|
|
Anterior Dislocation of the Shoulder
- Glenohumeral dislocation most common shoulder dislocation (85%)
- Glenohumeral joint dislocations make up >50% of all dislocations in the body
- Anterior / subcoracoid shoulder dislocation (96%)
- Mechanism
- External rotation and abduction and external rotation
- Age
- May be associated with
- Hill-Sachs defect (50%) is a depression fracture of posterolateral surface of humeral head from impaction of the head against glenoid rim in subglenoid type
- Best demonstrated on the AP projection with the arm internally rotated
- Bankart lesion is a fracture of anterior aspect of inferior glenoid rim
- Only cartilaginous portion of glenoid labrum may be fractured which may only be visible on MRI
- Fracture of greater tuberosity (15%)
- Complications
- Recurrent dislocations (40%)
- Post-traumatic arthritis
- Injury to axillary nerve or artery
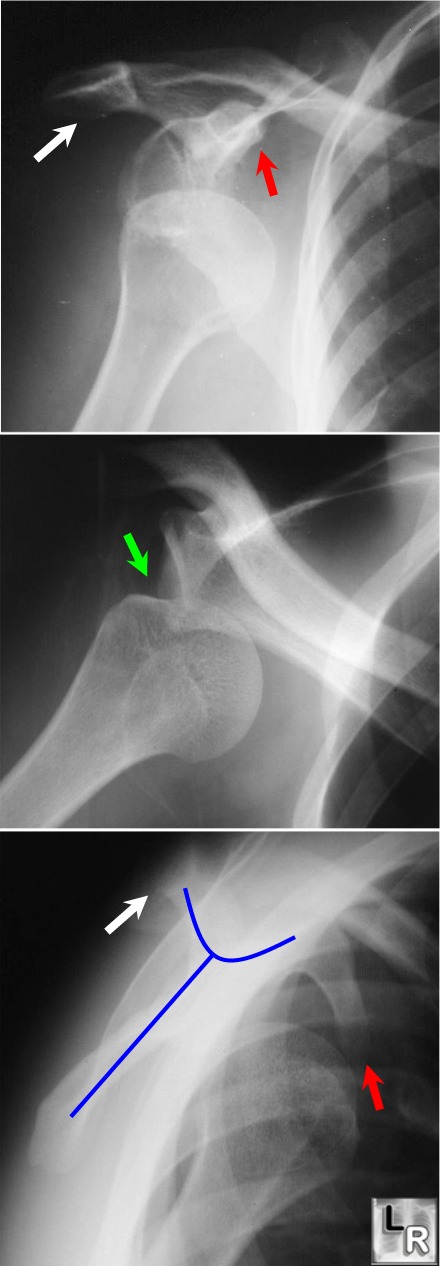
Anterior
Dislocation of the
Humeral Head: Top image shows
humeral head displaced
from glenoid
and lying inferior to
the coracoid process
(red arrow); the
middle image
demonstrates a defect
along the
posterolateral aspect
of the head, which is
the Hill-Sach's
deformity (green
arrow). The lower
image is the scapular
Y view (blue line
outlines scapula). The
head lies in a
subcoracoid (i.e.
anterior location). The white arrows point
to the acromion.
|
|
|