|
|
Subsegmental Atelectasis (SSA)
Discoid Atelectasis, Platelike Atelectasis
General Considerations
- Seen especially in post-operative patients, usually at the lung bases
- Can also be seen with pulmonary thromboembolic disease, obesity, ascites
- Believed to be caused by a decreased production or inactivation of surfactant which, when present normally, keeps the alveoli from collapsing by decreasing the surface tension
- Not caused by obstruction of bronchi
Clinical Findings
- Most patients have some form of splinting which prevents a full inspiration
- SSA is usually asymptomatic by itself; it is the result rather than the cause of limited inspiration
Imaging Findings
- Thin, linear opacities at one or both bases, 2-10 cm in length, usually horizontally oriented
- Crosses segmental boundaries
- May rarely occur in upper lobes and may be vertically oriented
- No associated signs of volume loss (no shift of fissures)
- Clears in a few days or less
Differential Diagnosis
- Linear scarring - may look the same on one radiograph; SSA will almost always clear in a few days; scarring will not
Treatment
- Incentive spirometry
- Chest physiotherapy
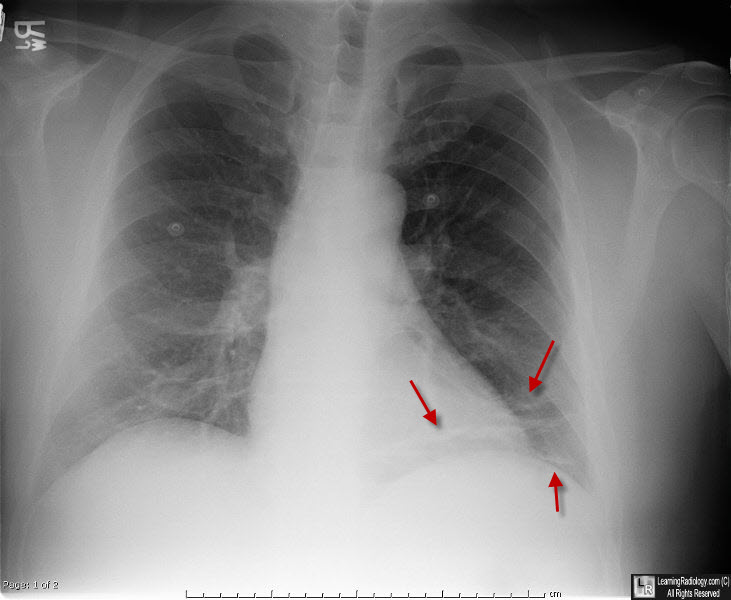
Subsegmental Atelectasis, Left Lung Base. There are multiple, thin, linear opacities (red arrows) at the left base oriented horizontally. The patient is post-operative colon surgery.
|
|
|