
The Other P.I.E.Pulmonary Infiltrates WithEosinophiliaEosinophilic Lung Disease
The Other P.I.E.Pulmonary Infiltrates WithEosinophiliaEosinophilic Lung Disease
© William Herring, MD, FACR

Pulmonary Infiltrates withEosinophilia
Pulmonary disease affecting majorairways and/or lung parenchymaassociated with blood and/or tissueeosinophilia

Eosinophilic Lung DiseaseClassification by Clinical Severity
BenignLoeffler’s syndrome
IntermediateEosinophilic pneumonia
SevereHypersensitivity AngiitisPolyarteritis nodosa

Idiopathic
Associated With Specific Etiology
Associated with Connective TissueDisease or Vasculitis
Eosinophilic Lung DiseaseClassification by Etiology

Loeffler’s syndrome
Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Chronic Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Hypereosinophilic syndrome
Eosinophilic Lung DiseaseIdiopathic

Atopic history common
May be asymptomatic or very symptomatic
High fever and dyspnea
Associated with blood eosinophilia
Biopsies also show eosinophils in infiltrate
Loeffler’s SyndromeGeneral Considerations

May present as reverse pulmonary edema
Infiltrates may be single or multiple
Usually transitory airspace opacities
Reduction in size of one infiltrate in 24hrs with appearance of a 2nd issuggestive
Infiltrates are usually peripheral
Loeffler’s SyndromeImaging Findings

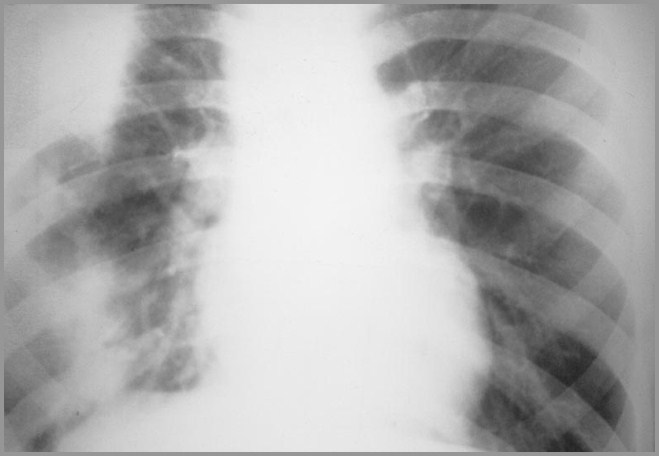
Loeffler’s syndrome

Chronic Eosinophilic PneumoniaGeneral
Very rare disease (188 cases)
More protracted course than Loeffler’s
Atopic history
Female:male 2:1

Chronic Eosinophilic PneumoniaPathology
High levels of circulating IgE
Eosinophilic abscesses in lung
Blood eosinophilia
Pathologically identical to Loeffler’s

Chronic Eosinophilic PneumoniaX-ray
Similar to Loeffler’s except infiltrateslast for many days or week withoutsteroids

Chronic Eosinophilic PneumoniaClinical
Most are asymptomatic or mild symptoms
Some have
High fever
Malaise
Weight loss
Respond within days to steroid therapy

Idiopathic
Associated With Specific Etiology
Associated with Connective TissueDisease or Vasculitis
Eosinophilic Lung DiseaseClassification of PIE by Etiology

Eosinophilic Lung DiseaseSpecific Etiology
Drug-induced
Nitrofurantoin
Penicillin
Sulfonamides
Parasite-induced
Ascariasis
Paragonomiasis
Parasite-induced
Strongyloidiasis
TropicalEosinophilia
Fungus-induced
ABPA

Eosinophilic Lung DiseaseDrug-induced
Interstitial edema
Most commonly nitrofurantin
Patchy, fleeting air space disease
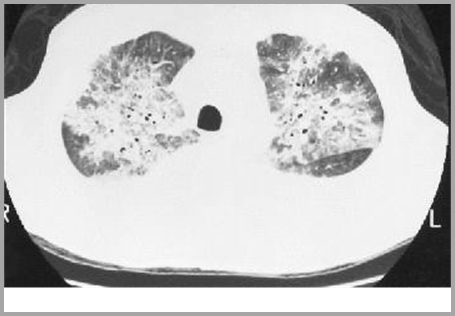
Amiodarone
Penicillin
Sulfonamides
Hydrochlorthiazide

Nitrofurantoin (Furadantin)
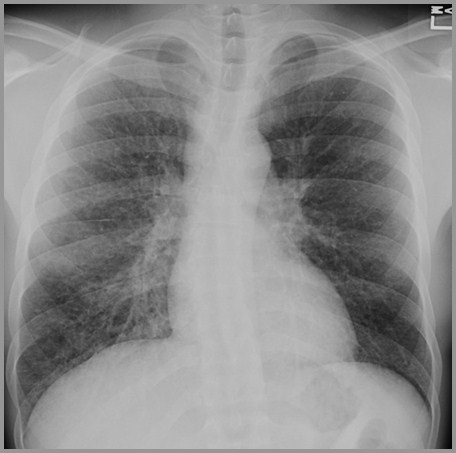
Diseasedisappearsshortly afterremoval ofantibiotic

Amiodarone

Eosinophilic Lung DiseaseParasite-induced
Most often from Ascaris lumbricoides
Caused by the larva as they passthrough lungs
Allergic response of patchy, fleetinginfiltrates
Blood eosinophilia

Idiopathic
Associated With Specific Etiology
Associated with Connective TissueDisease or Vasculitis
Eosinophilic Lung DiseaseClassification of PIE by Etiology

Rheumatoid Disease
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis(Wegener’s Granulomatosis)
Allergic Granulomatosis
Polyarteritis Nodosa
Eosinophilic Lung DiseaseConnective Disease or Vasculitis

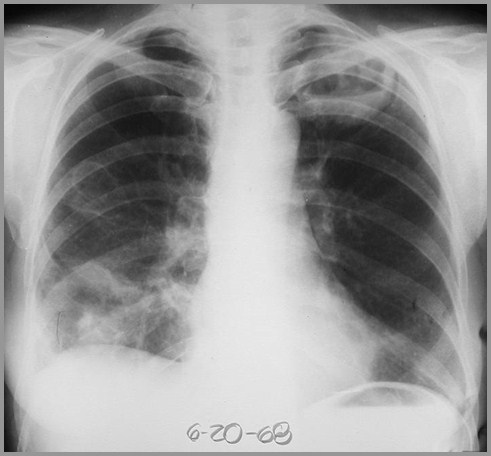
Multiple nodules ofvarying sizes withfrequent cavitation
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis

The End