|
|
Right Lower Lobe (RLL) Atelectasis
General Considerations
- All types of atelectasis involve loss of volume in some or all of a lung with resultant increased density of the involved lung
- The atelectasis referred to here is that caused by bronchial obstruction, usually a tumor (i.e. a bronchogenic carcinoma), a foreign body or a mucus plug
- In asthmatics, chronic inflammation along with the thicker and more viscous mucus leads to mucous plugging and impaction
Imaging Findings of Right Lower Lobe Atelectasis
- Increase in density of the affected lung
- In the case of RLL atelectasis, triangular density at the right lung base that silhouettes the right hemidiaphragm but not the right heart border
- Displacement of the fissures or the mediastinum towards the atelectasis
- For RLL atelectasis, the major fissure is displaced downward and medially on the frontal view and downward and posteriorly on the lateral view
- Crowding of the vessels and bronchial tree in the area of volume loss
- Elevation of the hemidiaphragm
- The medial and posterior portions of the right hemidiaphragm may not be visible in RLL atelectasis because they are silhouetted by the collapsed lung above it
- Overaeration of the upper and middle lobes
- Downward displacement of the right hilum
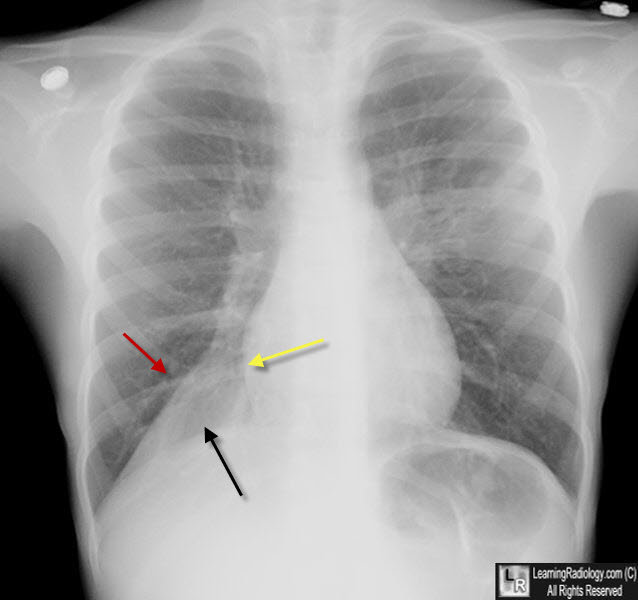
Atelectasis, Right Lower Lobe. There is a triangular or wedge-shaped density at the right lung base medially (black arrow) that displaces the major fissure inferiorly (red arrow), obscures the right hemidiaphragm and maintains the shadow of the right heart border (yellow arrow). The right hemithorax is filled by the overaerated right middle and upper lobes. The patient was an asthmatic and had a mucus plug in the RLL bronchus.
|
|
|