|
|
Rounded Atelectasis
- Occurs as a consequence of diseases with chronic pleural
scarring, especially asbestos-related pleural disease and TB
- Most often at the lung bases, posteromedially
- Must be subpleural in
position
Pathophysiology
- A rapidly forming pleural effusion
produces an adjacent area of passive
atelectasis
- A groove of visceral pleura may
infold into the area of atelectasis
and come to surround a part of it
- If the effusion recedes at once, the
lung will probably re-expand
- If fibrinous adhesions form or if
there is preexistent chronic pleural
disease, then the atelectatic area
of lung remains trapped by the
enfolded visceral pleura
- Asymptomatic: important because it resembles a bronchogenic ca
Imaging Findings
- Rounded density at lung base
- Contiguous to area of pleural
disease or superimposed on apparent
asbestos-related pleural disease or
TB
- Comet tail on CT: vessels and bronchi converge
upon and appear to swirl around mass
- Crow’s feet — linear bands radiating from mass
into lung parenchyma
- Linear densities radiate back toward hilum
- May have air bronchogram
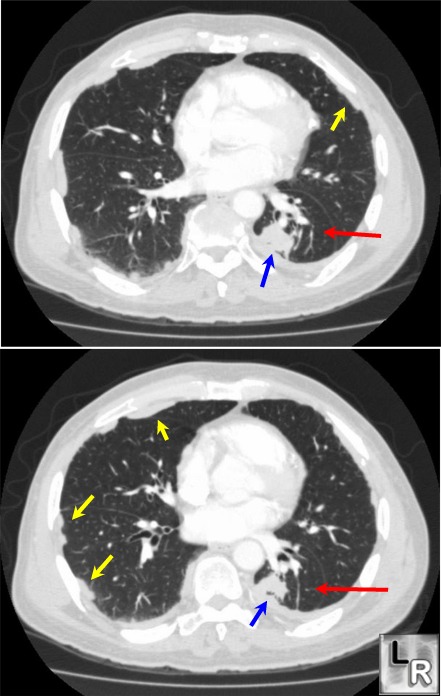
Rounded Atelectasis. Axial enhanced CT scan of the chest
shows a nodular-area of increased density
(blue arrow),
associated with pleural thickening and
pleural plaques (yellow arrows) consistent
with asbestos-
related pleural disease. Red arrow point
to "comet tail" density that surrounds
rounded atelectasis.
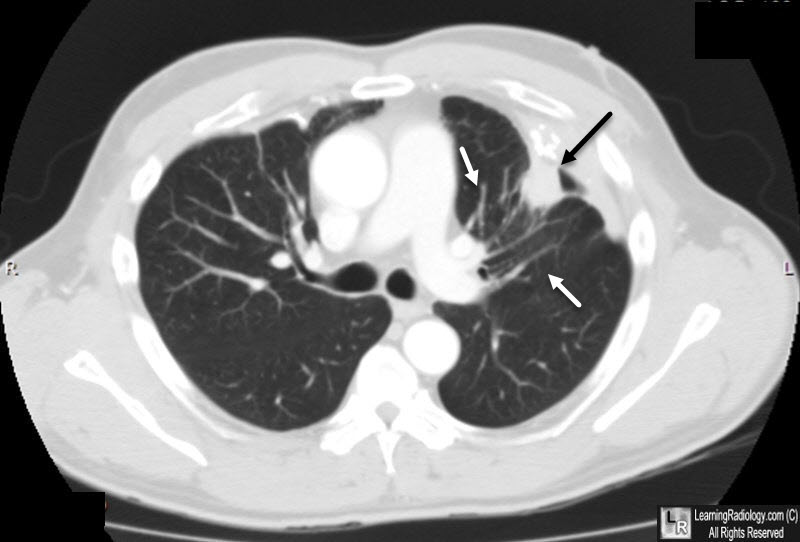
Rounded Atelectasis. Axial enhanced CT scan of the chest
shows a nodular-area of increased density
(black arrow),
associated with pleural thickening. White arrows point
to "comet tail" density that emanates from the lesion.
|
|
|