|
|
Vertebra Plana
General Considerations
- Complete or near-complete loss of the entire height of a vertebral body
- Also known as pancake vertebra
- Causes include:
- Eosinophilic granuloma (Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis)
- Most common in thoracic spine
- Usually in children 2-6 years old
- Osteoporosis
- Trauma
- Multiple myeloma
- Hemangioma of vertebral body
Clinical Findings
Imaging Findings
- Flattening of the vertebral body
Differential Diagnosis
- Collapse of a single vertebral body may be due to
- Ewing Sarcoma
- Aneurysmal Bone Cyst
- Osteomyelitis
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
- Collapse of multiple vertebral bodies, think of
- Mucopolysaccharidosis
- Gaucher Disease
- Multiple Myeloma
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Lymphoma
Treatment
- Bracing
- Lesions may spontaneously regress in young patients
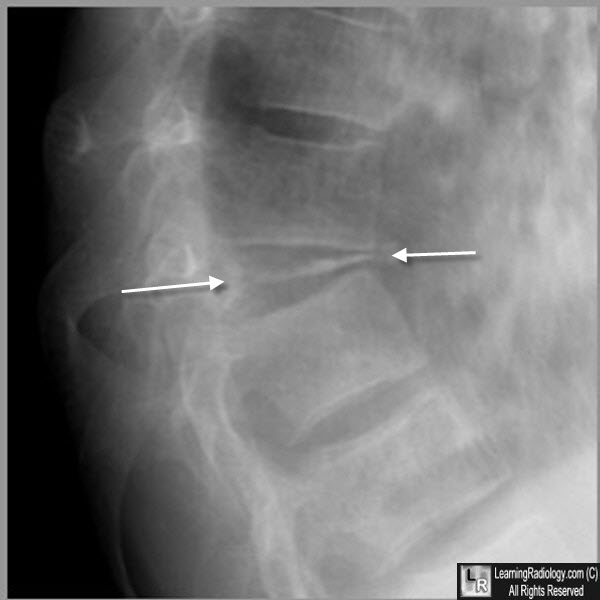
Vertebra Plana. There is complete compression of this lower thoracic vertebral body (white arrows). This was due to osteoporosis. In a child, eosinophilic granuloma should be considered.
|
|
|