
GastrointestinalRadiology
Differential Diagnoses
Reference and photos:Clinical Imaging, An Atlas of Differential Diagnosis, 2nd edition Eisenberg, RL
Submitted by Susan Summerton, MD
Submitted by Susan Summerton, MD

How This Works
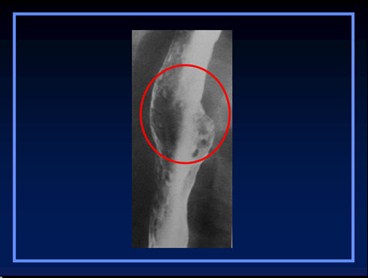
•Eachdifferentialstarts with aphoto of thefindings

How This Works
•With the nextadvance, a blueclue will appearin the lowerright-handcorner to give ageneral idea ofthe differentialbeing asked

How This Works
•The next slidegives the title ofthe differentialand the numberof items on thelist


How This Works
•The last slidein each setgives thedifferential

Start
Start

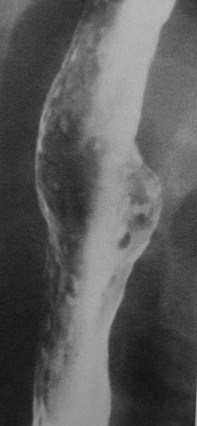
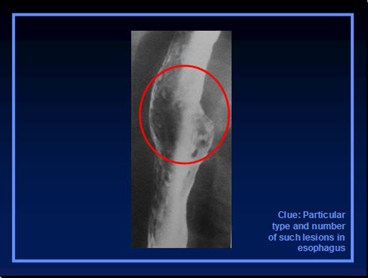
Clue: Particulartype and numberof such lesions inesophagus

Multiple Esophageal Ulcers
1.
2.
3.
4.

Multiple Esophageal Ulcers
1.Reflux
2.Infectious
a. HSV, Candida
3.Drug induced
4.Barrett’s

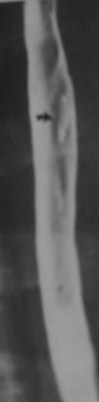
Clue: Particulartype and numberof such lesions inesophagus

Solitary Esophageal Ulcer
1.
2.

Solitary Esophageal Ulcer
1.HIV
2.CMV

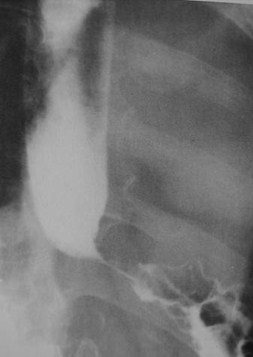
Clue: Particulartype of lesion andits location

Distal Esophageal Stricture
1.
2.
3.
4.

Distal Esophageal Stricture
1.Peptic strictures
2.Barrett’s
3.Carcinoma
a. Gastric,esophageal
4.Achalasia

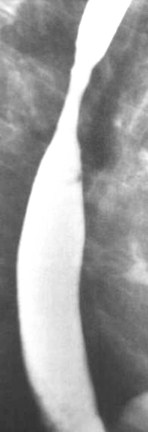
Clue: Particulartype of lesion andits location

Mid-esophageal stricture
1.
2.
3.
4.

Mid-esophageal stricture
1.Barrett’s
2.Radiation
3.Ingestion of corrosives
4.Metastases to mediastinum


Clue: Particulartype of lesion

Esophageal Mucosal Nodularity
1.
2.
3.
4.

Esophageal Mucosal Nodularity
1.Reflux
2.Candida
3.Glycogenic Acanthosis
4.Barrett’s

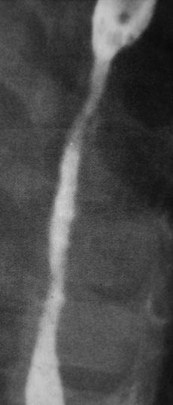
Clue: Length ofthe lesion and itslocation

Long esophageal stricture
1.
2.
3.

Long esophageal stricture
1.Lye
2.NG Tube (prolonged use)
3.Radiation

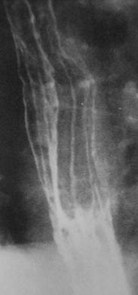
Clue: Nature andlocation of folds

Thickened esophageal folds
1.
2.
3.
4.

1.Varices
2.Varicoid carcinoma
3.Reflux esophagitis
4.Lymphoma
Thickened esophageal folds


Clue: Locationand number oflesions

Solitary esophageal mass
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.

Solitary esophageal mass
1.Leiomyoma
2.Fibrovascular polyp
3.Inflammatory esophagogastric polyp
4.Papilloma
5.Carcinoma

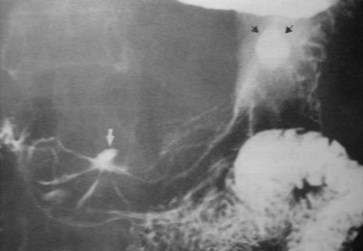
Clue: Type oflesion

Gastric ulcers, no mass
1.
2.
3.
4.

Gastric ulcers, no massCauses
1.H. Pylori
2.Aspirin
3.Crohn’s
4.Zollinger-Ellison syndrome


Clue: Type oflesion

Target lesions in GI tract
1.
2.
3.

Target lesions in GI tract
1.Hematogenous metastases
a. Breast, lung
2.Kaposi’s Sarcoma
3.Melanoma

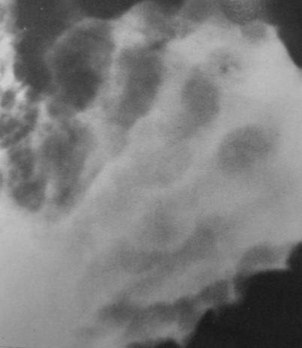
Clue: Nature oflesion in thisorgan

Thickened Gastric Folds
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.

1.Gastritis
a. Hypertrophic, H. Pylori
2.Menetrier’s disease
3.Zollinger Ellison syndrome
4.Varices
5.Lymphoma
Thickened Gastric Folds

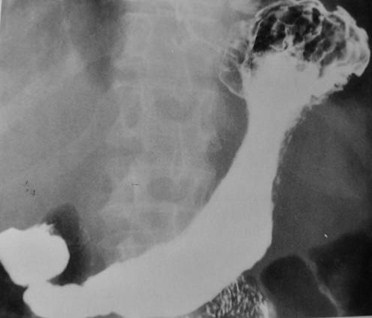
Clue: Nature oflesion in thisorgan

Gastric Non-distensibility
1.
2.
3.
4.

Gastric Non-distensibility
1.Carcinoma
a. Primary, metastatic
2.Lymphoma
3.Atrophic gastritis
4.Scarring from PUD

Linitis Plastica of the StomachDifferential Diagnosis
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.

Linitis Plastica
1.Pancreatic tumor
2.Lymphoma
3.Amyloid
4.Sarcoid/Syphilis
5.TB
6.Ingested Corrosives
7.CA of stomach
Mnemonic spells PLASTICA

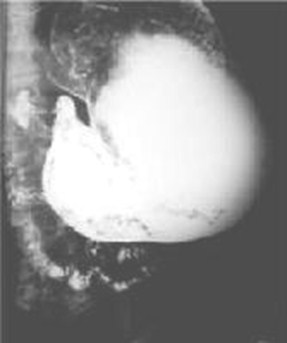
One hour after start of UGI
Clue: Nature oflesion in thisorgan

Gastric outlet obstruction
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.

Gastric outlet obstruction
1.Peptic ulcer disease
a. Acute or chronic
2.Carcinoma
a. Primary, Metastatic (pancreatic)
3.Gastric volvulus
4.Antral diaphragm/web
5.Pyloric stenosis in children

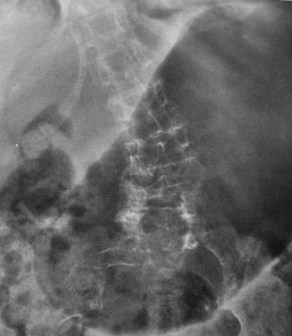
Clue: Nature oflesion in thisorgan

Gastric dilatation
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.

Gastric dilatation
1.Diabetes
2.Electrolyte/acid-base imbalance
3.Neuromuscular disorder
4.Abdominal surgery
5.Abdominal trauma

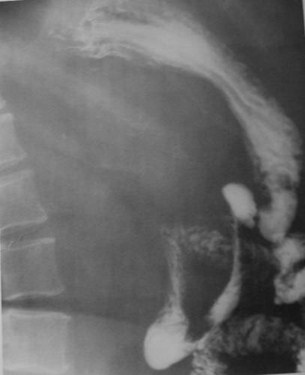
Clue: Nature oflesion in thisorgan

Widening of retrogastric space
1.
2.
3.
4.

Widening of retrogastric space
1.Pancreatic mass
2.Retroperitoneal mass
3.Exophytic posterior wall gastric tumor
4.Aortic aneurysm

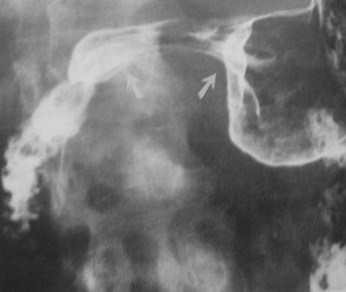
Clue: Type oflesion arrows arepointing to in thislocation

Antral Pad Sign
1.
2.
3.

Antral Pad Sign
1.Pancreatic cancer
2.Pancreatic pseudocyst
3.Gallbladder (normal or distended)

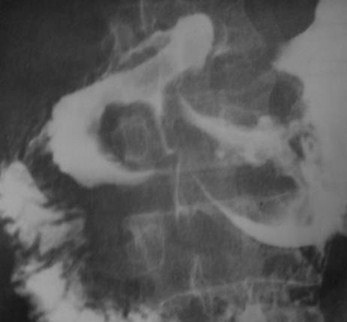
Clue: Extent oflesion

Diseases that cross the pylorus
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.

1.Lymphoma
2.Carcinoma
3.Crohn’s Disease
4.Peptic ulcer disease
5.TB
6.Eosinophilic Gastroenteritis
Diseases that cross the pylorus

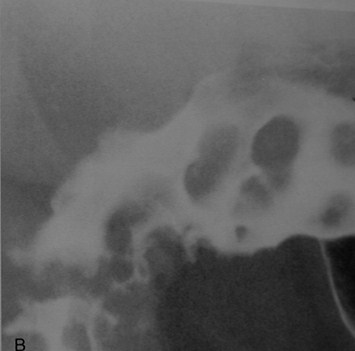
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

Multiple Duodenal Filling Defects
1.
2.
3.

Multiple Duodenal Filling Defects
1.Brunner’s gland hyperplasia
2.Polyps
1.Adenomatous, hyperplastic
3.Lymphoma

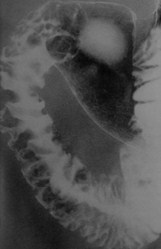
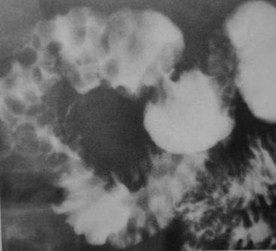
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

Thickened Duodenal Folds
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.

Thickened Duodenal Folds
1.Duodenitis
2.Chronic Renal Failure
3.Pancreatitis
4.Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
5.Varices
6.Lymphoma

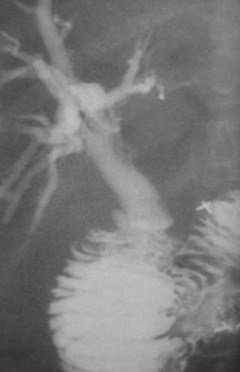
Clue: type oflesion

Duodenal-Biliary fistula
1.
2.
3.
4.

Duodenal-Biliary fistula
1.Prior sphincterotomy
2.Cholecystitis
3.Gallbladder carcinoma
4.Duodenal carcinoma

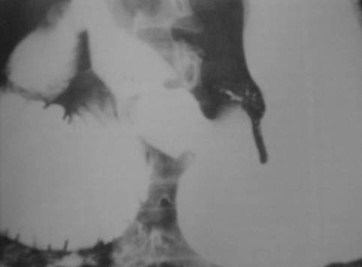
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

Duodenal Obstruction
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.

Duodenal Obstruction
1.Congenital duodenal atresia/stenosis
2.Annular pancreas
3.Midgut volvulus
4.Carcinoma
5.SMA syndrome
6.Intramural hematoma

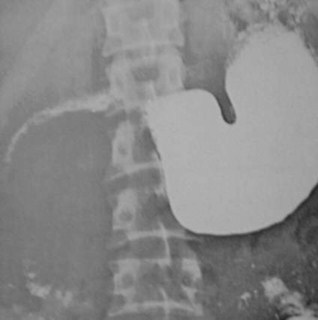
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan


Widening of duodenal sweep
1.
2.
3.
4.

Widening of duodenal sweep
1.Pancreatic Disease
a. Pancreatitis, pseudocyst, tumor
2.Lymphadenopathy
3.Aortic Aneurysm
4.Choledochal cyst

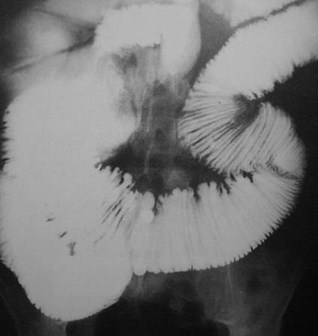
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

Dilated small bowelNo fold thickening
1.
2.
3.

Dilated small bowelNo fold thickening
1.Scleroderma
2.Sprue
3.Small Bowel Obstruction

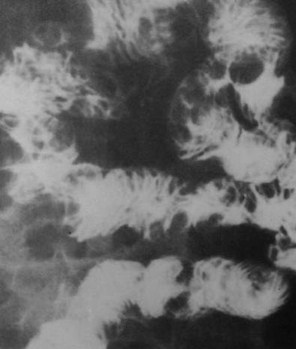
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

Multiple small bowel masses
1.
2.
3.

Multiple small bowel masses
1.Polyposis (Peutz-Jeghers)
2.Lymphoma
3.Metastases

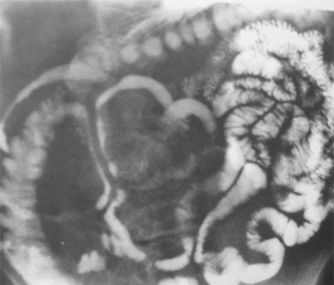
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

Separation of small bowel loops
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.

Separation of small bowel loops
1.Thickening of bowel wall
2.Carcinoid
3.Crohn’s Disease
4.Ascites
5.Peritoneal metastases
6.Retractile mesenteritis

Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan
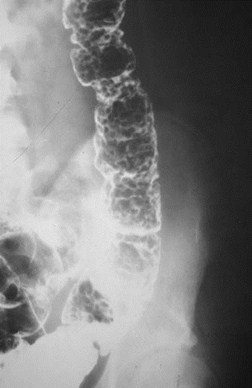

Multiple Colonic Filling Defects
1.
2.
3.
4.

Multiple Colonic Filling Defects
1.Polyps (polyposis)
2.Pseudopolyps (UC)
3.Lymphoma
4.Cystic Pneumatosis

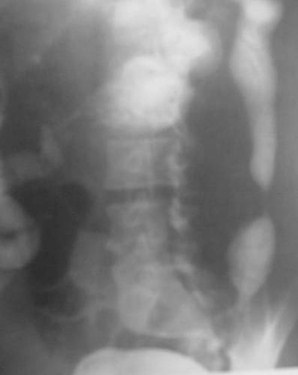
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

Smooth Colonic Stricture
1.
2.
3.
4.

Smooth Colonic Stricture
1.Ulcerative Colitis
2.Crohn’s Disease
3.Radiation
4.Ischemia

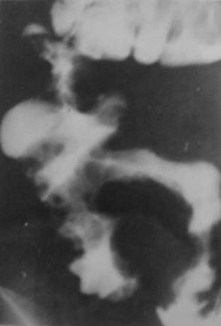
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

Ileocecal disease
1.
2.
3.
4.

Ileocecal Disease
1.Crohn’s Disease
2.Lymphoma
3.TB
4.Cancer(colon adenocarcinoma, carcinoid)

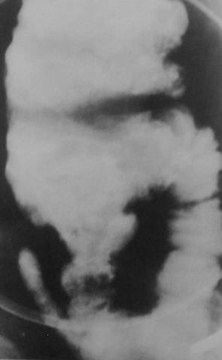
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

Coned Cecum
1.
2.
3.

Coned Cecum
1.Amebiasis
2.Crohn’s Disease
3.TB

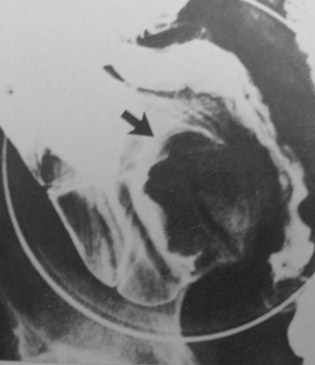
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

Cecal Filling defect
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.

Cecal Filling defect
1.Appendicitis/Mucocele
2.Crohn’s Disease
3.Cecal neoplasm
4.Ileocolic intussusception
5.Lymphoma

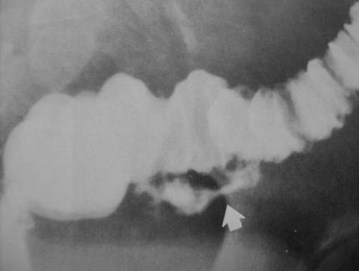
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

Double tracking of Colon
1.
2.
3.

Double tracking of Colon
1.Crohn’s Disease
2.Diverticulitis
3.Adenocarcinoma

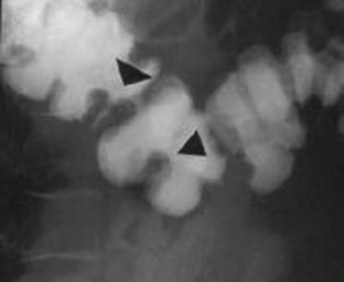
Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan


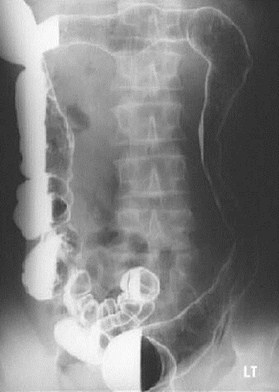
Colon Thumbprinting
1.
2.
3.
4.

Colon Thumbprinting
1.Ulcerative Colitis
2.Ischemia
3.Hemorrhage
4.Lymphoma

Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

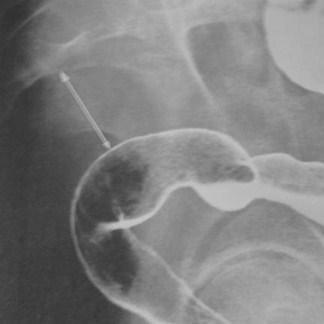
Smooth Colon
1.
2.
3.
4.

Smooth Colon
1.Ulcerative colitis
2.Cathartic Colon
3.Post ischemic
4.Post radiation

Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan


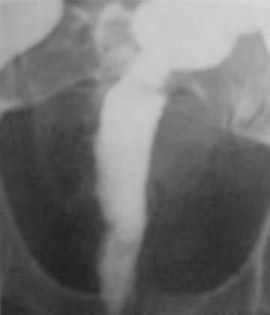
Widened Presacral space
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.

Widened Presacral space
1.Ulcerative colitis
2.Pelvic lipomatosis
3.Crohn’s Disease
4.Rectal tumor
5.Sacral tumor

Clue: type oflesion in thisorgan

Rectal Narrowing
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.

Rectal Narrowing
1.Ulcerative Colitis
2.Pelvic Lipomatosis
3.Lymphogranuloma Venereum (LGV)
4.Solitary Rectal Ulcer Syndrome
5.Radiation

The End