
Differential Diagnosis
In
Pulmonary Disease
© William Herring, MD, FACR

I
n
s
t
e
a
d
o
f
r
e
m
e
m
b
e
r
i
n
g
n
o
t
h
i
n
g
a
b
o
u
t
a
l
o
t
o
f
t
h
i
n
g
s
,
r
e
m
e
m
b
e
r
a
l
i
t
t
l
e
a
b
o
u
t
a
f
e
w
t
h
i
n
g
s

How This Works
Eachdifferentialstarts with aphoto of thefindings (in thiscase it’s theesophagus, butdisregard that)


How This Works
The next slidegives the title ofthe differentialand the numberof items on thelist


How This Works
The next slidein each setgives thedifferential


How This Works
The last slidein each setgives the“answer”
Start
Start



For what is this a differential diagnosis?

Anterior Mediastinal Masses
1.
2.
3.
4.

Anterior Mediastinal Masses
1.Thymoma
2.Teratoma
3.Substernal thyroid
4.Lymphoma

Teratoma




Day 1
Two days later
For what is this a differential diagnosis?

Acute Airspace Disease
1.
2.
3.
4.

Acute Airspace Disease
1.Pulmonary edema
2.Pneumonia
3.Aspiration
4.Hemorrhage

Non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema


Day 1
Two days later



Opacified Hemithorax
1.
2.
3.
4.

Opacified Hemithorax
1.Atelectasis
2.Pleural effusion
3.Pneumonia
4.Post-pneumonectomy

Pneumonectomy




Large Cavitary Lung Lesions
1.
2.
3.

Large Cavitary Lung Lesions
1.Abscess
2.Carcinoma
3.TB

Carcinoma of the Lung




Pneumomediastinum
1.
2.
3.
4.

Pneumomediastinum
1. Ruptured esophagus
2. Ruptured trachea/bronchus
3. Iatrogenic/trauma
4. Asthma

Asthmatic with pneumomediastinum



July ’65

June ‘72

Chronic Alveolar Disease
1.
2.
3.
4.

Chronic Alveolar Disease
1.Alveolar cell ca
2.Alveolar sarcoid
3.Lymphoma
4.Alveolar proteinosis

Alveolar Sarcoid

July ’65

June ‘72



Upper Lobe Disease
1.
2.
3.
4.

Upper Lobe Disease
1. TB (2° TB)
2. Silicosis
3. Eosinophilic granuloma
4. Ankylosing spondylitis

Progressive Massive Fibrosis in Silicosis




Bibasilar Interstitial Disease
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.

Bibasilar Interstitial Disease
1.B
2.A
3.D
4.A
5.S
6.S
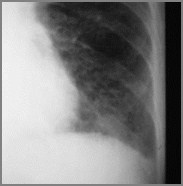

Bibasilar Interstitial Disease
1.Bronchiectasis
2.Aspiration (Chronic)
3.DIP
4.Asbestosis
5.Sickle Cell Disease
6.Scleroderma

Scleroderma


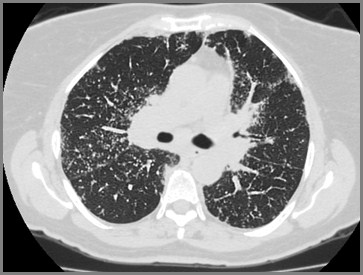

Micronodular Lung Disease
1.
2.
3.
4.

Micronodular Lung Disease
1.Mets
2.Sarcoid
3.Pneumoconiosis
4.Miliary TB

Sarcoid




Small Cavitary Lung Lesions
1.
2.
3.
4.

Small Cavitary Lung Lesions
1.Septic emboli
2.Rheumatoid nodules
3.Squamous or transitional cell mets
4.Wegener’s Granulomatosis

Septic emboli




Lymphangitic Spread to the Lungs
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.

Lymphangitic Spread to the Lungs
1.Lung ca
2.Breast ca
3.Stomach ca
4.Pancreas ca
5.Laryngeal ca
6.Cervical ca

Lymphangitic Spread of Lung Cancer




Multiple Lung Nodules
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.

Multiple Lung Nodules
1.Metastases
2.Metastases
3.Metastases
4.Metastases
5.Metastases

Multiple Lung Nodules
2.Wegener’s granulomatosis
3.Rheumatoid nodules
4.AVMs
5.Septic emboli

Metastases from colon carcinoma




Pulmonary Interstitial Edema
1.
2.
3.

Pulmonary Interstitial Edema
1.CHF
2.Lymphangitic spread
3.Allergic reaction

Congestive Heart Failure



Day 3

Day 0

Shifting Infiltrates
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
Any 3

Shifting Infiltrates
1. Aspiration
2.Loeffler’s syndrome
3.ABPA
4.Asthma
5.Polyarteritis
6.Viral pneumonia

Recurrent Aspiration

Day 3

Day 0


Unchanged in 8 mos

Chronic Interstitial DiseasePulmonary Fibrosis
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.

Chronic Interstitial DiseasePulmonary Fibrosis
1.Pneumoconiosis
2.Interstitial Pneumonia
3.Granulomatous disease
4.Neoplastic disease
5.Idiopathic fibrosis
6.Collagen vascular disease

Sarcoid




Inspiration
Expiration

Unilateral Hyperlucent Lung
1.
2.
3.
4.
Any 3

Unilateral Hyperlucent Lung
1.Swyer-James syndrome
2.Pulmonary embolism
3.Pneumothorax
4.Obstructive emphysema

Obstructive Emphysema


Inspiration
Expiration



Hours later
3/29/09

Rapidly Clearing Airspace Disease
1.
2.
3.
4.
Any 3

Rapidly Clearing Airspace Disease
1.Hemorrhage
2.Pulmonary edema
3. Aspiration
4.Pneumococcal pneumonia

Pulmonary Edema


Hours later
3/29/09



Masses with Air Bronchograms
1.
2.
3.

Masses with Air Bronchograms
1.Lymphoma
2.Alveolar cell ca
3.Pseudolymphoma (Maltoma)

Lymphoma




Cavitating Pneumonia
1.
2.
3.
4.
Any 3

Cavitating Pneumonia
1.Staph
2.Strep
3.TB
4.Gram negative (Klebsiella)

Staphylococcal Pneumonia




Middle Mediastinal Masses
1.
2.
3.
4.
Any 3

Middle Mediastinal Masses
1.Lymphadenopathy
2.Aneurysms
3.Esophageal duplication
4.Bronchogenic cysts


Bronchogenic Cyst
M=2



Hilar AdenopathyBilateral or Unilateral
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Any 3

Hilar AdenopathyBilateral or Unilateral
1. Sarcoid (B/L)
2. TB (U/L)
3. Lymphoma (B/L)
4. Bronchogenic ca (U/L)
5. Mets (B/L)

Sarcoid




Cavities Containing Masses
1.
2.
3.

Cavities Containing Masses
1.Aspergillosis
2.Cavitating bronchogenic ca
3.Tuberculosis

Aspergilloma




Airspace Dz with Effusion
1.
2.
3.
4.
Any 3

Airspace Dz with Effusion
1.Staph pneumonia
2.Strep pneumonia
3.TB
4.Pulmonary infarct

Staph Pneumonia




“Mass”+ ipsilateral adenopathy
1.
2.
3.

“Mass”+ ipsilateral adenopathy
1.Bronchogenic ca
2.Lymphoma
3.TB

Bronchogenic Carcinoma
Bronchogenic Carcinoma





Solitary Pulmonary Nodule
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Any 3

Solitary Pulmonary Nodule
1. Bronchogenic ca
2. Hamartoma
3. Histoplasmoma
4. TB granuloma
5. Carcinoid tumor
6. Solitary met
7. Round pneumonia
8. Rounded atelectasis

Hamartoma





Left-sided Pleural Effusion
1.
2.
3.

Left-sided Pleural Effusion
1. Boerhaave’s Syndrome
2. Dissecting aortic aneurysm
3. Pancreatitis

Dissecting Aortic Aneurysm




Pleural Effusion
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
Any 3

Pleural Effusion
1.CHF
2.Mets
3.Pancreatitis
4.Pulmonary embolism
5.Trauma
6.Empyema
7.Collagen vascular
8.Ovarian tumor (Meig’s Syndrome)
9.Chylothorax

Congestive Heart Failure




Multiple Small Calcifications
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Any 3

Multiple Small Calcifications
1.Histoplasmosis
2.Silicosis
3.Chicken pox pneumonia
4.Pulmonary ossification 2° MS
5.Alveolar microlithiasis

Histoplasmosis





Posterior Mediastinal Masses
1.
2.
3.

Posterior Mediastinal Masses
1.Neurogenic tumors
2.Lymphadenopathy
3.Extramedullary hematopoesis

Neurofibroma





Mediastinal Adenopathy
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Any 3

Mediastinal Adenopathy
1.Bronchogenic ca
2.Lymphoma
3.TB
4.Mets
5.Sarcoid

Lymphoma




Lung Disease & Rib Destruction
1.
2.
3.
4.
Any 3

Lung Disease & Rib Destruction
1.Bronchogenic ca, i.e Pancoast tumor
2.Actinomycosis
3.Blastomycosis
4.Multiple myeloma

Pancoast Tumor




Pleural Calcification
1.
2.
3.

Pleural Calcification
1.Old TB empyema
2.Asbestos exposure
3.Hemothorax

Asbestos Exposure





“Masses” in Cardiophrenic Angle
1.
2.
3.

“Masses” in Cardiophrenic Angle
1.Sequestration
2.Diaphragmatic hernia
3.Pericardial cyst

Pericardial Cyst





Unilateral Pulmonary Edema
1.
2.
3.
4.
Any 3

Unilateral Pulmonary Edema
1. Rapid expansion of PTX
2. Rapid drainage of hemothorax
3. Postural
4. Disease in other lung, e.g. COPD

Re-expansion Pulmonary Edema




Reverse “Pulmonary Edema”
1.
2.
3.

Reverse “Pulmonary Edema”
1.Eosinophilic lung disease, e.g. Loeffler’s
2.Sarcoid
3.Pulmonary contusions

Loeffler’s Syndrome


The End
