|
|
Osteopetrosis
Albers-Schönberg Disease, Marble Bone Disease
General Considerations
- Rare hereditary disorder
- Defective osteoclast function with
failure of proper reabsorption produces
sclerotic bone
- Structurally weak
Types
- Infantile autosomal recessive type
- Failure to thrive
- Premature senility in facies
- Dental caries
- Anemia, leukocytopenia, thrombocytopenia
- Cranial nerve compression (optic
atrophy, deafness)
- Hepatosplenomegaly (extramedullary
hematopoiesis)
- Lymphadenopathy
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage may occur
(due to thrombocytopenia)
- May be associated with:
- Renal tubular acidosis
- Cerebral calcification
- Prognosis: survival beyond middle age
is uncommon (death due to recurrent infection, massive hemorrhage,
terminal leukemia)
- Benign adult autosomal dominant type
- 50% asymptomatic
- Recurrent fractures
- Mild anemia
- Cranial nerve palsy (rarely)
- Prognosis: normal
- X-ray findings
- Diffuse osteosclerosis
- Cortical thickening with medullary
encroachment
- Erlenmeyer flask deformity = clublike long bones due to lack of tubulization + flaring of ends
- Bone-within-bone appearance
- "Sandwich"
vertebrae=alternating sclerotic + radiolucent transverse
metaphyseal lines (phalanges, iliac bones) indicate fluctuating
course of disease
- Longitudinal metaphyseal striations
- Mandible least involved
- Complications:
- Fractures (common because of brittle
bones) with abundant callus + normal healing
- Crowding of marrow (myelophthisic
anemia + extramedullary hematopoiesis)
- Frequently terminates in acute
leukemia
- Rx: bone marrow transplant
- DDx:
- Heavy metal poisoning
- Melorheostosis (limited to one extremity)
- Hypervitaminosis D
- Pyknodysostosis
- Fibrous dysplasia of skull / face
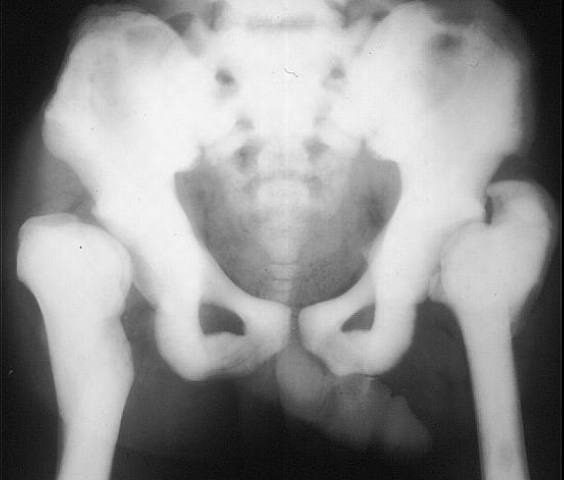
Osteopetrosis. All of the bones are markedly dense. There is dysplasia of both femoral heads and necks. The marrow cavity has been replaced.
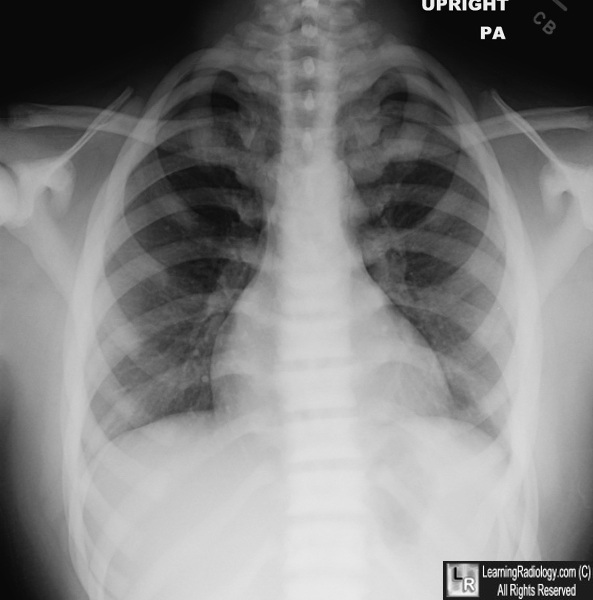
Osteopetrosis. All of the bones are abnormally dense in this individual. This can especially be appreciated by the stark visualization of the anterior ribs, which are often difficult to see at first glance on a normal frontal chest radiograph. The scapulae are also abnormally dense.
|
|
|