|
|
Ankle Joint Effusion
Teardrop Sign
General Considerations
- Teardrop-shaped soft tissue density seen on lateral conventional radiographs of the ankle at the anterior junction of the tibia and talus
- Fluid in the inferior portion of the anterior ankle joint compartment
- Its presence suggests a more serious injury
- Is best seen anteriorly because ligaments --deltoid and talofibular—restrict medial and lateral expansion of the joint capsule.
- Dorsiflexion may lead to false positives and plantar flexion false negatives
- Causes include:
- Trauma
- Gout
- Infectious arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Synovitis
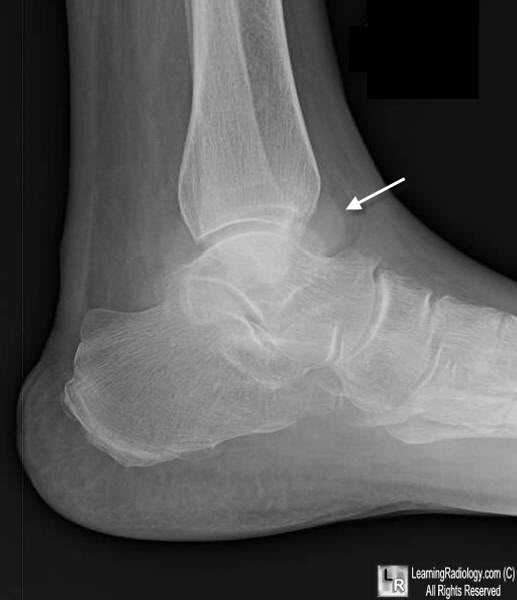
Ankle Joint Effusion. This lateral radiograph of the ankle shows the normal fat lucency anterior to the tibiotalar joint replaced by an ovoid soft tissue density (white arrow) representing fluid in the inferior portion of the anterior recess.
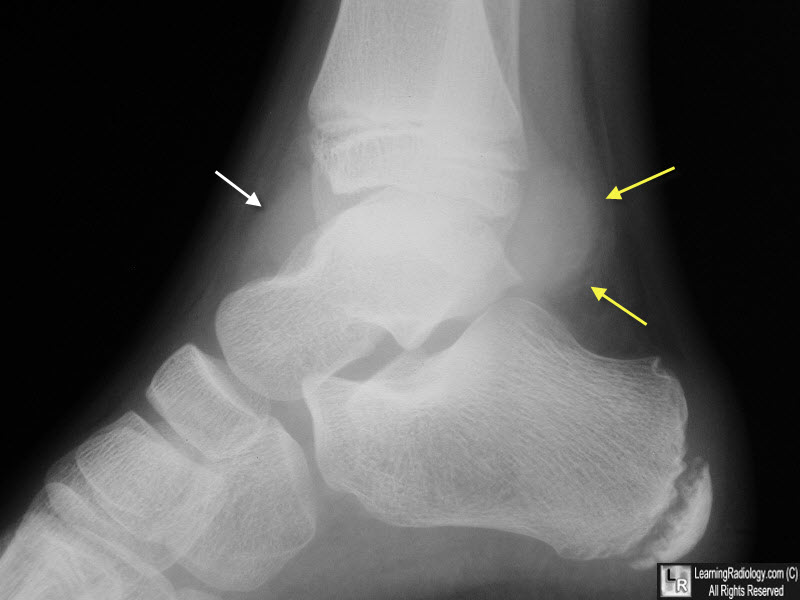
Ankle Joint Effusion. Yellow arrows point to a lobular soft-tissue density extending posteriorly from the ankle joint and another anteriorly (white arrow). The patient was a hemophiliac and this was a hemarthrosis.
Signs in Imaging: The Ankle Teardrop Sign. JP Dodge. Radiology, June 2004, Volume 231, Issue 3
|
|
|