Location usually middle third of esophagus
•
Large, bulky, polypoid intraluminal mass which may be pedunculated
• Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
• Spread
is facilitated by the esophagus’ lack of a serosa
Symptoms
• Dysphagia
• Weight loss
• Retrosternal pain
• Regurgitation
Location
Upper
1/3
|
20%
|
Middle
1/3
|
50%
|
Lower
1/3
|
30%
|
Radiologic
types
·
Polypoid/fungating form
(most common)
Sessile, polyp
Apple-core lesion
·
Ulcerating form
Large ulcer within mass
·
Infiltrating form
Gradual narrowing resembling benign stricture
·
Varicoid
form=superficial spreading carcinoma
Thickened nodular folds looks like varices
• Squamous cell carcinomas of the distal esophagus almost never
invade the stomach whereas adenocarcinomas arising from a Barrett’s does
Metastases
• To lymphatics-especially supraclavicular nodes
• Hematogenous: lung, liver, adrenal
• About 5-10% of patients with esophageal ca will develop
esophageal-airway fistulae, frequently following XRT
Prognosis
• 3-20% 5 year survival
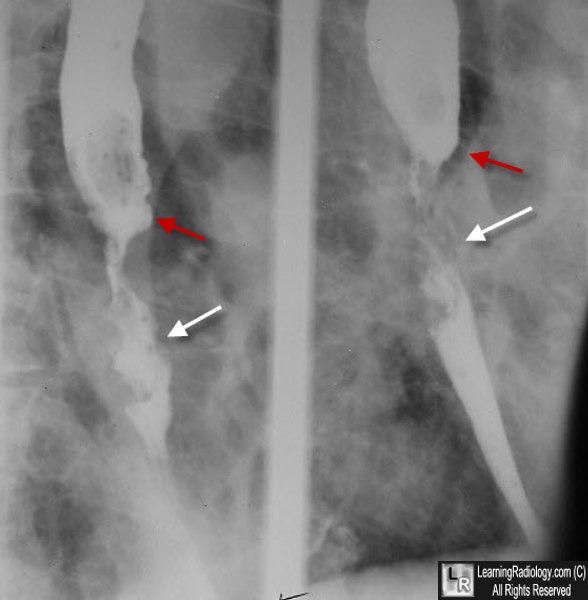
Carcinoma of the Esophagus. Two slightly different images of the distal esophagus from a barium swallow demonstrate an irregular, somewhat nodular filling defect (white arrows) stretching for a considerable part of the distal esophagus, narrowing the lumen. There is a shelf-like defect approximately where the tumor begins (red arrows).
|