|
|
Mounier-Kuhn Syndrome
Tracheobronchomegaly
- Congenital abnormality of the trachea and main bronchi\
- Characterized by cystic dilatation of the tracheobronchial tree
- Pathologic findings
- Atrophy or absence of elastic fibers and thinning of muscle of the trachea and central bronchi
- Rapid change to normal caliber at the 4th-5th order of bronchi
- Especially African Americans
- Only 5% of patients with the disease are female
- Occurs most often during the third and fourth decades of life
- Has an autosomal recessive type of inheritance
- Allows trachea and main bronchi to become markedly dilated on inspiration with narrowing or collapse on expiration
- Abnormal airway dynamics and pooling of secretions in broad outpouchings predispose to the development of
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Emphysema
- Bronchiectasis
- Chronic pulmonary suppuration
- Recurrent pneumonia
- Dyspnea
- Cough
- Hoarseness
- Production of copious amounts of purulent sputum consistent with bronchiectasis
- Signs and symptom range from minimal disease with preservation of pulmonary function to progressive disease leading to respiratory failure and death
- Imaging Findings
- Tracheobronchomegaly (see below)
- Tracheal size increases with Valsalva and narrows with Muller maneuver
- Saclike outpouchings between tracheal cartilages
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Bulla
- Bronchiectasis
- Has been associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Normal Dimensions of Trachea and Bronchi |
|
Trachea |
Main Bronchi |
|
Transverse |
Sagittal |
Right |
Left |
Men |
>25mm |
>27mm |
>21.1mm |
>18.4mm |
Women |
>21mm |
>23mm |
>19.8mm |
>17.4mm |
- The diagnosis can be confirmed by computed tomography
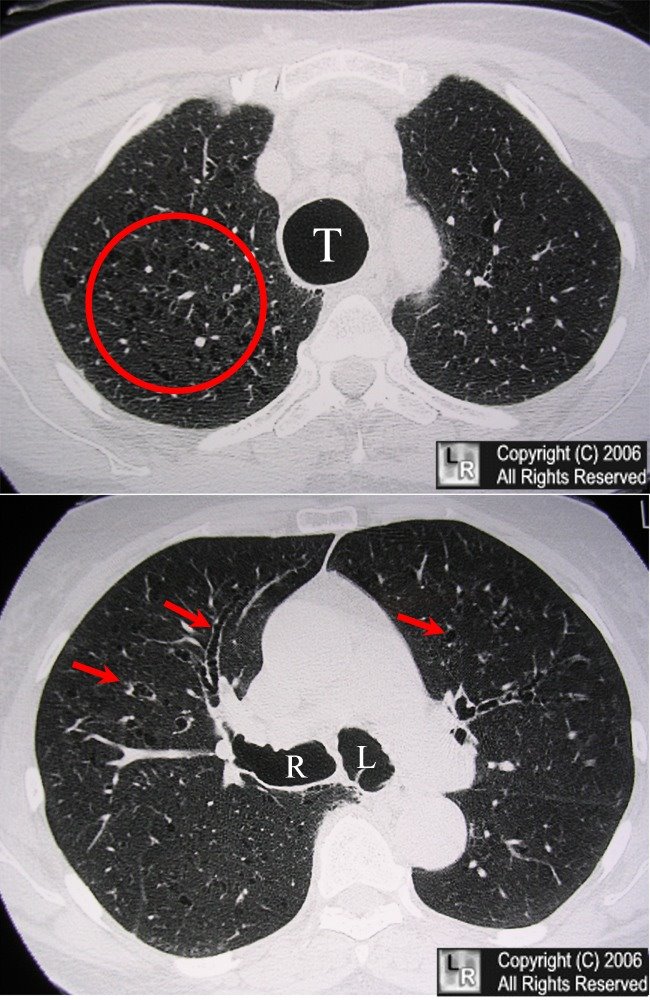
Mounier-Kuhn Syndrome. Two axial CT images of the thorax demonstrate marked dilatation of the trachea (T)
and right (R) and left (L) main bronchi in this patient with Mounier-Kuhn syndrome. Notice the bronchiectasis
(red arrows and red circle) in which the bronchi are larger than their accompanying blood vessel
and there is tram=tracking of thickened bronchial walls seen in profile.
For the same photo without the arrows, click here
eMedicine Carol A Boles, MD Wrist, Scaphoid Fractures and Complications
|
|
|