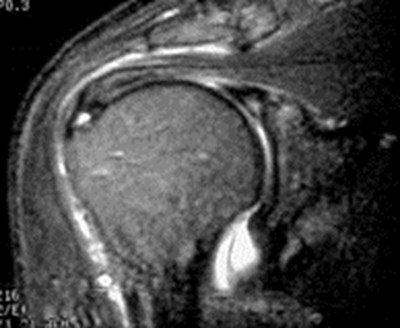
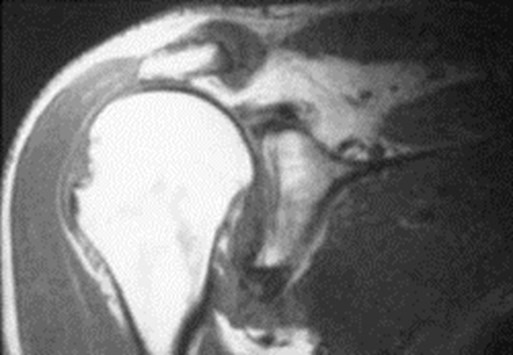
Large Joint MRIAn overview
Adam Guttentag M.D.Adam Guttentag M.D.
All photos retain the copyrights of their original authors
© 2005 Adam Guttentag, MD


Imaging questions:
Whom to image?Whom to image?
Appropriate imaging?Appropriate imaging?
Special considerationsSpecial considerations
Arthrography?Arthrography?
Contrast?Contrast?


Large Joint MRI
ShoulderShoulder
HipHip
KneeKnee


Shoulder
Shoulder pathology vs. radicular pain from C-spine disease?Shoulder pathology vs. radicular pain from C-spine disease?
ArthritisArthritis
Rotator cuffRotator cuff
Internal derangementInternal derangement
Labral tear/SLAP lesionLabral tear/SLAP lesion
Occult bone pathologyOccult bone pathology
Chronic painChronic pain


Shoulder pain — which test?
Young patientsYoung patients
InstabilityInstability
History of dislocationHistory of dislocation
Rotator cuff tear uncommon unlesstrauma history or overhead athleteRotator cuff tear uncommon unlesstrauma history or overhead athlete
MR arthrography often usefulMR arthrography often useful


Shoulder pain—which test?
Older patientsOlder patients
ArthritisArthritis
BursitisBursitis
Rotator cuff tear and tendinopathyRotator cuff tear and tendinopathy
Standard MRI is all that is needed ingeneral.Standard MRI is all that is needed ingeneral.


Normal rotator cuff tendon
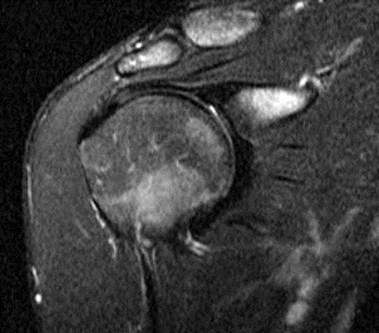


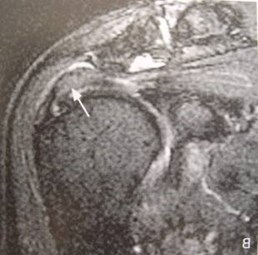
Tendon is thickened onT1WI
Tendon has diffuselyhigher signal on T2WI
Tendinopathy of rotator cuff


A-C Joint degenerative changes
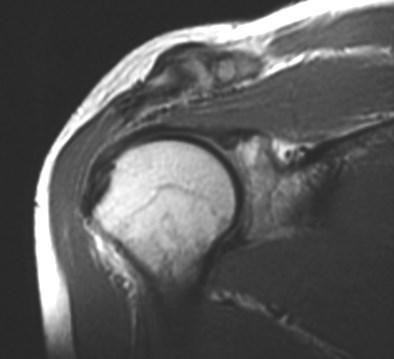


Subacromial bursitis
Supraspinatus tendon
Fluid in subacromial bursa


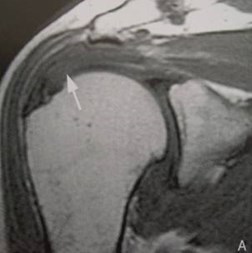
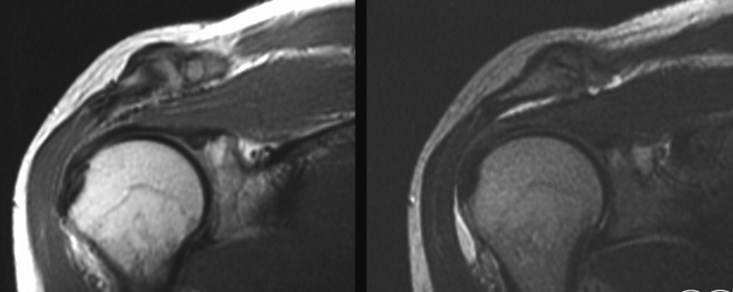
Partial Thickness Tear
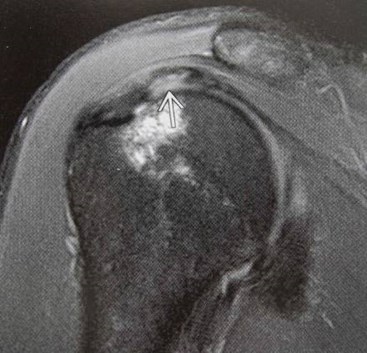


Calcific tendinopathy
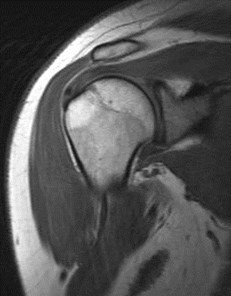
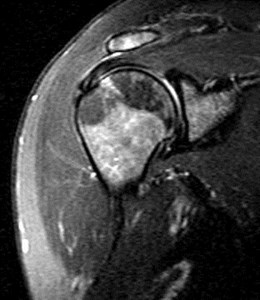
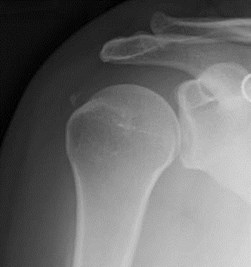
Don’t forget to look at the x-rays!


Supscapularis tendon rupture
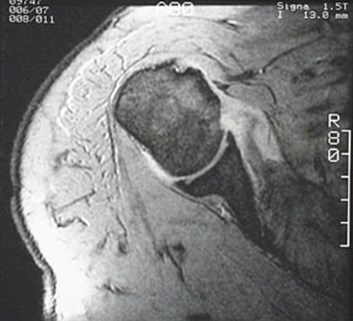
Normal tendon
Ruptured tendon
Usually seen in the setting of dislocation


Glenoid labrum
Fibrous connective tissueFibrous connective tissue
Deepens shallow glenoid fossaDeepens shallow glenoid fossa
Attaches to hyaline cartilage of theglenoidAttaches to hyaline cartilage of theglenoid
Static and dynamic shoulderstabilizationStatic and dynamic shoulderstabilization
Normal variants commonNormal variants common
Best seen with joint distended with fluid.Best seen with joint distended with fluid.


MR arthrography
Fluoroscopically guided injection of~15cc of saline with a tiny amount of Gdcontrast.Fluoroscopically guided injection of~15cc of saline with a tiny amount of Gdcontrast.
Rapid, well tolerated by patient.Rapid, well tolerated by patient.
Fill joint with fluid to see all surfaces ofglenoid labrumFill joint with fluid to see all surfaces ofglenoid labrum
Evaluate for leakage of fluid into orthrough torn rotator cuff tendonsEvaluate for leakage of fluid into orthrough torn rotator cuff tendons
Most cuff tears seen with standardMRIMost cuff tears seen with standardMRI


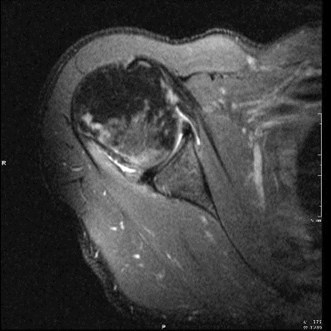
MR arthrogrambetter evaluation of labrum
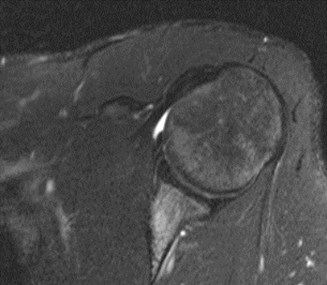
standard
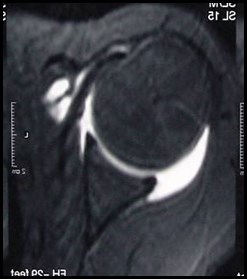
arthrogram


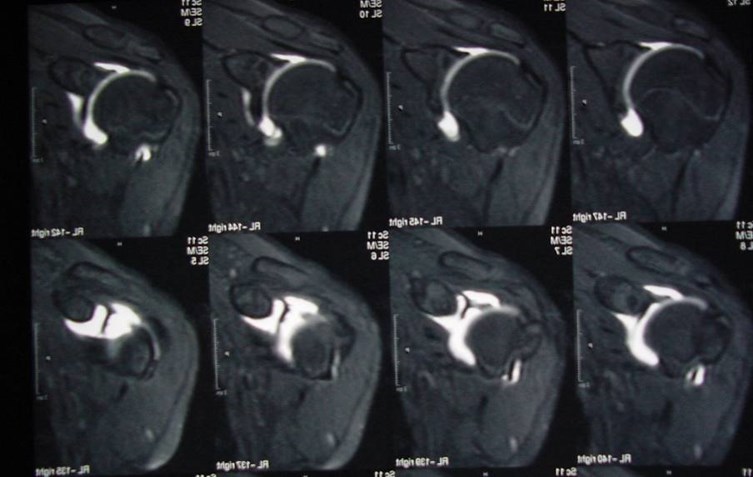
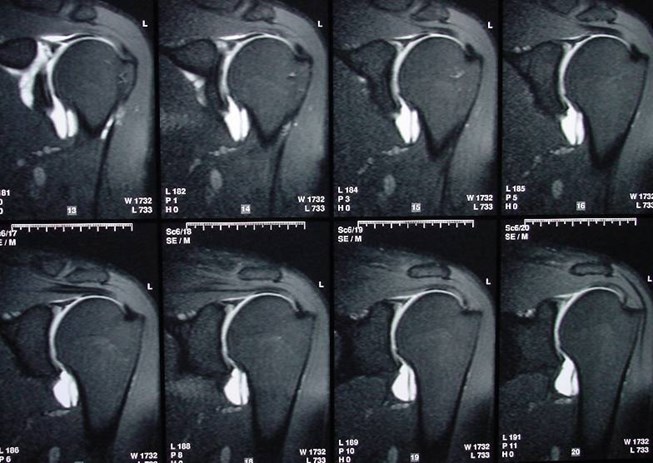
MR Arthrogram — coronal plane
Biceps tendon attachment
Superior labrum


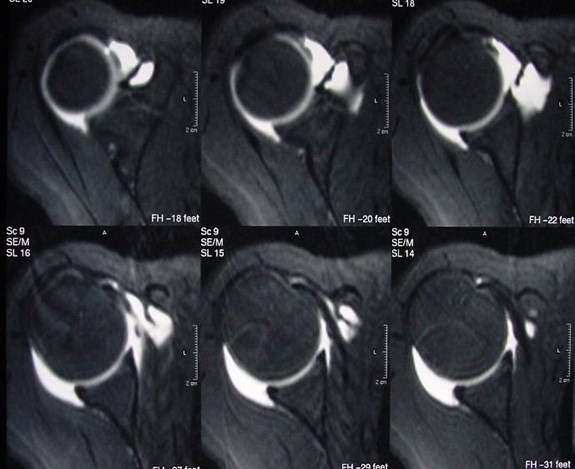
MR Arthrogram — Axial plane
Anterior labrum
Posterior labrum


“SLAP” lesion


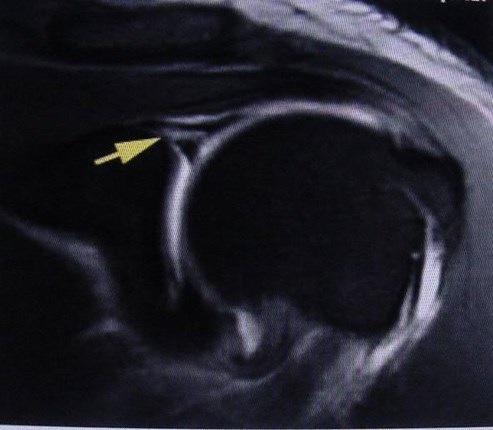
“SLAP” lesion


CT arthrogram
May be performed in patients with MRcontraindication.May be performed in patients with MRcontraindication.
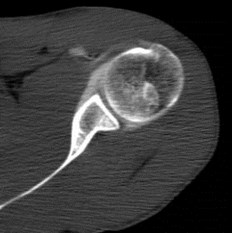
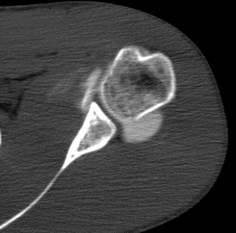
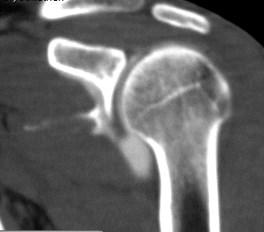


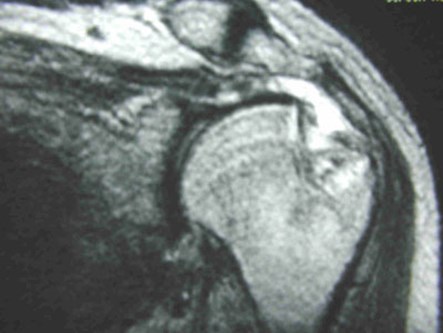
Hill-Sachs lesion
••Impaction fracture from anterior dislocation.
••Anterior glenoid impacts on superior posteriorhumeral head


Large Joint MRI
ShoulderShoulder
HipHip
KneeKnee


Hip
Many pathologies are radiographicallyoccultMany pathologies are radiographicallyoccult
MRI should be the next test for mostpatients with hip pain and normal x-raysMRI should be the next test for mostpatients with hip pain and normal x-rays


Hip pain — normal x-ray
AVNAVN
Chronic steroid useChronic steroid use
TraumaTrauma
EtOHEtOH
Long list of other causesLong list of other causes
Bilateral in >50%Bilateral in >50%
Insufficiency fractureInsufficiency fracture
Osteoporotic bone, normal activity, minortraumaOsteoporotic bone, normal activity, minortrauma
Stress fractureStress fracture
Normal bone, high activityNormal bone, high activity
BursitisBursitis
Transient osteoporosisTransient osteoporosis


Hip pain after a fall
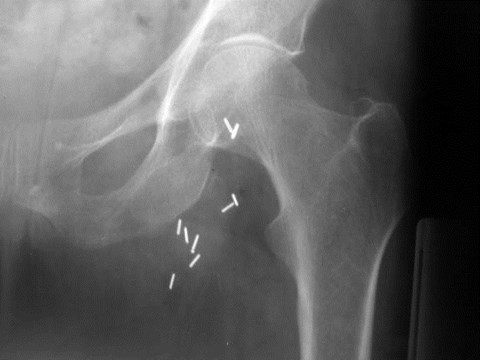


Occult femoral neck fracture
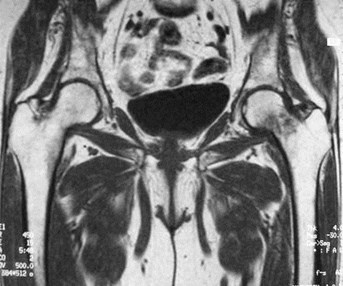
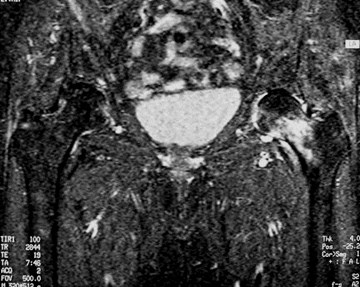


Occult intertrochanteric fracture
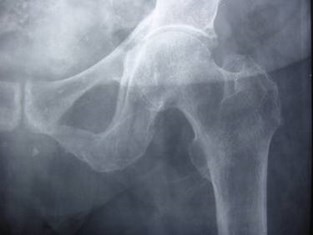
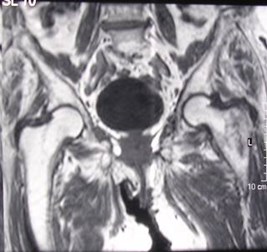
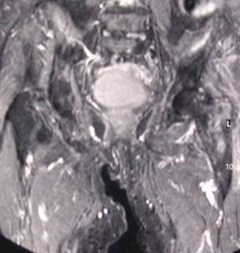


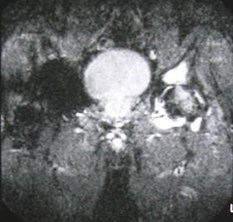
Insufficiency fracture
Chronic hip soreness, patient with chronic renal failure
Occurs in the setting of underlying abnormal bone


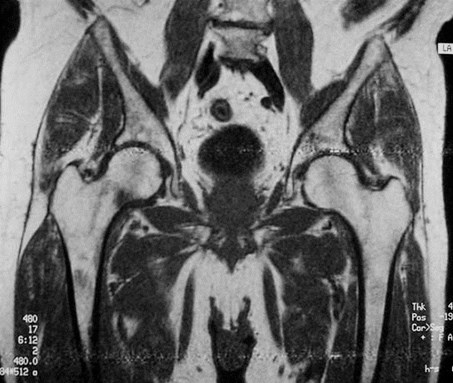
Acetabular stress fracture
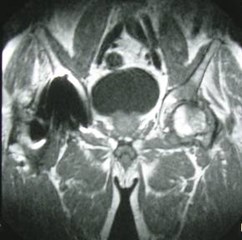
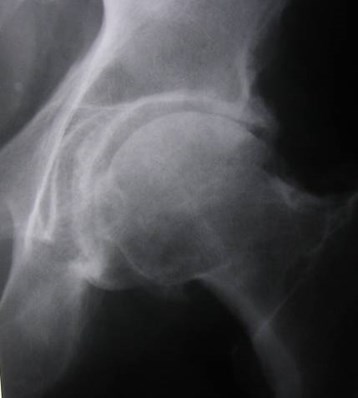
Chronic hip pain


Avascular necrosis — SLE
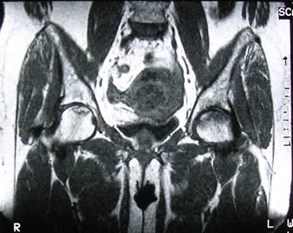
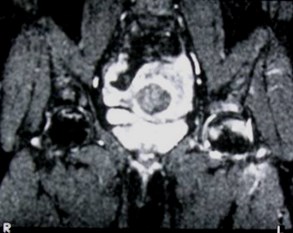
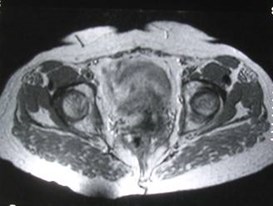
Serpiginousdark line
Bone marrowedema
Left hip pain


Chronic right hip pain
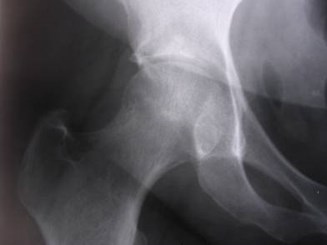
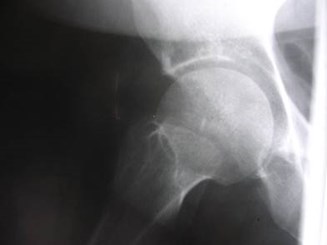


Avascular necrosis
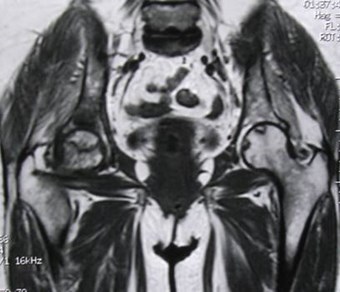
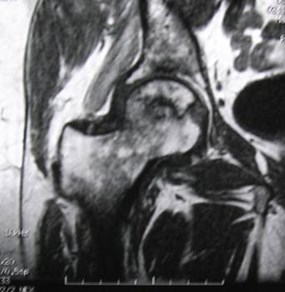


Acetabular and hip AVN — old XRT
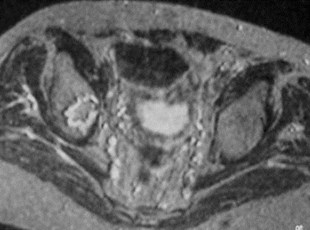
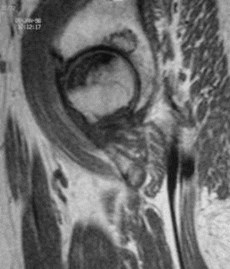
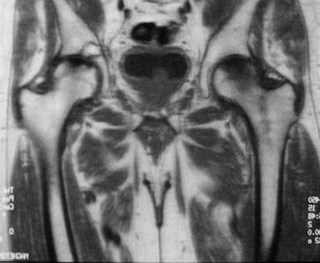


Rheumatoid arthritis
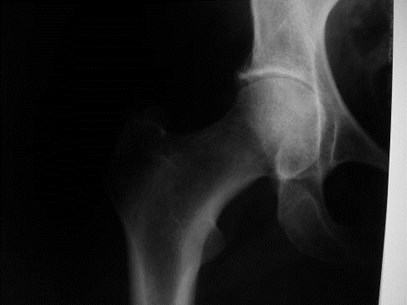
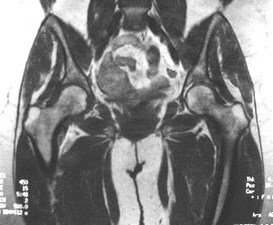
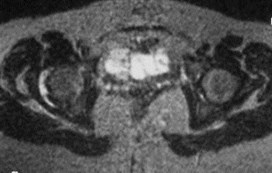
Concentric narrowing of joint
Thickened synovium


Trochanteric bursitis
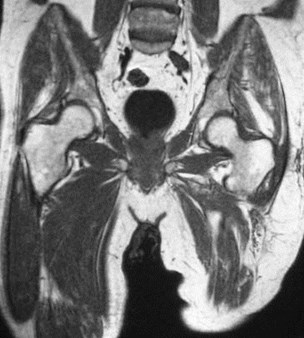
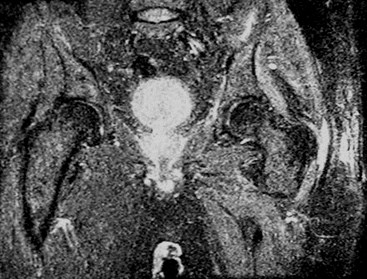


Iliopsoas bursitis
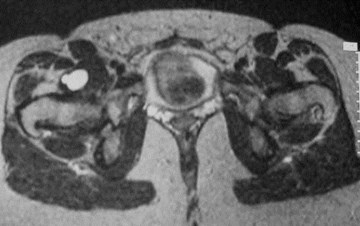
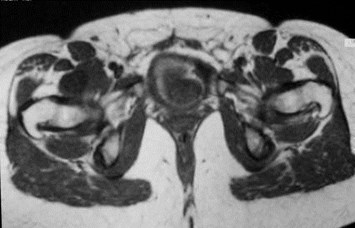


Metastatic deposits
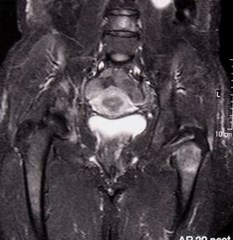
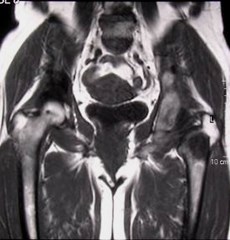
Breast cancer and hip pain


Left hip pain
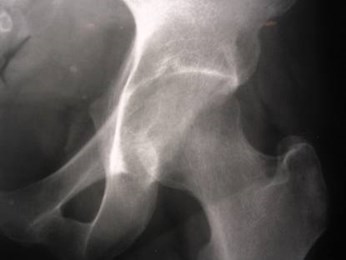
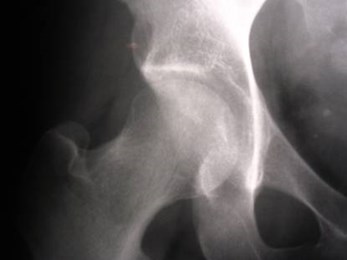


Transient osteoporosis
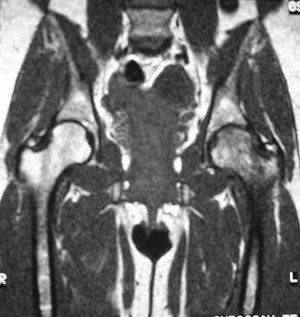
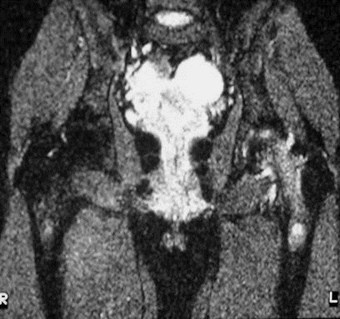


MR Arthrogram
Should not be the first test ordered.Should not be the first test ordered.
For evaluation of persistent hip painwith negative noninvasive workupFor evaluation of persistent hip painwith negative noninvasive workup
Limited indications:Limited indications:
Evaluate labral pathologyEvaluate labral pathology
Hip labrum often injured in athletes orwith twisting injuryHip labrum often injured in athletes orwith twisting injury


MR arthrogram
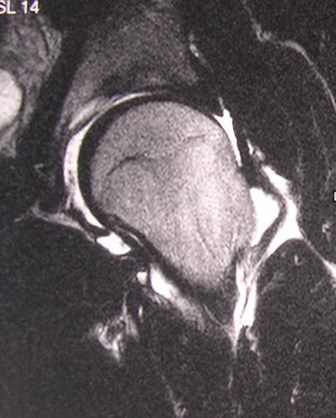
labrum


Large Joint MRI
ShoulderShoulder
HipHip
KneeKnee


Knee — chronic pain
Are there X-ray findings?Are there X-ray findings?
Obvious arthritis…need for MRI?Obvious arthritis…need for MRI?
Osteochondritis dessicansOsteochondritis dessicans
MRI for internal derangement, occultbone abnormality.MRI for internal derangement, occultbone abnormality.


Meniscal injury
Most common knee injury (rare <age 10)Most common knee injury (rare <age 10)
Peaks in young adulthood, >55Peaks in young adulthood, >55
Chronic pain, instabilityChronic pain, instability
Locking if there is a displaced fragmentLocking if there is a displaced fragment
Medial >lateral, posterior>anteriorMedial >lateral, posterior>anterior
Intrameniscal degeneration is common inadults over 40 and ≠ tear.Intrameniscal degeneration is common inadults over 40 and ≠ tear.
MRI >90% sensitive, >80% specific formeniscal tears.MRI >90% sensitive, >80% specific formeniscal tears.


Meniscal tears
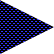
normal
degeneration
Horizontaltear
“fibrillation”
Displacedfragment


Degenerated medial meniscus
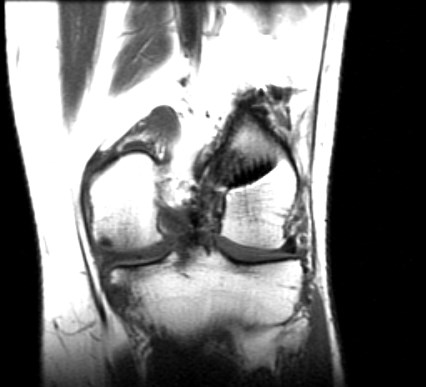


Lateral meniscus horizontal tear
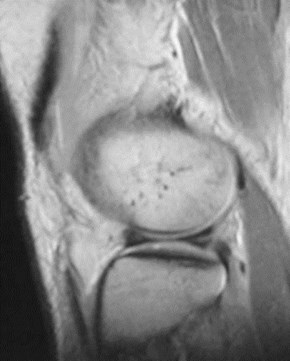
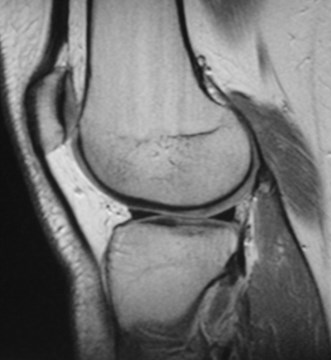
Normal


“Bucket handle” meniscal tear
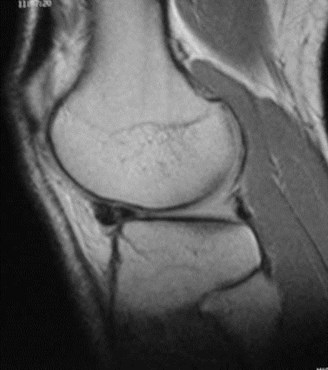

Normal
Normal anterior horn
Flipped posterior horn


Knee — acute pain or trauma
Acute internal derangementAcute internal derangement
MeniscusMeniscus
Collateral and cruciate ligamentsCollateral and cruciate ligaments
Extensor tendons (patellar and quad)Extensor tendons (patellar and quad)
“Bone bruise”“Bone bruise”
MRI excellent for global evaluationMRI excellent for global evaluation


ACL tear
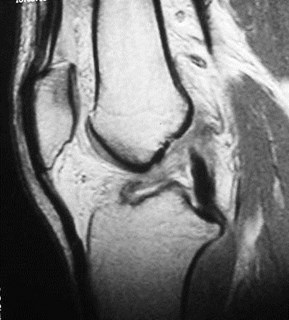
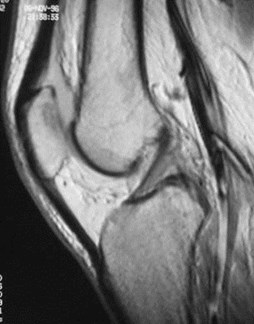
Normal


PCL tear
Less common than ACL injuryLess common than ACL injury
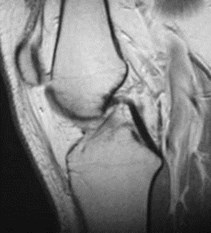
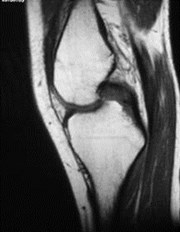
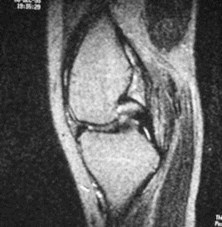
normal
T1 sag
Thickenedligament, notpurely black
T2 sag
Bright signalin superiorligament


Collateral ligaments
MCL tearMCL tear
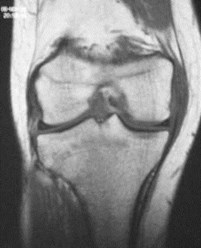
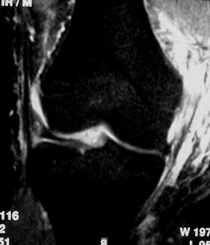
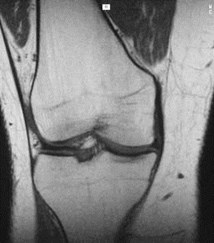
normal
T1 sag
Thickenedligament, notpurely black
T2 sag
Edema atsite of tornligament


Bone bruise
“microtrabecular” fracture“microtrabecular” fracture
No cortical break or instabilityNo cortical break or instability
Heals with restHeals with rest
Often associated with other injuriesOften associated with other injuries
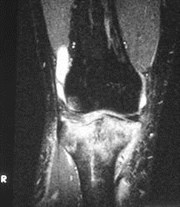
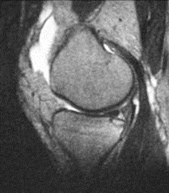
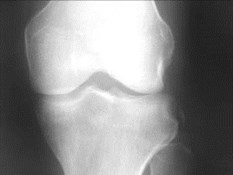


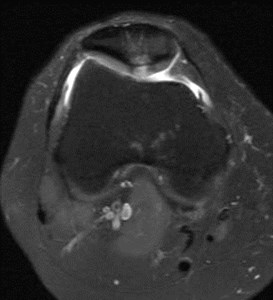
Chondromalacia patellae
Degenerative process of patellar cartilageDegenerative process of patellar cartilage
Early stages reversible, well seen with MRIEarly stages reversible, well seen with MRI
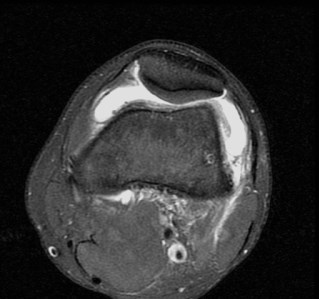
Normal


Review Questions


Hip MRI: True or False?
1.MRI is more sensitive than radiography foravascular necrosis of the hip.1.MRI is more sensitive than radiography foravascular necrosis of the hip.
2.MR arthrography is indicated as initialevaluation in chronic hip pain.2.MR arthrography is indicated as initialevaluation in chronic hip pain.
3.MRI may show occult fractures of the pelvison hip examinations.3.MRI may show occult fractures of the pelvison hip examinations.
4.Bursitis is difficult to identify on MRexaminations.4.Bursitis is difficult to identify on MRexaminations.


Knee MRI: True or False?
1.MRI is accurate in diagnosis ofmeniscal injuries.1.MRI is accurate in diagnosis ofmeniscal injuries.
2.Bone bruises are easily seen on MRI2.Bone bruises are easily seen on MRI
3.Chondromalacia patellae is only seenin its late stages with MRI.3.Chondromalacia patellae is only seenin its late stages with MRI.
4.Meniscal degeneration is common inmiddle aged adults.4.Meniscal degeneration is common inmiddle aged adults.


Shoulder MR: True of False?
1.MR arthrography is best suited for patientswith questionable rotator cuff tear.1.MR arthrography is best suited for patientswith questionable rotator cuff tear.
2.Rotator cuff tears are most common inyoung adults.2.Rotator cuff tears are most common inyoung adults.
3.Labral injuries are associated withinstability.3.Labral injuries are associated withinstability.
4.The labrum is best seen with MRarthrography.4.The labrum is best seen with MRarthrography.


Additional reading
Stabler A et al. Musculoskeletal MR: Knee. Eur.Radiol. 2000; 10:230-241.Stabler A et al. Musculoskeletal MR: Knee. Eur.Radiol. 2000; 10:230-241.
Petersilge, CA MR Arthrography for Evaluation of theAcetabular Labrum. Skeletal Radiol. 2001; 30:423-430.Petersilge, CA MR Arthrography for Evaluation of theAcetabular Labrum. Skeletal Radiol. 2001; 30:423-430.
Oka M et al Prevalence and Patterns of Occult HipFractures and Mimics Revealed by MRI. AJR 2004;182:283-288.Oka M et al Prevalence and Patterns of Occult HipFractures and Mimics Revealed by MRI. AJR 2004;182:283-288.
Beltran J MR Arthrography of the Shoulder: Variantsand Pitfalls. Radiographics 1997; 17:1403-1412.Beltran J MR Arthrography of the Shoulder: Variantsand Pitfalls. Radiographics 1997; 17:1403-1412.



The End
Use the back button on the browser to exit the program