
Teratomas, Seminomas andChoriocarcinomas
Germ Cell Neoplasms of AnteriorMediastinum
© William Herring, MD, FACR

Group Includes
Benign and malignant teratomas
Seminomas
Choriocarcinomas
Benign dermoid cysts
Embryonal cell carcinomas

TeratomasGeneral
10% of all mediastinal masses
About same frequency as thymomas
Occur in 3rd and 4th decades
Thymomas occur later in life
5% of teratomas occur in mediastinum
Rare site for occurrence of teratomas, mostbeing ovarian in origin

TeratomaDefinitions
Epidermoid=all ectodermal derivatives
Dermoid= ectoderm and mesoderm
Teratoma= ectoderm, mesoderm andendodermal components

TeratomasClinical
Usually asymptomatic
Rare rupture of dermoid into trachea willlead to trichoptysis—expectoration ofhair

TeratomasPhysiologic Activity
Thyroid hormone
Alpha fetoprotein
HCG
Amylase
Lipase

TeratomasEmbryology
Arise from primitive germ cell rests whichshould migrate along urogenital ridge toprimitive gonad but whose journey isinterrupted in mediastinum
Arise from primitive germ cell rests whichshould migrate along urogenital ridge toprimitive gonad but whose journey isinterrupted in mediastinum

TeratomasMalignancy
Most cystic lesions are benign
Most solid lesions are malignant
Overall about 30% are malignant

TeratomasImaging
May be cystic or solid
Most are cystic
Most occur in anterior mediastinum
Near junction of great vessels and heart
Calcification may occur rarely
Of no help since thymomas also calcify
Exception would be very rare occurrence of atooth or bone in dermoid

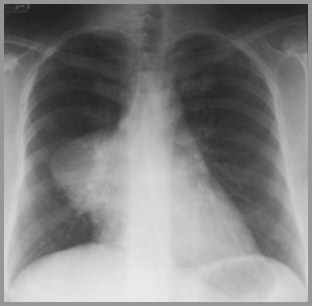
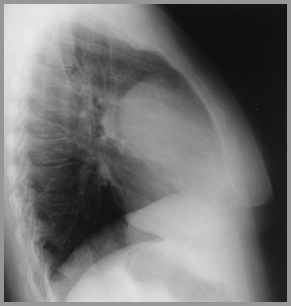
Teratoma

TeratomasCT Appearance
CT shows fatty mass
Globular calcifications
Rarely a tooth or bone
Benign lesions are usually smooth
Malignant masses tend to be lobulated
Rapid increase in size usually meanshemorrhage into a cyst rather thanmalignancy

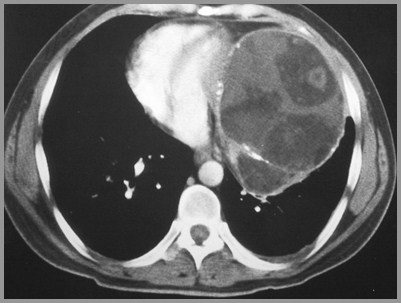
Teratoma with fat, calcium and soft tissue


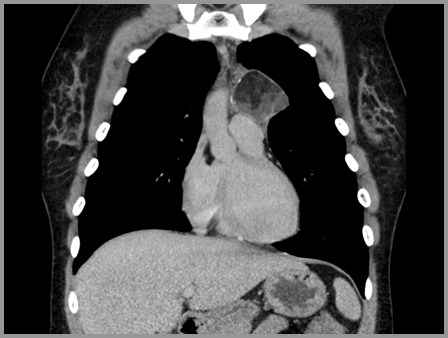
Teratoma

Mediastinal Seminoma
Rare
Almost always in young men
Identical to testicular seminoma andovarian dysgerminoma
May be well-encapsulated or invasive
Tends to be lobulated
Cannot be differentiated from teratoma

Primary Choriocarcinoma-1
Even rarer than seminoma in mediastinum
Only 23 reported in the literature, almostall in men
Occur between 20-30 years
May be lobulated

Primary Choriocarcinoma-2
May have elevated beta sub unit of HCG
Growth is very rapid leading to dyspnea,hemoptysis, stridor
Gynecomastia and a + Aschheim-Zondektest can occur
Rapidly fatal

The End