
Pancoast Tumor
© William Herring, MD, FACR

Pancoast TumorGeneral
Arises in superior sulcus of lung
Groove formed by subclavian artery
Unique among parenchymal processesfor its propensity to violate pleuralbarrier and involve chest wall

Pancoast TumorGeneral
Bone destruction is common — 1st ribmost often affected
Squamous cell most common cell type

Pancoast TumorComplications
Brachial plexus involvement
Horner’s syndrome
Ptosis
Myosis
Anhydrosis
And rarely, enopthalmus
Superior vena caval obstruction
When tumor occurs on right

Pancoast TumorImaging
Apical cap on affected side
Flat, uniform density
DDX: apical pleural thickening
Other side usually normal in Pancoast,thickened with apical pleural thickening

Pancoast TumorImaging
Bone involvement
Key to diagnosis
AP of cervical spine frequently shows rib destruction
Bone scan may be needed if clinical suspicion high
MR helpful in showing involvement of
Blood vessel
Brachial plexus
Vertebral canal

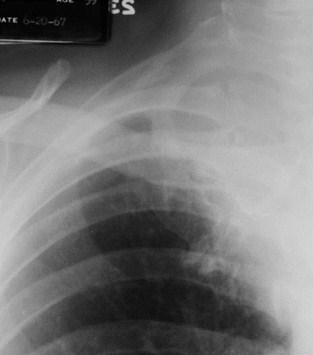
Pancoast Tumor- Right apical soft tissue mass (redarrow) with destruction of the 2nd posterior rib(yellow arrow)

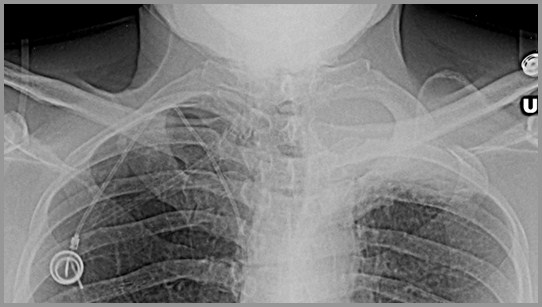
Pancoast Tumor- Left apical soft tissue mass (redarrow) with destruction of the 2nd posterior rib(yellow arrow)

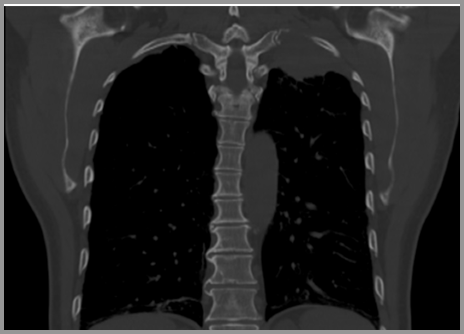
Pancoast Tumor- Left apical soft tissue mass (redarrow) with destruction of the 1st posterior rib(yellow arrow)

The End