|
|
Lipoid Pneumonia
-
Exogenous
accumulation of fat in the lung most
often from mineral oil:
-
Older
people who are constipated, have a swallowing disorder 2° neurologic
disease
-
In
infants with feeding difficulties
-
In
the past, could be from oily nose drops
-
Accumulation
of fat in the lung may also occur from endogenous sources such as fat
embolism, alveolar proteinosis lipid storage diseases
-
Animal
fatty acids (like fat embolus) produces hemorrhagic bronchopneumonia
-
Mineral
oil produces a giant cell foreign
body reaction
-
Starts as an alveolar infiltrate
-
Moves
to thicken interstitial septa, then
-
Into
macrophages enlarging lymphatics
-
Finally produces a fibrosing reaction
Imaging
-
Usually lower lobes with predilection
for the right
-
Alveolar
consolidation, may be well-circumscribed
-
May
present as a peripheral mass with fuzzy or distinct margins simulating BrCa
-
Fat attenuation
on CT
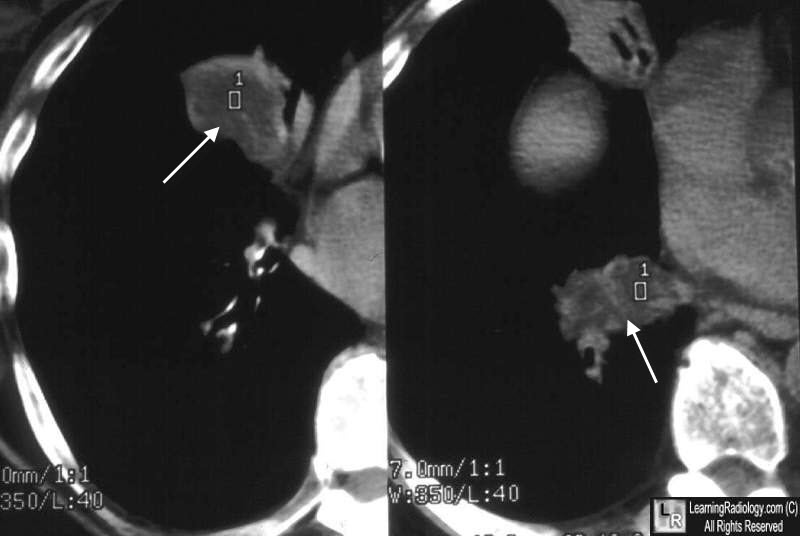
Lipoid Pneumonia. Low-attention masses in right lung (white arrows), both with fat density measurements represent lipoid pneumonia.
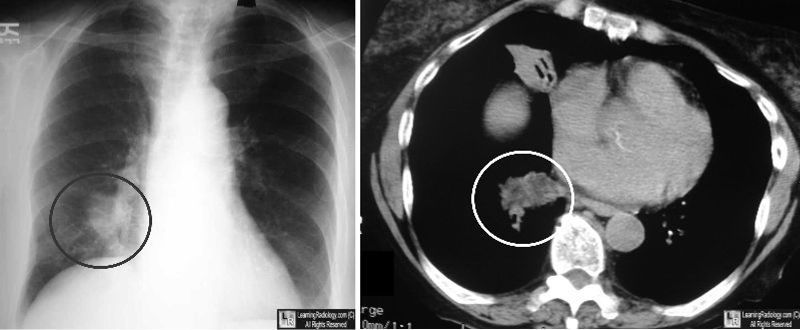
Lipoid Pneumonia. Same case as above showing chest radiograph on right with area of consolidation in lower lobe (black circle) which contains fat on CT (white circle).
Clinical
Diagnosis
|
|
|