|
|
Hemangioblastoma
- Benign neoplasm
- 80% found in cerebellum
- Remainder are located in spinal cord >
medulla > cerebrum
- Account for 10% of posterior fossa masses
(vestibular schwannomas and metastases rule here.)
- Most often occurs in ages 30 to 40
- Relationship to von Hippel-Lindau disease
- 20% occur in patients with von
Hippel-Lindau disease (multiple lesions).
- 35-60% of von Hippel-Lindau disease
patients have hemangioblastomas
- von Hippel-Lindau disease consists of
- Retinal, spinal, cerebellar and
medullary hemangioblastomas
- Renal cysts and carcinomas
- Pancreatic cysts
- Pheochromocytomas
- Papillary Cystadenoma of the epididymis
- Clinical findings
- Headache
- Ataxia
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Vertigo
- Polycythemia caused by increased
erythropoietin found in 40%.
- Spinal lesions may present with
subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Findings on CT and MRI:
- Cystic lesion in the cerebellum with an
avidly enhancing mural nodule (75%)
- Purely solid enhancing lesion (10%)
- Enhancing lesion with multiple cystic
areas (15%)
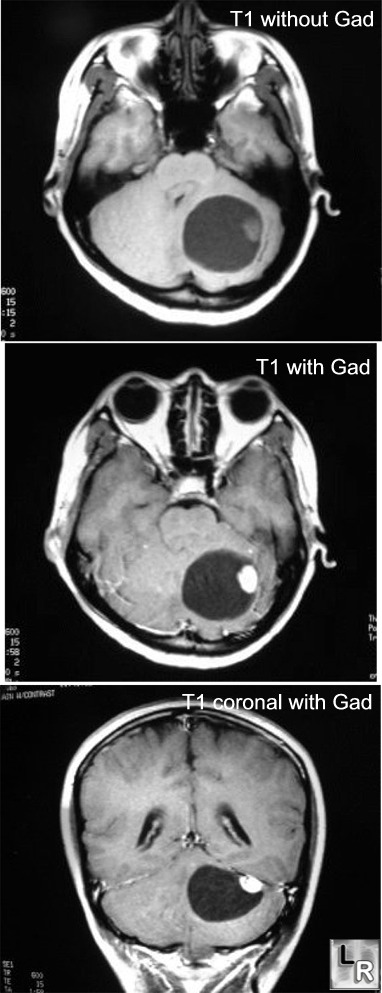
MRI of brain shows a cystic lesion in the cerebellum
with an enhancing nodule (post-Gadolinium)
- Findings on angiography:
- Vascular nodule within an avascular mass
- Serpentine vessels
- Treated with surgical removal of solid
nodule
- Cystic component is not neoplastic
- DDx:
o Similar appearance to Juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma
§ But that is typically found in patients 5 to 15 years
of age.
|
|
|