|
|
Alkaptonuria
Ochronosis
-
Rare hereditary disorder
-
Insufficiency of homogentisic acid oxidase
-
Results in excessive homogentisic acid
excreted in urine and deposited in soft tissue
-
Urine may be “black”
-
Sclera may be grey-brown or yellow
-
Cartilage of nose and ears may be bluish in
color
-
Clinical findings are combination of
spondylitis and arthritis of major joints
-
When deposited in cartilage, synovial
thickening develops
-
This results in:
-
Usually affects large joints-knees,
shoulders, hips
-
Chondrocalcinosis of appendicular joints
may develop
-
In the spine:
-
Changes of degenerative disc disease
-
Ligamentous structures mat be involved
-
Resembles ankylosis spondylitis
-
Universal disc space calcification is
common
-
Universal disc calcification and DJD of root
joints (hips and shoulders) in younger patient are pathognomonic
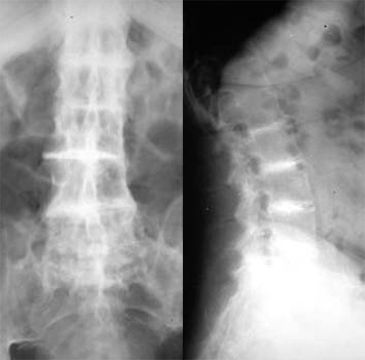
Ochronosis. There is universal disc calcification, a finding that is highly suggestive of ochronosis.
Murray and Jacobson, 2nd ed, vol.2
|
|
|