|
|
Psoriatic Arthritis
Major points
- Almost always accompanies skin disease, especially nail changes
- Mostly involves DIP
joints of hands > feet
- Classical deformity is
called “cup-and-pencil deformity”
- Erosion of one end of
bone with expansion of the base of the contiguous metacarpal
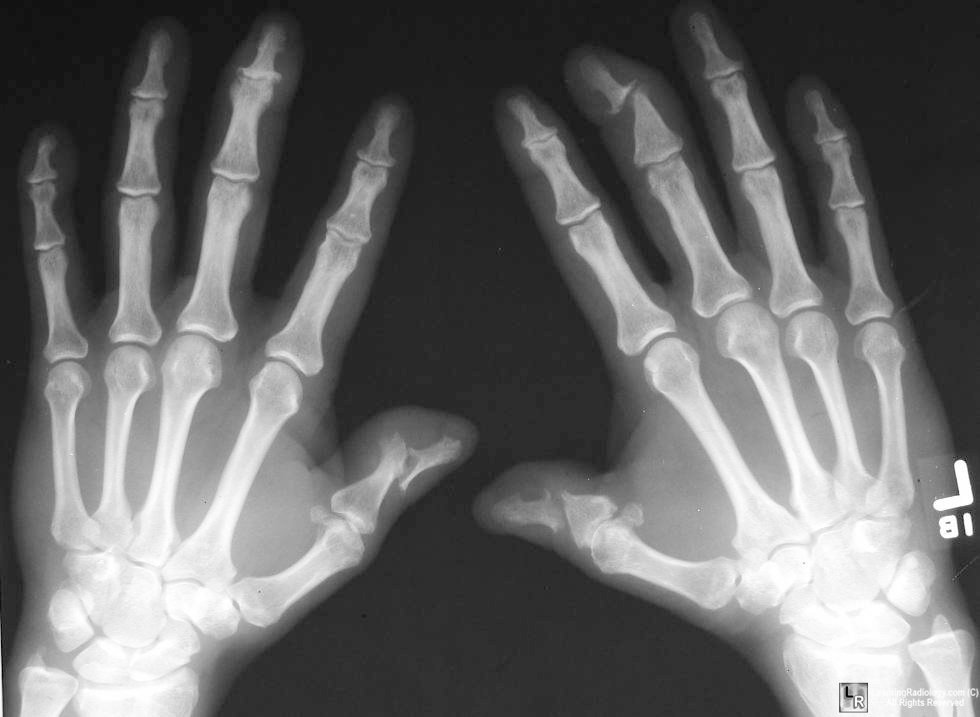
Psoriatic Arthritis. Radiograph of both hands demonstrates
cup-and-pencil deformities of
both thumbs and erosion of DIP joint of left middle finger
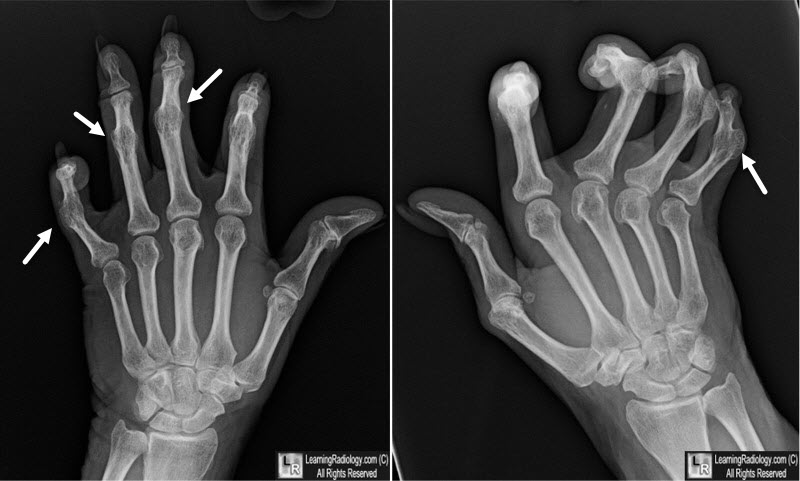
Psoriatic Arthritis. Radiograph of both hands demonstrates
ankylosis of numerous proximal and distal
interphalangeal joints (white arrows), flexion deformities and lack of significant osteoporosis.
- There is often resorption of terminal phalanges
- There is usually no
osteoporosis
- Most are HLA-B27 positive, RA factor negative
- Characteristic findings
- Tends to involve smaller joints of hand and
foot more than larger joints
- Asymmetrical joint involvement
- Affects both the juxta-articular and articular
margins of joint
Seronegative
Spondyloarthropathies |
Ankylosing
spondylitis |
Psoriatic
arthritis |
Reiter’s syndrome |
- As with ankylosing
spondylitis and Reiter’s syndrome, bone proliferation is a
major feature. Manifests itself with:
- Bony excrescences
- Periosteal new bone formation (common)
- Entire phalanx may become “cloaked” in new
bone
- “Ivory phalanx”
- Most frequent in terminal phalanges of
toes, especially first
- Ankylosis is common
- Especially in PIP and DIP joints of hands
and feet
- Feature common to seronegative
spondyloarthropathies
- Whiskering at sites of tendinous insertion
(enthesopathy) occurs
- Soft tissue swelling of an entire digit (sausage
digit)
- Destruction of IP joint of great toes with
exuberant callous formation is characteristic
- Resorption of tufts of terminal phalanges is
characteristic
- Spine
- Asymmetric paravertebral ossification
- Usually thicker and larger than
syndesmophytes of ankylosing
spondylitis or inflammatory bowel disease
- Occasionally, there are incomplete
non-marginal syndesmophytes similar to AS
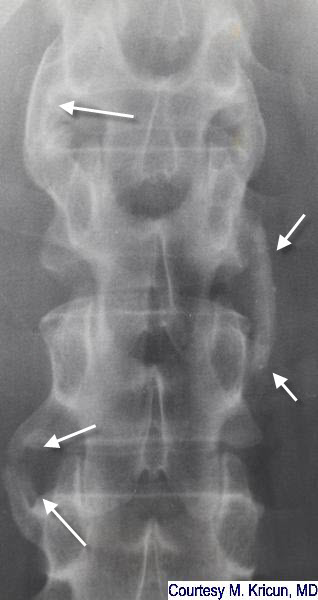
Psoriatic Spondylitis. There are large, asymmetric osteophytes (white arrow). They are thicker than the syndesmophytes of ankylosing spondylitis and their asymmetric distribution should raise suspicion of psoriatic disease.
- Bilateral sacroiliitis is most common
- May produce erosions and sclerosis
- May produce widening of the SI joints
- SI joint involvement occurs in about 10-25% of
patients with moderate to severe psoriasis
Patterns of Psoriatic Arthritic Changes |
Arthritis involving multiple joints with DIP joint involvement |
Arthritis resembling Rheumatoid Arthritis |
Sacroiliitis and spondylitis |
Arthritis mutilans |
Resnick, 4th Edition
|
|
|