|
|
Posterior Mediastinal Masses
Neurogenic Tumors
Peripheral nerve origin
• Neurofibromas
• Neurilemomas (Schwannomas)
Sympathetic nerve origin
• Ganglioneuromas—usually benign
• Neuroblastomas—usually malignant
• Sympathicoblastomas—usually malignant
Paraganglionic cells
• Pheochromocytoma
• Chemodactomas (paragangliomas)—benign or malignant
-
In adults, neurofibroma and
neurilemomas (Schwannomas) are most common
-
Neurofibroma contains
Schwann cells plus nerve cells; occur in 3rd or 4th decade
-
Schwannoma
derived from sheath of Schwann without nerve cell
o
Produces “ iron-filings” appearance to sutures in the skull infiltrated
with tumor
Imaging
Other
posterior mediastinal masses
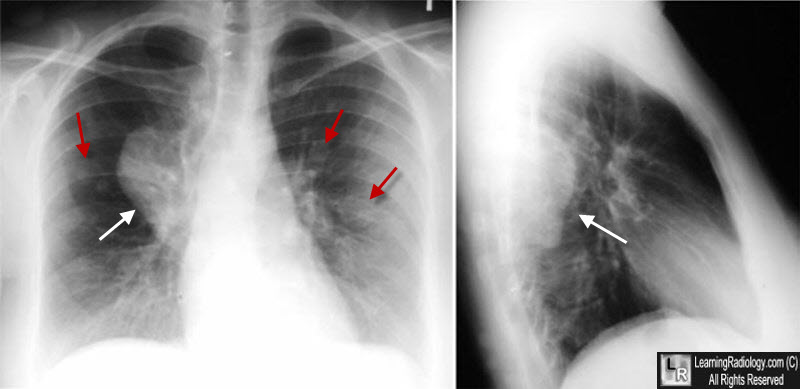
Neurofibromatosis. There is a posterior mediastinal mass seen on the frontal (white arrow) and lateral views (white arrow). The mass lies in the paravertebral gutter. There are also multiple subcutaneous nodules superimposed on the chest (red arrows) from subcutaneous neurofibromas.
|
|
|