|
|
Pneumomediastinum
Mediastinal Emphysema
·
Traumatic – 2° closed chest trauma
o
Same mechanism as
spontaneous
·
Rupture
of the esophagus – Boerhaave's Syndrome
o
May occur with vomiting,
labor, severe asthmatic attacks and strenuous exercise (each of these can
produce pneumomediastinum without rupturing the esophagus)
o
LEFT,
POSTEROLATERAL WALL, DISTAL 8 CM
Symptoms
– infants – none.
-
Adults
– chest pain (retrosternal) radiating down both arms aggravated by respiration and swallowing; Hamman’s
sign – crunching sound heard over the apex of the heart with
cardiac cycle
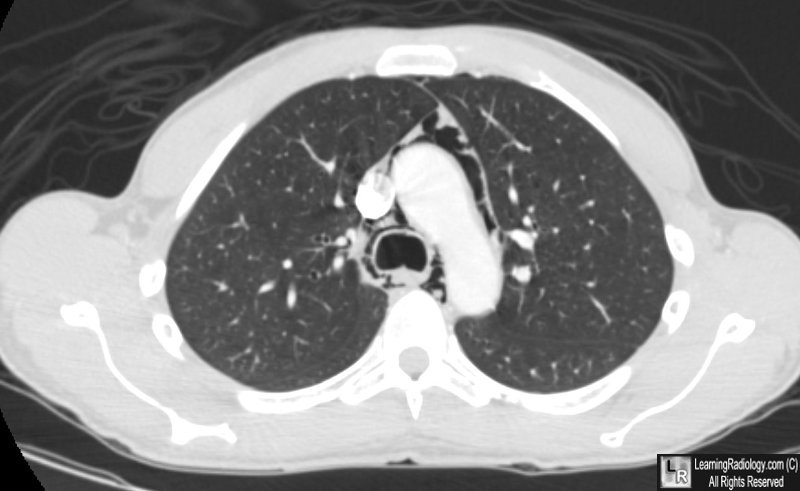
Pneumomediastinum. There is air in the mediastinum surrounding the aorta and trachea. The patient was an asthmatic who presumably ruptured a bleb with air dissecting back along the bronchovascular bundles of the lung to the mediastinum.
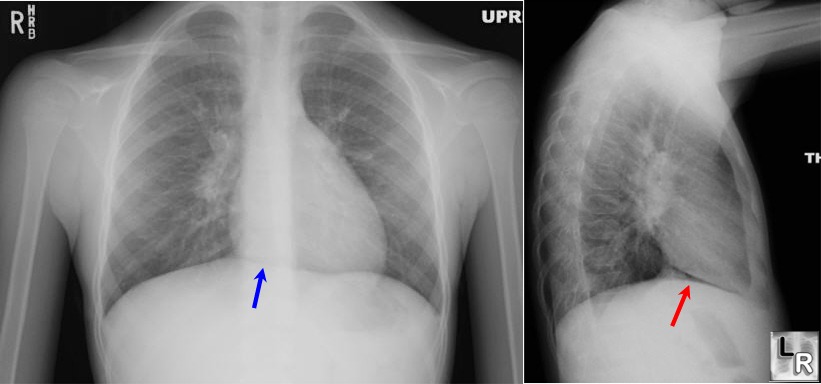
Blue arrow points to
"continuous diaphragm sign." The entire diaphragm is visualized
from one side to the other
because air in the mediastinum outlines the central portion
which is usually obscured by the heart and mediastinal soft
tissue structures that are in contact with the diaphragm. The
red arrow points to the air beneath and posterior to the heart.
|
|
|