|
|
Air in the Biliary System
Pneumobilia
General Considerations
- Air in the biliary tree, also known as pneumobilia
- Most frequently from the following causes
- Incompetent Sphincter of Oddi
- Recent instrumentation, as in ERCP, or surgery, as in spincterotomy
- Fistulous connection with the GI tract, as in gallstone ileus
- It is rarely due to gas-forming infection, as in cholangitis or emphysematous cholecystitis
Clinical Findings
- Usually benign or asymptomatic when caused by incompetent sphincter or surgery
Imaging Findings
- Several, air containing-tubular structures seen in the region of the hilus of the liver
- The common bile duct is frequently recognizable
- There may be other, left and right biliary radicals, filled with air
- Since air produces echogenic artifacts on ultrasound, pneumobilia is visible on US
Differential Diagnosis
- Portal venous gas
- Usually a more ominous finding than pneumobilia
- Can be differentiated by the peripheral nature of innumerable air-containing branching structures near the outer edge of the liver rather than centrally
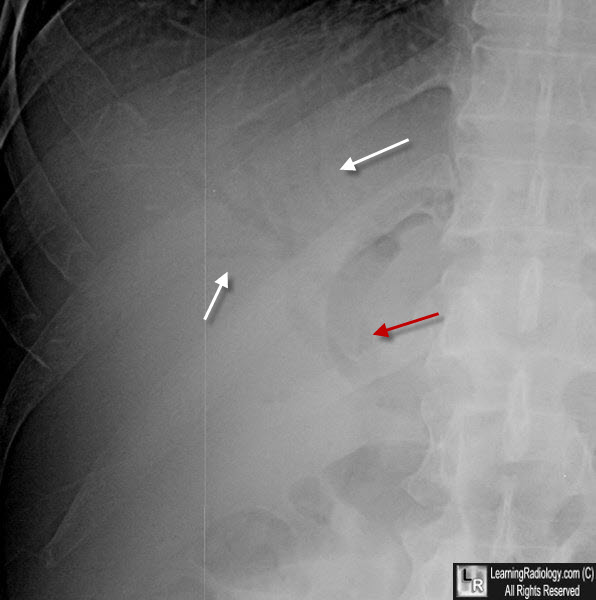
Air in the Biliary System. Close-up of the right upper quadrant shows a tubular structure containing air (red arrow) representing the common bile duct and several air-containing biliary radicals (white arrows).
The air-filled left hepatic duct: the saber sign as an aid to the radiographic diagnosis of pneumobilia.BJ Lewandowski, C Withers, and F Winsberg. Radiology. 1984;153 (2): 329-32.
|
|
|