|
|
Tuberous Sclerosis
-
Autosomal dominant characterized by
adenoma sebaceum, seizures and mental retardation
-
Hamartomas in various organ systems
-
50 percent mentally retarded
-
80 percent have angiomyolipomas of
kidneys
-
Two-thirds have intracranial
calcifications
-
Calcifications in brain and dentate
nucleus and basil ganglia
-
Calcification usually multiple 75%
-
Usually central - periventricular
-
Rarely in the cerebellum
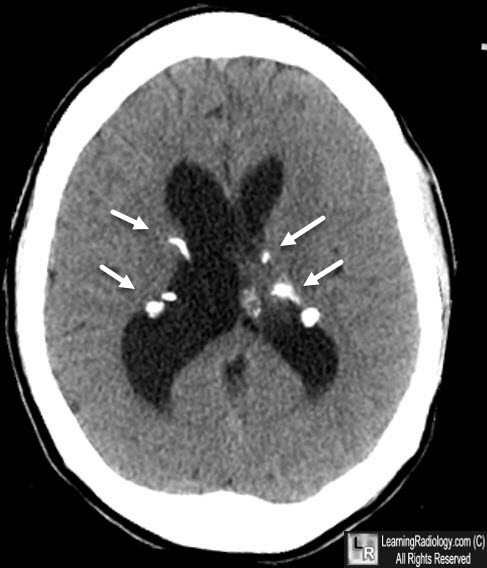
Tuberous Sclerosis. There are multiple, central, punctate calcifications (white arrows) in a periventricular distribution.
-
Also may have calvarial calcification in
40 to 50 percent of cases
-
75 percent are dead by age 20 of CNS
involvement
-
CNS almost always involved by hamartomas
-
Mostly periventricular.
-
X-rays may show periventricular,
intracerebral and cranial vault calcifications
-
Usually multiple, increase with age
-
Produce candle guttering on CT
-
Differential diagnosis from
toxoplasmosis and CMD
-
Adenoma sebaceum pink nodules on face in
90% are actually angiofibromas
-
Also subungual fibromas and Shagreen
patches
-
About 65 percent have angiomyolipomas of
kidney
-
About one half of patients with
angiomyolipoma have tuberous sclerosis
-
Usually asymptomatic, grow very slowly
-
May be lucent on plain film
-
Angiography may not be able to
differentiate from hypernephromas
-
Bone
-
Most common are local areas of
osteosclerosis
-
Ovoid with poorly defined margins,
-
Tendency for the lesions to cluster on
the iliac side of the SI joints
-
Lung
|
|
|