|
|
Stress Fracture
- Fractures produced as a result of repetitive stress on bone
- Most common locations
- Lower extremity (calcaneus, tibia, fibula)
- Thoracic vertebra
- Sacrum
- Ilium
- Pubic bone
- General risk factors
- New / different / rigorous repetitive activity
- Female sex
- Increased age
- Caucasian race
- Low bone mineral density
- Low calcium intake
- Specific risk factors and bones involved
- Clay shoveler’s fracture
- Spinous process of lower cervical / upper thoracic spine
- Clavicle
- Postoperative (radical neck dissection)
- Coracoid process of scapula
- Ribs
- Carrying heavy pack, golf, coughing
- Distal shaft of humerus
- Coronoid process of ulna
- Pitching ball, throwing javelin, pitchfork work, propelling wheelchairs
- Hook of hamate
- Swinging golf club / tennis racquet / baseball bat
- Spondylolysis
- Ballet, lifting heavy objects, scrubbing floors
- Femoral neck
- Ballet, long-distance running
- Femoral shaft
- Ballet, marching, long-distance running, gymnastics
- Obturator ring of pelvis
- Stooping, bowling, gymnastics
- Patella
- Tibial shaft
- Fibula
- Long-distance running, jumping, parachuting
- Calcaneus
- Jumping, parachuting, prolonged standing, recent immobilization
- Navicular
- Stomping on ground, marching, prolonged standing, ballet
- Metatarsal (commonly 2nd MT)
- Marching, stomping on ground, prolonged standing, ballet, postoperative bunionectomy
- Sesamoids of metatarsal
- Imaging Findings
- 15% sensitive in early fractures, increasing to 50% on follow-up
- Sclerotic band (due to trabecular compression and callus formation) usually perpendicular to cortex
- Intracortical radiolucent striations (early)
- Solid thick lamellar periosteal new bone formation
- Endosteal thickening (later)
- Follow-up radiography after 2-3 weeks of conservative therapy may reveal fracture not seen earlier
- Nuclear medicine
- “Gold standard" = almost 100% sensitive
- Abnormal uptake within 6-72 hours of injury (prior to radiographic abnormality)
- "Stress reaction" is a focus of subtly increased uptake
- Focal fusiform area of intense cortical uptake
- Abnormal uptake persists for months
- MRI
- Very sensitive modality
- Fat saturation technique most sensitive to detect increase in water content of medullary edema / hemorrhage
- Diminished marrow signal intensity on T1WI
- Increased marrow signal intensity on T2WI
- Differential diagnosis
- Osteoid osteoma (eccentric, nidus, solid periosteal reaction, night pain)
- Chronic sclerosing osteomyelitis─ Brodie’s abscess ─ (dense, sclerotic, involving entire circumference, little change on serial radiographs)
- Osteomalacia (bowed long bones, looser zones, gross fractures, demineralization)
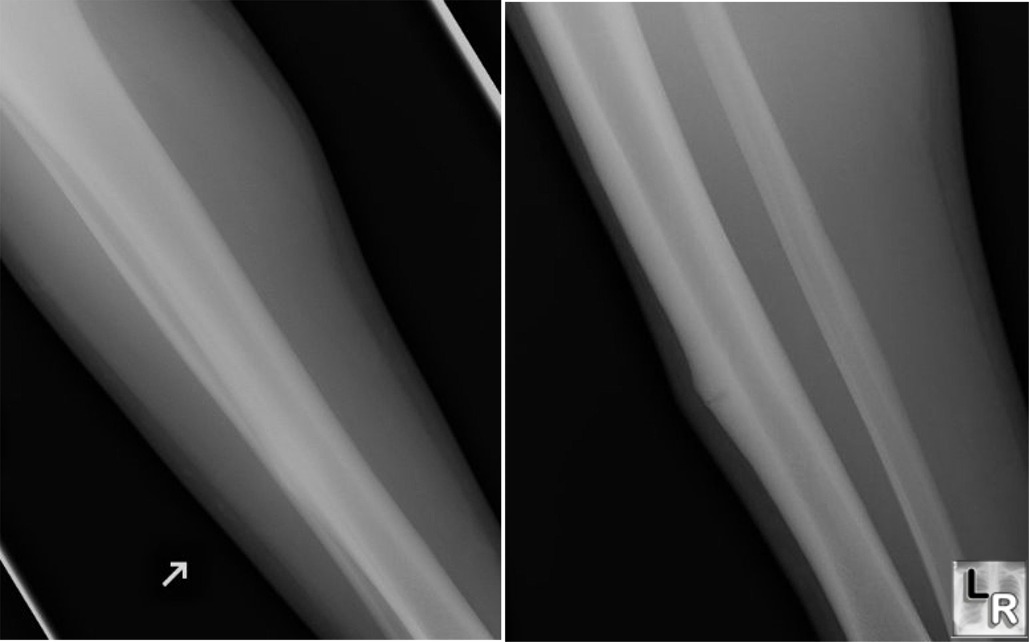
Stress Fracture. Two views of
the tibia and
fibula in a
younger woman
show a
transverse
lucency in the
cortex
surrounded by
cortical
thickening.
There is no
periosteal
reaction. The
patient was a
dancer. The
tibia is a
relatively
common site for
stress
fractures.
|
|
|