|
|
Asbestos-Related Pleural Disease
General Considerations
- Salts of salicic acid
- 90% of asbestos in the USA is white asbestos (chrysotile) occurs in automotive workers, shipfitters, construction workers
- Asbestos particles invoke a hemorrhagic response in the lung
- Fibers are then coated with a ferritin-like material resulting in ferruginous bodies
- Produces its damage in respiratory bronchioles and alveoli
- Affects lower lobes first
- The presence of pulmonary parenchymal changes differentiates asbestosis from asbestos-related pleural disease
Imaging Findings
- Opacities are small and irregularly shaped
- Cardiac silhouette may become shaggy
- All patients with asbestos-related pleural disease have, by definition, some pleural involvement
- Pleural involvement without parenchymal disease is common
- Pleural plaque
- Parietal pleural plaques in the mid lung are the most common asbestos-related disorder and are usually bilateral
- They occur most often in the 6th-9th interspaces usually sparing the apices and lung bases and involve the parietal pleura
- Diffuse pleural thickening
- Less common than pleural plaques
- Diffuse pleural thickening involves diaphragmatic pleura, blunting of costophrenic sulci and lateral pleural thickening
- Pleural calcification
- Pleural calcification occurs in about 50% with asbestos-related disease, especially along the diaphragmatic pleura
- Calcified pleural plaques seen en face have a characteristic rolled edge along their margins, denser than in the central portion of the plaque
- The appearance of the entire plaque has been likened to a holly leaf
- Later manifestation of pleural disease, calcification may occur in plaque or diffuse pleural thickening (less often)
- Pleural effusion
- Effusion alone may occur early in the disease (first 20 years) in about 3% of cases
- Exudative, occasionally bloody, one-sided or bilateral
- In contrast to silicosis, hilar lymph nodes are rarely affected
Associations with lung cancer and mesothelioma
- Estimated to occur in 20-25% of those heavily exposed to asbestos
- Asbestos-related lung cancer is usually either squamous cell or adenocarcinoma
- Bronchogenic carcinoma is almost always associated with cigarette smoking
- Increases risk of bronchogenic carcinoma up to 100x over that in non-smoking, non-asbestos exposed population
- Mesotheliomas are not related to cigarette smoking
- Mesotheliomas most often due to crocidolite particles
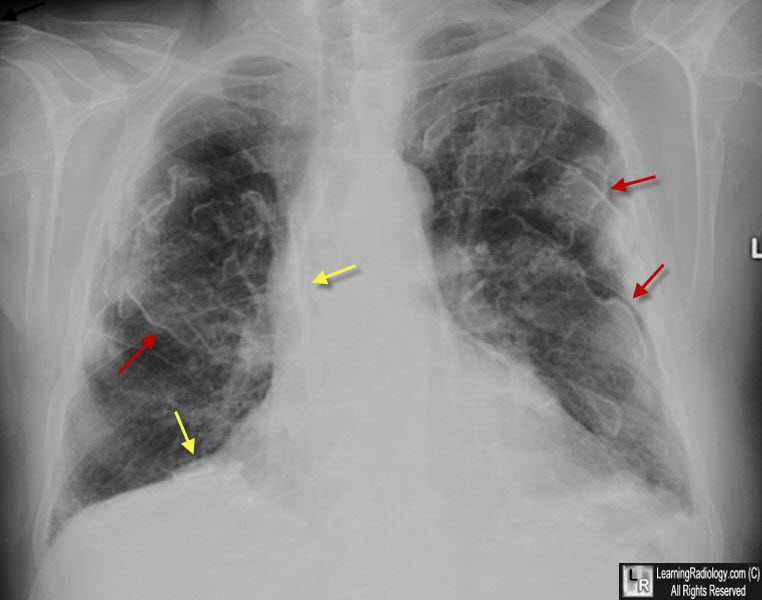
Asbestos-Related Pleural Disease. There are innumerable pleural plaques, seen mostly en face. They have a typical appearance called a "rolled-edge" (red arrows. They have been likened to the appearance of a "holly leaf." There is also plaque-like, pleural calcification present (yellow arrows).
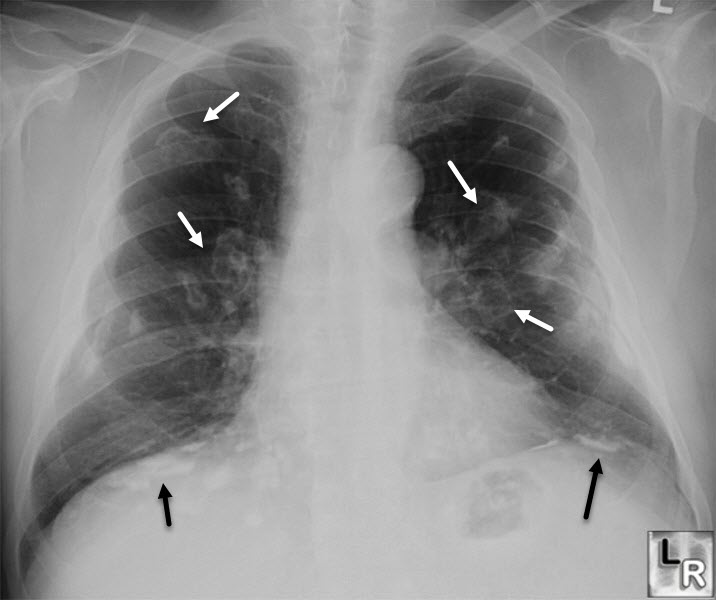
Asbestos-Related Pleural Disease. Again, there are innumerable pleural plaques, seen both en face (white arrows) and in profile (black arrows).
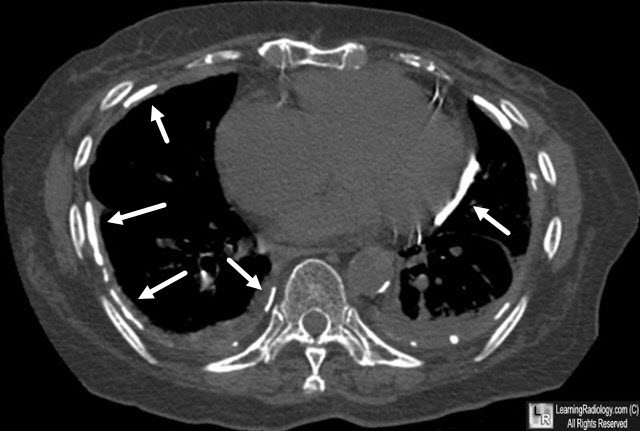
Asbestos-Related Pleural Disease. Numerous calcified pleural plaques are seen bilaterally (white arrows).
|
|
|