|
|
Leiomyoma of Esophagus
General Considerations
- Most common benign tumor of esophagus
- Leiomyomas are also the most common benign tumor of the small bowel but are not common in the colon
- Typically occurs in young males
- Found most often in distal third of esophagus
- Usually solitary, but may be multiple (3%)
Clinical Findings
- Usually asymptomatic
- May produce dysphagia or hematemesis if large
Imaging findings
- Smooth, sharply-marginated mass
- Well-defined, intramural (wall) mass lesion that typically intersects wall at 90 degree angle when viewed in profile
- As a wall lesion, it may narrow the lumen in one plane and widen it in the orthogonal view (a plane at 90 degrees to the original)
- May have coarse calcifications (only calcifying esophageal tumor)
- Rarely ulcerates
- May demonstrate diffuse contrast-enhancement on CT
Differential Diagnosis
- Neurofibromas
- Hemangiomas
- Lipomas
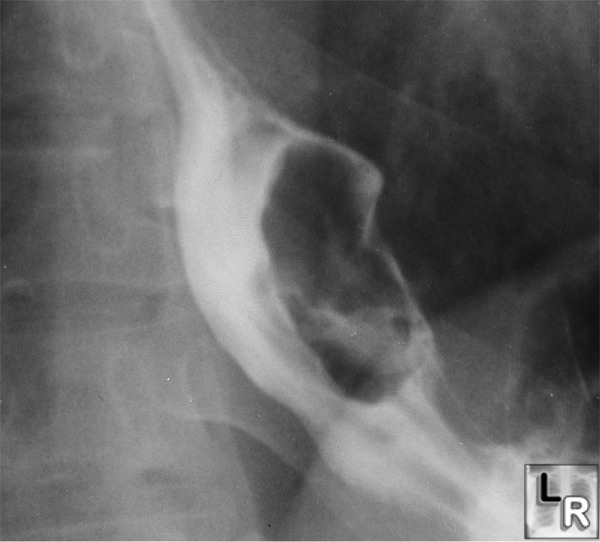
Leiomyoma of the Esophagus. There is a large filling defect in the barium column in the distal esophagus which is widening the lumen. An amorphous collection of barium seen in or through the mass suggests the possibility of ulceration.
|
|
|