|
|
"Nightstick Fracture"
General Considerations
- Typically caused by the defensive action of holding one's arm in front of one's head to avoid being struck by a blunt object, such as a policeman's baton or nightstick
Clinical Findings
- Pain and swelling at point of injury
Imaging Findings
- Transverse fracture of the shaft of the ulna
- Mid-diaphysis is common location
- Frequently, non-displaced
Treatment
- Immobilization
- Open-reduction usually not performed unless there are more than 5 mm of displacement or 10-15 degrees of angulation
- Non-union can occur in up to 5% of cases
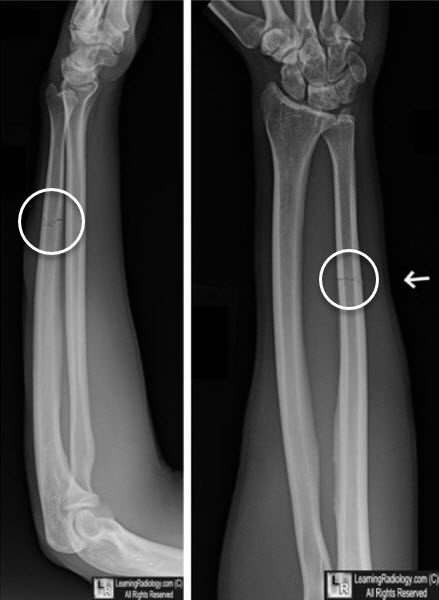
Nightstick Fracture. Lateral (left image) and frontal views of the forearm demonstrate a non-displaced, transverse fracture of the ulna (white circles).
|
|
|