|
Hamartoma of Lung
•
Hamartoma is composed of tissues normally found at this location but in
abnormal quantity, mixture or arrangement
INCIDENCE
• 0.25% in population
• 8% of all solitary pulmonary nodules
• Most common benign lung tumor
• 5th and 6th decade peak
• Male to female ratio of 3:1
CLINICAL
• Mostly asymptomatic
• Cough
• Fever (with postobstructive pneumonia)
• Hemoptysis (rare)
LOCATION
• 2/3 are peripheral
• Endobronchial in 10%
• Rarely multiple
X-ray
• Round, smooth mass—increase
in size slowly
• Calcification in 15% — pathognomonic if popcorn type
• Fat in 50% —detected by CT
• Cavitation extremely rare
DDX
• Other causes of a solitary pulmonary nodule
• Bronchial adenoma
• Bronchogenic ca
• Granuloma
• Lipoid pneumonia (both contain fat)
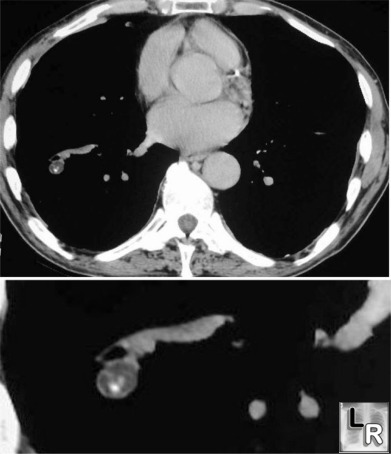
Hamartoma of the right lung seen on axial CT (upper) and close-up (lower)
contains both calcification and fat, characteristic of a hamartoma
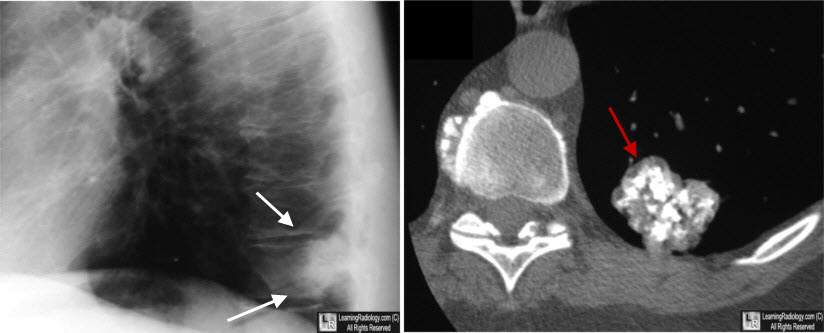
Hamartoma of the left lower lobe. On the lateral chest radiograph, there is a nodule seen at the lung base (white arrows) that appears quite dense suggesting calcification. The close-up view of the CT scan of the left lower lobe demonstrates the typical "popcorn" calcification of a hamartoma (red arrow).
|