|
|
Cervical Rib
General Considerations
- Rare anomalies, occurring in just 1% of population
- The rib or ribs arise from the 7th cervical vertebral body
- They are usually bilateral (80%)
- More common in females
- The anterior end of the cervical rib may attach to the first rib, the sternum or the cartilage of the first rib; it may be a fibrous band or it may have no anterior attachment
Clinical Findings
- Most are asymptomatic
- Less than 10% of those with cervical ribs will be symptomatic
- Their clinical importance is their association with thoracic outlet syndrome
- Neurogenic Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Most common form of thoracic outlet syndrome
- Caused by compression of the lower portion of the brachial plexus
- Clinical manifestations may include pain in the neck and shoulder which radiates into the upper extremity affecting course of the ulnar nerve-hand and inner forearm
- Paresthesias
- Hand weakness, numbness, and clumsiness
- Arterial thoracic outlet syndrome (least common)
- Most serious form of the syndrome
- Men and women affected equally
- Digital vasospasm, potential thrombosis or embolism, aneurysm, muscle atrophy, and gangrene
- Venous thoracic outlet syndrome
- Accounts for about 4% of all cases
- Young men are most often affected
- Characterized by arm claudication, edema, cyanosis, and venous dilatation
- Results from the compression of the subclavian vein
Imaging Findings
- Accessory rib arising from the 7th cervical vertebral body, usually bilaterally
Treatment
- Most patients improve with exercise and physical therapy
- Surgical intervention is unusual
- Indications for surgical resection of the accessory rib may include disabling pain, paresthesias and failure of conservative treatment
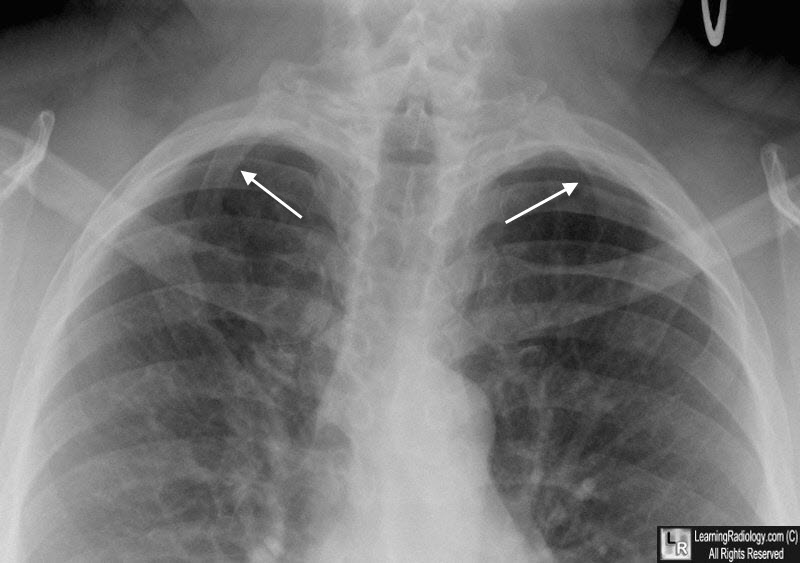
Bilateral cervical ribs. There are bilateral accessory ribs arising from the 7th cervical vertebral body (white arrows).
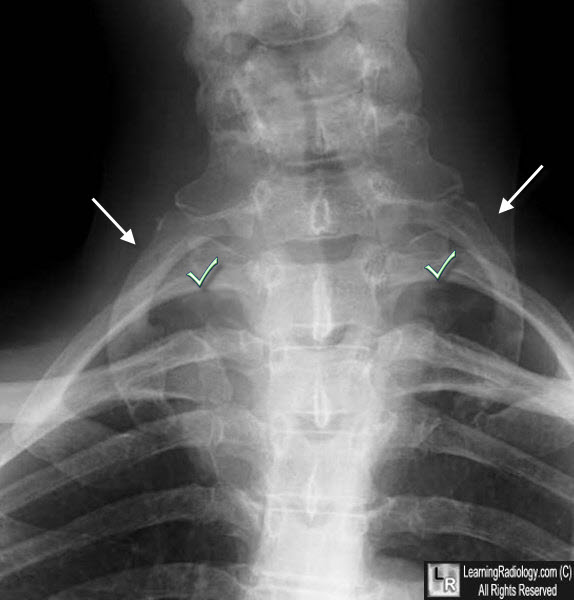
Bilateral cervical ribs. There are bilateral accessory ribs arising from the 7th cervical vertebral body (white arrows). The check marks show the normal, first ribs.
Adams et al., Principles of Neurology, 6th ed, p214
Wise R. Seventh cervical rib associated with subclavian artery occlusion and multiple infarcts. J Neurosci Nurs. 2008;40:169-172.
|
|
|