
The ABC’s ofThe ABC’s of
Heart DiseaseHeart Disease
© William Herring, MD, FACR
With AcknowledgementFor Its Creation toBernard J. Ostrum, M.D.
With AcknowledgementFor Its Creation toBernard J. Ostrum, M.D.

What It Is
An approach
For congenital or acquired heartdisease in adults
Asking systematic set of questions
Answers based on certainfundamental observations
Visible on frontal chest x-ray alone


Cardio-thoracicRatioCardio-thoracicRatio
<50%
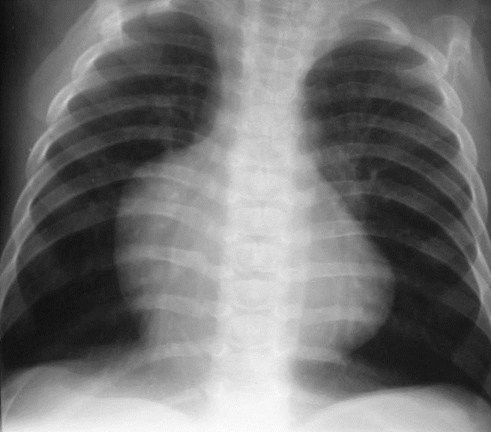
One of the easiestobservations to make issomething you alreadyknow: the cardio-thoracicratio which is the widestdiameter of the heartcompared to the widestinternal diameter of the ribcage
One of the easiestobservations to make issomething you alreadyknow: the cardio-thoracicratio which is the widestdiameter of the heartcompared to the widestinternal diameter of the ribcage

Sometimes, CTR is more than 50%But Heart is Normal
Extracardiac causes of cardiacenlargement
Portable AP films
Obesity
Pregnant
Ascites
Straight back syndrome
Pectus excavatum

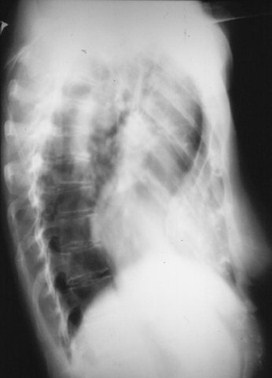
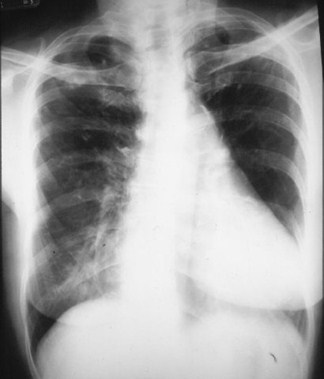
>50%
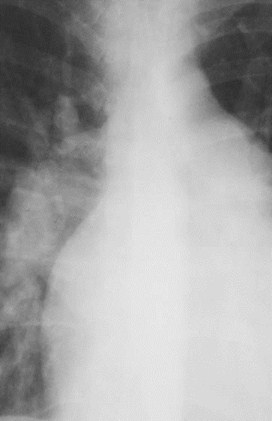
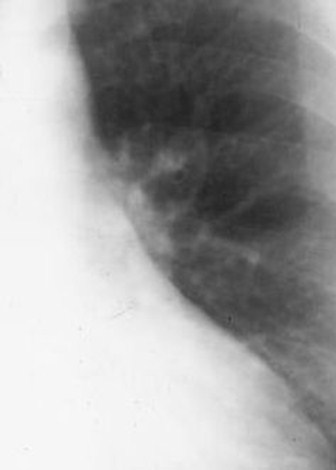
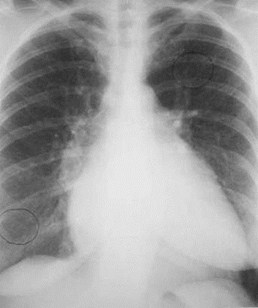
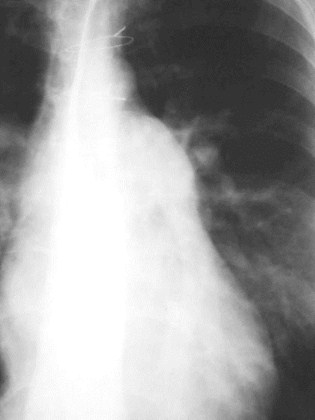
Here is a heart that is larger than 50% of the cardiothoracic ratio, but it is still a normal heart.This is because there is an extracardiac cause for the apparent cardiomegaly. On the lateralfilm, the arrows point to the inward displacement of the lower sternum in a pectus excavatumdeformity.

Obstruction to outflow of the ventricles
Ventricular hypertrophy
Must look at cardiac contours
Sometimes, CTR is less than 50%But Heart is Abnormal

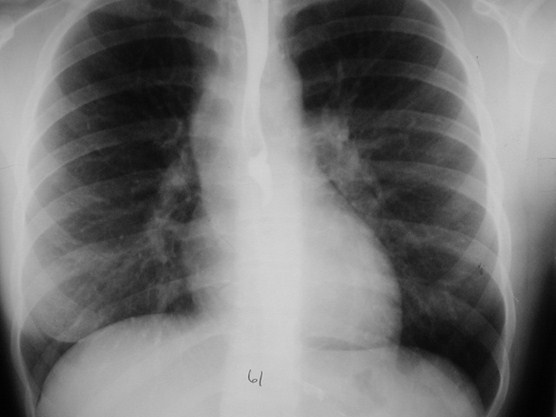
<50%
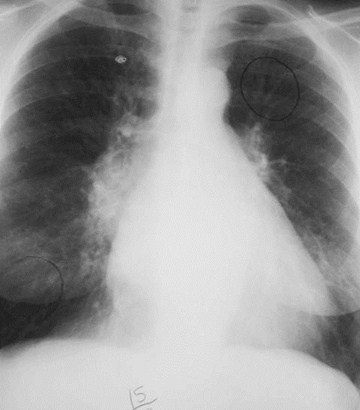
Here is an example of a heart which is less than 50% of the CTRin which the heart is still abnormal. This is recognizable becausethere is an abnormal contour to the heart (yellow arrows).
Here is an example of a heart which is less than 50% of the CTRin which the heart is still abnormal. This is recognizable becausethere is an abnormal contour to the heart (yellow arrows).


Ascending Aorta
Ascending Aorta
“Double density”of LA enlargement
“Double density”of LA enlargement
Right atrium
Right atrium
Left ventricle
Left ventricle
Indentation forLA
Indentation forLA
Main pulmonaryartery
Main pulmonaryartery
Aortic knob
Aortic knob
The Cardiac Contours
The Cardiac Contours
There are 7 contours to the heart in the frontal projection in this system.


Ascending Aorta
Ascending Aorta
“Double density”of LA enlargement
“Double density”of LA enlargement
Right atrium
Right atrium
Left ventricle
Left ventricle
Indentation forLA
Indentation forLA
Main pulmonaryartery
Main pulmonaryartery
Aortic knob
Aortic knob
The Cardiac Contours
The Cardiac Contours
But only the top five are really importantin making a diagnosis.


Low density,almost straightedgerepresents sizeof ascendingaorta
Low density,almost straightedgerepresents sizeof ascendingaorta
Ascending Aorta
Ascending Aorta

Small
Prominent
Ascending Aorta
Ascending Aorta


Indentationwhere “doubledensity” of leftatrialenlargement willappear
Indentationwhere “doubledensity” of leftatrialenlargement willappear
Double density of left atrialenlargement
Double density of left atrialenlargement


Left atriumLeft atrium
sits in middle ofheartposteriorlysits in middle ofheartposteriorly
Left atriumLeft atrium
sits in middle ofheartposteriorlysits in middle ofheartposteriorly
Left atriumLeft atrium
forms no borderof normal heartin PA viewforms no borderof normal heartin PA view
Left atriumLeft atrium
forms no borderof normal heartin PA viewforms no borderof normal heartin PA view
LA
RA
LV
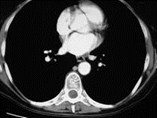
Even though we are on the right side of the heart, we cansee left atrial enlargement. Normally the left atrium sitsright in the middle of the heart posteriorly and does notform a normal border on the frontal film.
Even though we are on the right side of the heart, we cansee left atrial enlargement. Normally the left atrium sitsright in the middle of the heart posteriorly and does notform a normal border on the frontal film.
This inset from a CT scan of the chestshows how RA and LV obscure LA fromforming a heart border on the frontal film.


“DoubleDensity”of left atrialenlargement“DoubleDensity”of left atrialenlargement
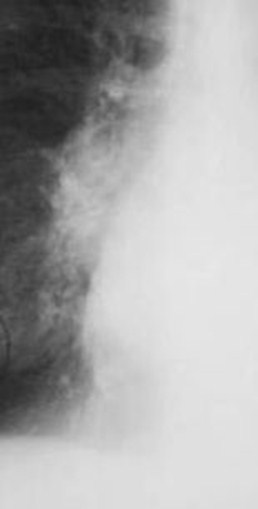
When the LA enlarges, it will do something on the leftside of the heart we’ll talk about in a minute. And it mayproduce a “double-density” on the right side of the heart.
When the LA enlarges, it will do something on the leftside of the heart we’ll talk about in a minute. And it mayproduce a “double-density” on the right side of the heart.

RA
LALA
Two shadows,the yellowarrow pointingto the LA andthe red arrowto the RAoverlap eachother wheretheindentationbetween theascendingaorta and rightheart bordermeet
Two shadows,the yellowarrow pointingto the LA andthe red arrowto the RAoverlap eachother wheretheindentationbetween theascendingaorta and rightheart bordermeet


Right atrium–not importantcontour inadults
Right atrium–not importantcontour inadults
The last bump on the right side is the right atrium. Sincethere is no disease in an adult that causes isolatedenlargement of the RA, we’ll consider the RA togetherwith the RV later.The last bump on the right side is the right atrium. Sincethere is no disease in an adult that causes isolatedenlargement of the RA, we’ll consider the RA togetherwith the RV later.
The last bump on the right side is the right atrium. Sincethere is no disease in an adult that causes isolatedenlargement of the RA, we’ll consider the RA togetherwith the RV later.The last bump on the right side is the right atrium. Sincethere is no disease in an adult that causes isolatedenlargement of the RA, we’ll consider the RA togetherwith the RV later.


Aortic knobshouldmeasure< 35mm
Aortic knobshouldmeasure< 35mm
Aortic Knob
Aortic Knob
The first bump onthe left-side is theaortic arch. We canmeasure the knobfrom the lateralborder of air in thetrachea to theedge of the aorticknob.
The first bump onthe left-side is theaortic arch. We canmeasure the knobfrom the lateralborder of air in thetrachea to theedge of the aorticknob.

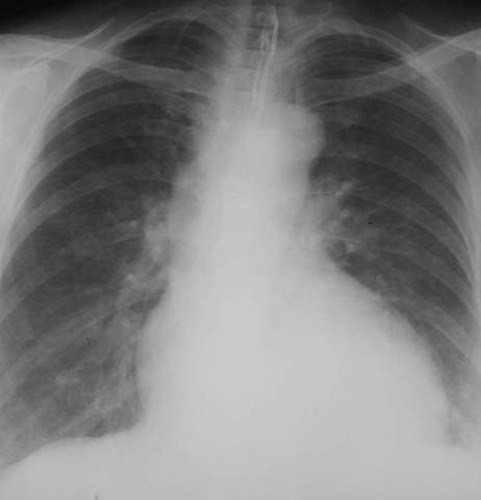
42mm
Enlarged with:
Increased pressure
Increased flow
Changes in aortic wall
Aortic Knob
Aortic Knob


ImportantImportant
ImportantImportant
MainPulmonaryArtery
MainPulmonaryArtery
The next bump down is themain pulmonary artery and isthe keystone of this system.


Finding theMainPulmonaryArtery
Finding theMainPulmonaryArtery


Adjacent to leftpulmonary artery
Adjacent to leftpulmonary artery
Finding theMainPulmonaryArtery
Finding theMainPulmonaryArtery
We can measure the main pulmonary artery . . .

If we draw atangent linefrom the apexof the leftventricle to theaortic knob(red line) andmeasure alongaperpendicularto that tangentline (yellowline)
The distancebetween thetangent andthe mainpulmonaryartery (betweentwo smallgreen arrows)falls in a rangebetween 0 mm(touching thetangent line) toas much as 15mm away fromthe tangent line

0 mm0 mm
MainPulmonaryArteryMainPulmonaryArtery
AoAo
15 mm15 mm
MainPulmonaryArteryMainPulmonaryArtery
AoAo
LVLV
LVLV
Main pulmonaryartery ranges from0 mm–15mmfrom tangent line
Main pulmonaryartery ranges from0 mm–15mmfrom tangent line

Two Major Classifications
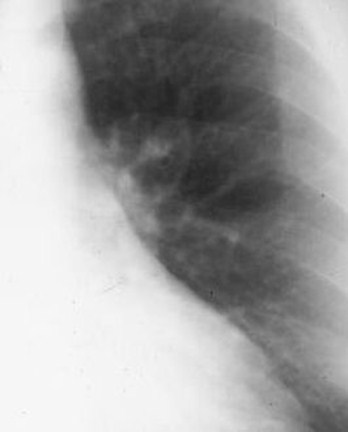
The main pulmonary artery (MPA)projects beyond the tangent line
The main pulmonary artery is morethan 15 mm away from the tangent line
Because the MPA is small or absent
Because the tangent line is being pushed awayfrom the MPA

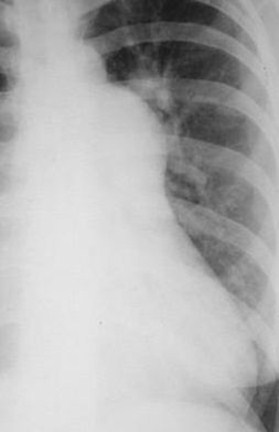
Increasedpressure
Increased flow
Mainpulmonaryarteryprojectsbeyondtangent
Mainpulmonaryarteryprojectsbeyondtangent

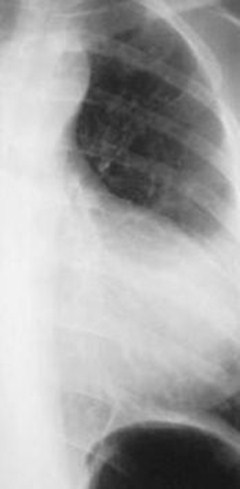
27
Small pulmonaryartery
Truncus arteriosus
Tetralogy of Fallot
Main pulmonaryartery is morethan 15 mmfrom tangent
Main pulmonaryartery is morethan 15 mmfrom tangent

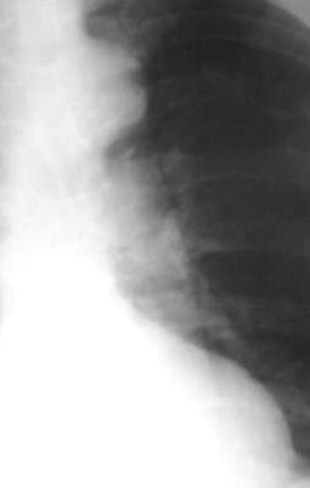
Left ventricleand/or aorticknob push thetangent away
Common
29
Main pulmonaryartery is morethan 15 mmfrom tangent
Main pulmonaryartery is morethan 15 mmfrom tangent

0 - 15 mm0 - 15 mm

0 - 15 mm0 - 15 mm
Torecapitulate:


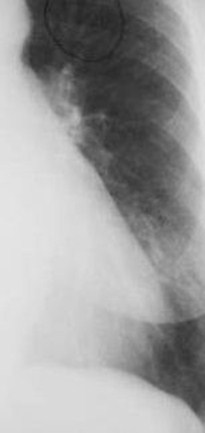
Concavity where Latrium will appear onleft side whenenlarged
Concavity where Latrium will appear onleft side whenenlarged
Left atrial enlargement
Left atrial enlargement


“Straightening of theleft heart border”
“Straightening of theleft heart border”
Left atriummay enlargewithoutproducingdoubledensityLeft atriummay enlargewithoutproducingdoubledensity
Left atriummay enlargewithoutproducingdoubledensityLeft atriummay enlargewithoutproducingdoubledensity
Left atrial enlargement
Left atrial enlargement

MainPulmonaryArteryMainPulmonaryArtery
MainPulmonaryArteryMainPulmonaryArtery
LeftAtrialAppendageLeftAtrialAppendage
LeftAtrialAppendageLeftAtrialAppendage
In the example on theright, not only is theleft atrium enlarged,but the left atrialappendage is too. Sothere is a convexityoutward where thereis normally aconcavity inward.


Left Ventricle
Left Ventricle
Left ventricle
Left ventricle

Which Ventricle is Enlarged?
The best way to determine whichventricle is enlarged is to look atthe corresponding outflow tract foreach ventricle

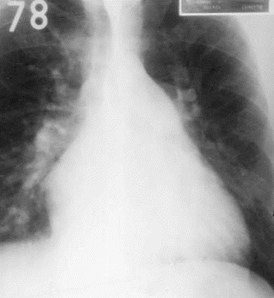
If Heart Is Enlarged,And Main PulmonaryArtery is Big
>50%
Which Ventricle is Enlarged?
Then Right Ventricle isEnlarged

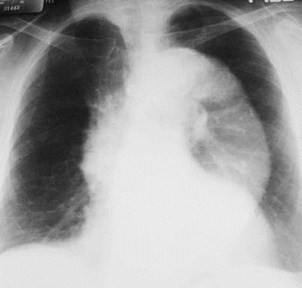
If Heart Is Enlarged,And Aorta is Big
>50%
Which Ventricle is Enlarged?
Then Left Ventricleis Enlarged

Which ventricle is enlarged?
The best way to determine whichventricle is enlarged is to look atthe corresponding outflow tractfor each ventricle
Aorta for the LV
MPA for the RV

Once one ventricle is enlarged,it’s impossible to tell if other ventricleis also enlarged
Which Ventricle is Enlarged?


Ascending Aorta
Ascending Aorta
“Double density”of LA enlargement
“Double density”of LA enlargement
Right atrium
Right atrium
Left ventricle
Left ventricle
Indentation forLA
Indentation forLA
Main pulmonaryartery
Main pulmonaryartery
Aortic knob
Aortic knob
The Cardiac Contours
The Cardiac Contours


Ascending Aorta
Ascending Aorta
“Double density”of LA enlargement
“Double density”of LA enlargement
Right atrium
Right atrium
Left ventricle
Left ventricle
Indentation forLA
Indentation forLA
Main pulmonaryartery
Main pulmonaryartery
Aortic knob
Aortic knob
The Cardiac Contours
The Cardiac Contours

The PulmonaryVasculatureThe PulmonaryVasculature

Five States of the PulmonaryVasculature
Normal
Pulmonary venous hypertension
Pulmonary arterial hypertension
Increased flow
Decreased flow

What We’re Going to Evaluate
Right Descending Pulmonary Artery
Distribution of flow in the lungs
Upper versus lower lobes
Central versus peripheral


What to EvaluateWhat to Evaluate
11
33
22
22


RightDescendingPulmonaryArtery
RightDescendingPulmonaryArtery
Serves rightmiddle andlower lobes
Serves rightmiddle andlower lobes
1. Right Descending Pulmonary Artery1. Right Descending Pulmonary Artery

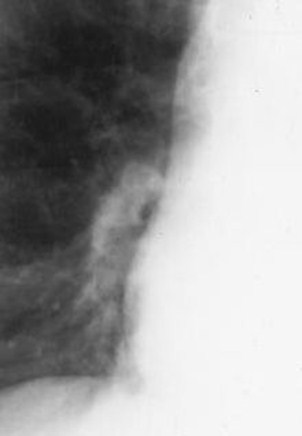
Diameter canbe measured(beforebifurcation)
Diameter canbe measured(beforebifurcation)
RDPA< 17 mm
1. Right Descending Pulmonary Artery1. Right Descending Pulmonary Artery
Normally, therightdescendingpulmonaryartery shouldnot be morethan 17mm indiameter


2. Normal Distribution of FlowUpper Versus Lower Lobes
2. Normal Distribution of FlowUpper Versus Lower Lobes
In erect position,blood flow tobases > than flowto apices
In erect position,blood flow tobases > than flowto apices
Size ofvessels atbases isnormally> than sizeof vesselsat apex
You can’t measure size ofvessels at the left basebecause the heart obscuresthem


Normaltapering ofvesselsfromcentral toperipheral
Normaltapering ofvesselsfromcentral toperipheral
Central vesselsgive rise toprogressivelysmaller peripheralbranches
Central vesselsgive rise toprogressivelysmaller peripheralbranches
3. Normal Distribution of FlowCentral versus peripheral
3. Normal Distribution of FlowCentral versus peripheral


11
33
22
22
Normal Vasculature - review
Normal Vasculature - review
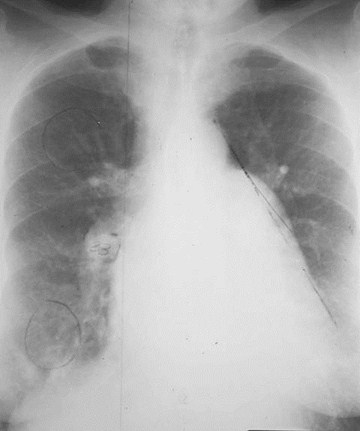
RDPA< 17 mm indiameter
Lower lobevesselslarger thanupper lobevessels
Gradualtapering ofvesselsfrom centraltoperipheral

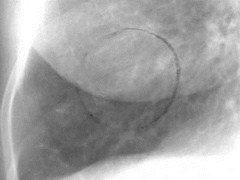
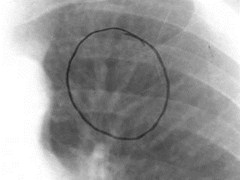

RDPA usually > 17 mm
Upper lobevessels equalto or largerthan size oflower lobevessels =Cephalization
Upper lobevessels equalto or largerthan size oflower lobevessels =Cephalization
Venous Hypertension
Venous Hypertension

Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
RDPA usually> 17 mm
RDPA usually> 17 mm
MainPulmonaryArteryprojectsbeyondtangent line
MainPulmonaryArteryprojectsbeyondtangent line
23

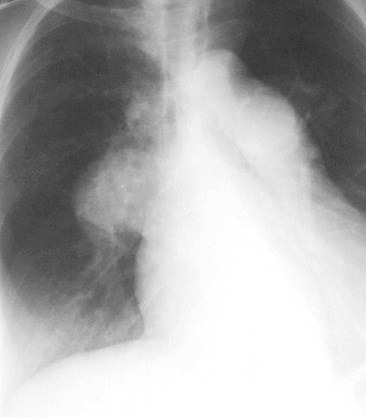
Rapidcutoff insize ofperipheralvesselsrelative tosize ofcentralvessels
Rapidcutoff insize ofperipheralvesselsrelative tosize ofcentralvessels
Central vesselsappear toolarge for size ofperipheralvessels whichcome fromthem =
Pruning
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
31

Increased Flow
Increased Flow
RDPA usually> 17 mm
RDPA usually> 17 mm
All of blood vessels everywhere inlung are bigger than normal
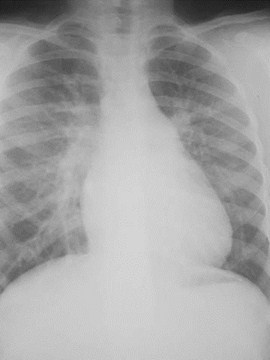

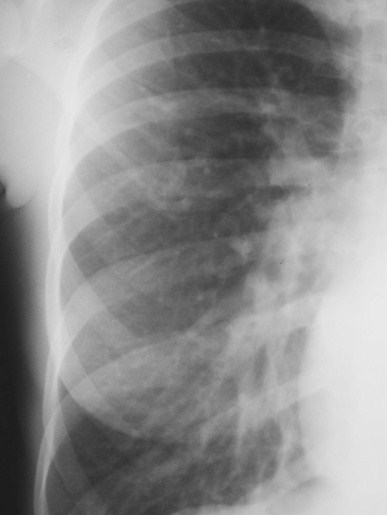
Increased Flow
Increased Flow
Distribution offlow ismaintained asin normal
Lower lobevessels biggerthan upperlobe
Gradualtapering fromcentral toperipheral

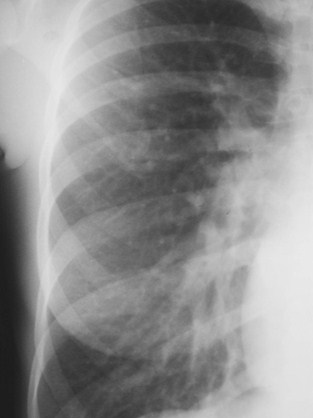
Increased Flow
Increased Flow
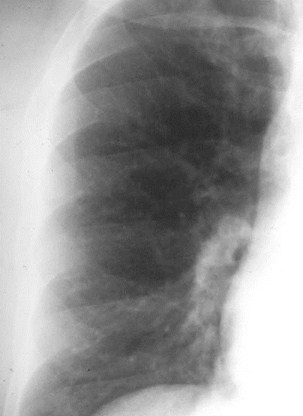
Normal
Normal

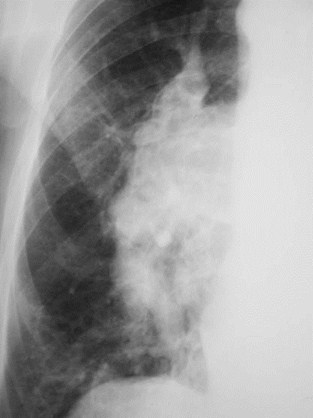
PAH
PAH

Increased Flow
Increased Flow

Unrecognizablemost of thetime
Small hila
Fewer thannormal bloodvessels
Decreased Flow
Decreased Flow

The Pulmonary Vasculature
Normal
Pulmonary venous hypertension
Pulmonary arterial hypertension
Increased flow
Decreased flow - mostlyunrecognizable even when it ispresent

A
Is the Left
Atrium
Enlarged?
If yes,
then
If no,
then
Look at the
Pulmonary
Vasculature
Normal
Increased
Pulmonary
venous
hypertension
B
Is the Main
Pulmonary
Artery Big
or
Bulbous?
If yes,
then
If no,
then
Look at the
Pulmonary
Vasculature
C
Is the Main
Pulmonary
Artery
Segment
Concave?
If yes,
then
If no,
then
D
Is the
Heart
Dilated or
Delta-
Shaped?
If yes,
then
Don't Look at
Pulmonary
Vasculature.
Look at Aorta
Normal
Increased
Pulmonary
hypertension
Cardiomyopathy
Pericardial
Effusion
Molt. valve dz
Mitralregurg
Mitral
Stenosis
L Myxoma
VSD, PDA
Plum.
stenosis
ASD
(VSD)
Idiopathic
(1°)
Normal
Ascending
dilated
Whole Ao
Dilated
Cardiomyopathy
Ao
Stenosis
Ao regurg
HBP
The ABC’s
The ABC’s

The System
Those were all of the answers
Now here are the questions
The system is successful only if youask the questions in this order
The answers are the fundamentalobservations you make on the frontalfilm alone

A
A
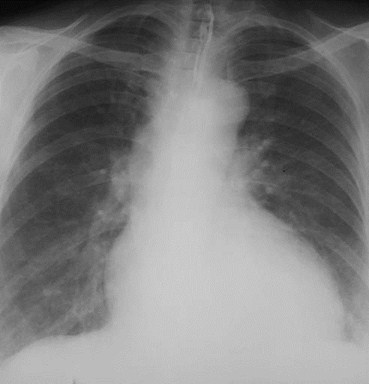
Is The Left AtriumEnlarged ?

Straight orconvex atsite ofnormalconcavity
“Doubledensity” atsite of normalindentation
A
A
To answer that question

If Answer To Question “A” Is YES
A
A
Look At Pulmonary Vasculature

If Answer To Question “A” Is NO
Then...
A
A

B
B
Is The Main PulmonaryArtery Big ?

Mainpulmonaryartery projectsbeyondtangent line
B
B
To answer that question

If Answer To Question “B” Is YES
B
B
Look At Pulmonary Vasculature

If Answer To Question “B” Is NO
Then...
B
B

C
C
Is The Main PulmonaryArtery Concave ?

Mainpulmonaryartery is >15mmaway fromtangentline
C
C
To answer that question
25

If Answer To Question “C” Is YES
Look At Configuration of Aorta
C
C

If Answer To Question “C” Is NO
Then...
C
C

D
D
Is The Heart a Dilated OrDelta-Shaped Heart ?

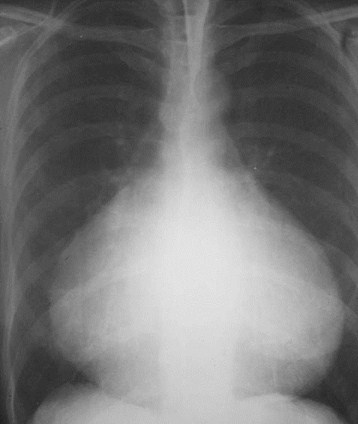
Cardio-thoracic ratio > 65%
D
D
1. Pericardial effusion2. Cardiomyopathy1. Pericardial effusion2. Cardiomyopathy

A
Is the Left
Atrium
Enlarged?
If yes,
then
If no,
then
Look at the
Pulmonary
Vasculature
Normal
Increased
Pulmonary
venous
hypertension
B
Is the Main
Pulmonary
Artery Big
or
Bulbous?
If yes,
then
If no,
then
Look at the
Pulmonary
Vasculature
C
Is the Main
Pulmonary
Artery
Segment
Concave?
If yes,
then
If no,
then
D
Is the
Heart
Dilated or
Delta-
Shaped?
If yes,
then
Don't Look at
Pulmonary
Vasculature.
Look at Aorta
Normal
Increased
Pulmonary
hypertension
Cardiomyopathy
Pericardial
Effusion
Multiple valve dz
Mitralregurgitation
Mitral
Stenosis
L Myxoma
VSD, PDA
Pulmonic
stenosis
ASD
(VSD)
Idiopathic
2° to lung dz
Normal
Ascending
dilated
Whole Aorta
Dilated
Cardiomyopathy
Aortic
Stenosis
Aorticregurgitation
HBP

The End