|
|
Sacral Insufficiency Fracture
Honda Sign
- General considerations
- Normal sacrum almost never sustains an isolated fracture
- They usually occur associated with other pelvic fracture and imply a force frequently sufficient to injure pelvic organs
- Insufficiency and fatigue fractures are subgroups of stress fractures
- Insufficiency fractures are fractures in abnormal bone (e.g. osteoporosis) which undergoes normal stress
- In the sacrum, such fractures occur in
- Postmenopausal women with osteoporosis (more common after age 60)
- Long-term corticosteroid use
- Those who have undergone radiation therapy to the pelvis
- Clinical findings
- Sudden onset of pain in lower back, hip or groin with no trauma
- Pain may be significant and disabling
- Imaging findings
- Conventional radiographs are usually normal
- Some may show vertical or horizontal sclerotic lines in sacrum sclerotic, or
- A break in one or more of the three normal arcuate lines that form the roves of the sacral foramina
- Difficult to see with overlying bowel gas and because the underlying bone is osteoporotic
- The fractures are usually better visualized using bone scintigraphy scans following the injection of Technetium 99m HDP which demonstrate increased radiotracer uptake (hotter, whiter areas) in a pattern that has been called the “Honda sign” after the carmaker’s insignia or the “butterfly sign”
- The characteristic appearance is that of fracture lines running vertically through both the left and right sacral ala, medial to the SI joints, and a transverse fracture just below the level of the SI joints
- The fractures appear as a hot, geographic lesions confined to the sacrum and often have a characteristic "butterfly" or "Honda sign" appearance
- Sacral fractures may also be demonstrated by MRI or CT scan
- CT may have trouble in demonstrating fractures in the plane of the image (transverse fracture)
- Sacral insufficiency fractures may be associated with insufficiency fractures elsewhere, such as
- Pubic rami (strong association)
- Symphysis pubis
- Supra-acetabular region
- Femoral neck
- Tibia
- Calcaneus
- Sternum
- Ribs
- Treatment
- Conservative management
- Bed rest
- Pain medication
- Reduced weight-bearing
- Prognosis is good but complete healing may take many months (4-9 months)
- Protect patient from possible sacral decubiti
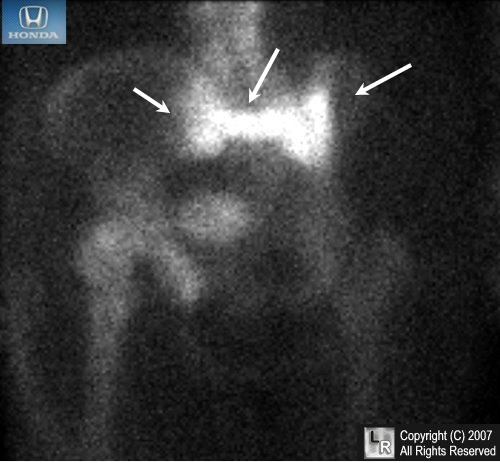
Sacral insufficiency fracture. Following administration of Technetium 99m HDP, a close -up view of the pelvis shows an "H" shaped area of increased tracer uptake in the sacrum (white arrows) representing areas of increased activity near both SI joints and transversely across the sacrum. This has the characteristic appearance of a sacral insufficiency fracture and is called the "Honda sign" after the shape of the carmaker's insignia (see upper left corner of photo).
For this same photo without the arrows, click here
Shearman, C and El-Khoury, G: Pitfalls in the Radiologic Evaluation of Extremity Trauma, American Family Physician 3.15.98
Wheeless’ Textbook of Orthopedics
|
|
|