|
|
Lymphangiomyomatosis and Tuberous Sclerosis
LAM
General Considerations
- Similar in pathology and x-ray appearance
- Widespread proliferation of smooth muscle in pleura, alveolar septa, bronchi, pulmonary vessels and lymphatics as well as lymph nodes, especially in posterior mediastinum and retroperitoneum
- Focal emphysema develops as result of narrowing of airways
- Thoracic duct may be obliterated
- Produce multiple small cysts with a hamartomatous proliferation of smooth muscle in their walls
Characteristic imaging triad of:
- Progressive, diffuse interstitial disease
- Recurrent chylous effusions and sometimes chylous ascites
- Recurrent pneumothorax
- Tuberous sclerosis is inherited as a dominant with variable penetrance:
- Mental defects
- Epilepsy
- Retinal phacoma
- Angiomyolipomas of the kidneys
- Rhabdomyomas of the heart
- Intracranial calcifications
- Sclerotic skull lesions
- Adenoma sebaceum
- Subungual fibromas
- Pulmonary lymphangiomyomatosis (syn:pulmonary myomatosis)
- Exclusively in females ages 17-47 years
- Rare
Imaging findings
- Identical in both tuberous sclerosis and lymphangiomyomatosis and indistinguishable from pulmonary fibrosis except for decreased lung volume in fibrosis and increased lung volume in the others
- CT
- Coarse, reticular interstitial pattern
- Normal/increased lung volume
- Numerous thin-walled pulmonary cysts and honeycombing
- Various sizes/surrounded by normal lung parenchyma
- Unilateral or bilateral pleural effusions which are usually large and recurrent
- Spontaneous pneumothorax is common
Clinically
- Progressive exertional dyspnea and cough
- Hemoptysis
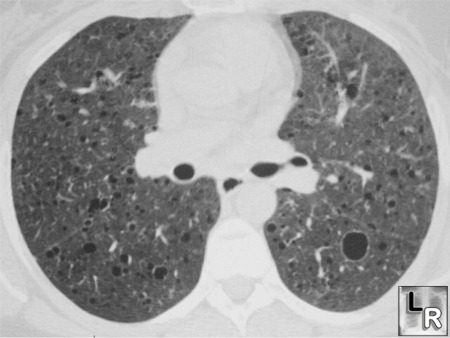
Lymphangiomyomatosis. Note multiple thin-walled cysts throughout both lungs.
|
|
|