|
|
Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernias
Bochdalek Hernia
General Considerations
- If defective development, diaphragmatic hernia develops
Anterior – Morgagni
- Anteromedial parasternal defect (Space of Larrey)
- Maldevelopment of septum transversum
- Tends to occur in overweight, middle-aged, women
- Right > left (heart protects)
- Usually not large
- Usually unilateral
- Associated with
- Pericardial defects
- Omental fat in pericardial space
Posterior – Bochdalek
- Most common
- Occurs through old pleuroperitoneal canals
- Just lateral to the spine on either side
- More frequent on left side
- Possibly due to “protection” of right-side by liver
- Hernia may contain intestine, stomach, spleen, liver or omentum
- If hernia occurs on right
- Intestine and liver or only liver may herniate
- If the defect is large, newborns usually present with
- Severe respiratory distress
- Cyanosis
- Scaphoid abdomen
- Entire diaphragm is almost never absent
- Some part of diaphragm is usually found at surgery, even if defect is very large
- Hypoplasia of ipsilateral lung occurs from mass effect of bowel
- Most often these are isolated congenital abnormalities
- But they can have
- Congenital Heart Disease
- 13 ribs
- Malrotation of GI tract frequently present
Imaging findings
- Initially, hemithorax may appear opaque because loops are fluid-filled
- Paucity of bowel loops beneath the diaphragm
- Once air swallowing begins, multiple lucencies contained within bowel are seen in chest
- Respiratory distress may increase as intestine occupies more of thorax
- Some loops may remain fluid-filled
- Mediastinal shift to the opposite side
- Relative paucity of gas in abdomen
- If stomach remains in abdomen, it is more centrally located than normal
- Contrast through an NGT is diagnostic but often not needed
Differential diagnosis of lucent cysts in infant lung
- Cystic adenomatoid malformation
- Staphylococcal pneumonia
- In both, abdomen contains normal amount of air-filled loops
- Delayed herniation of bowel may occur in older infants following streptococcal pneumonia
Mortality around 50%
- Pulmonary hypoplasia
- Persistent Fetal Circulation Syndrome
Treatment
- Surgical repair
- Many demonstrate ipsilateral pulmonary hypoplasia for years after repair
- Obstructive emphysema can occur in either lower lobe
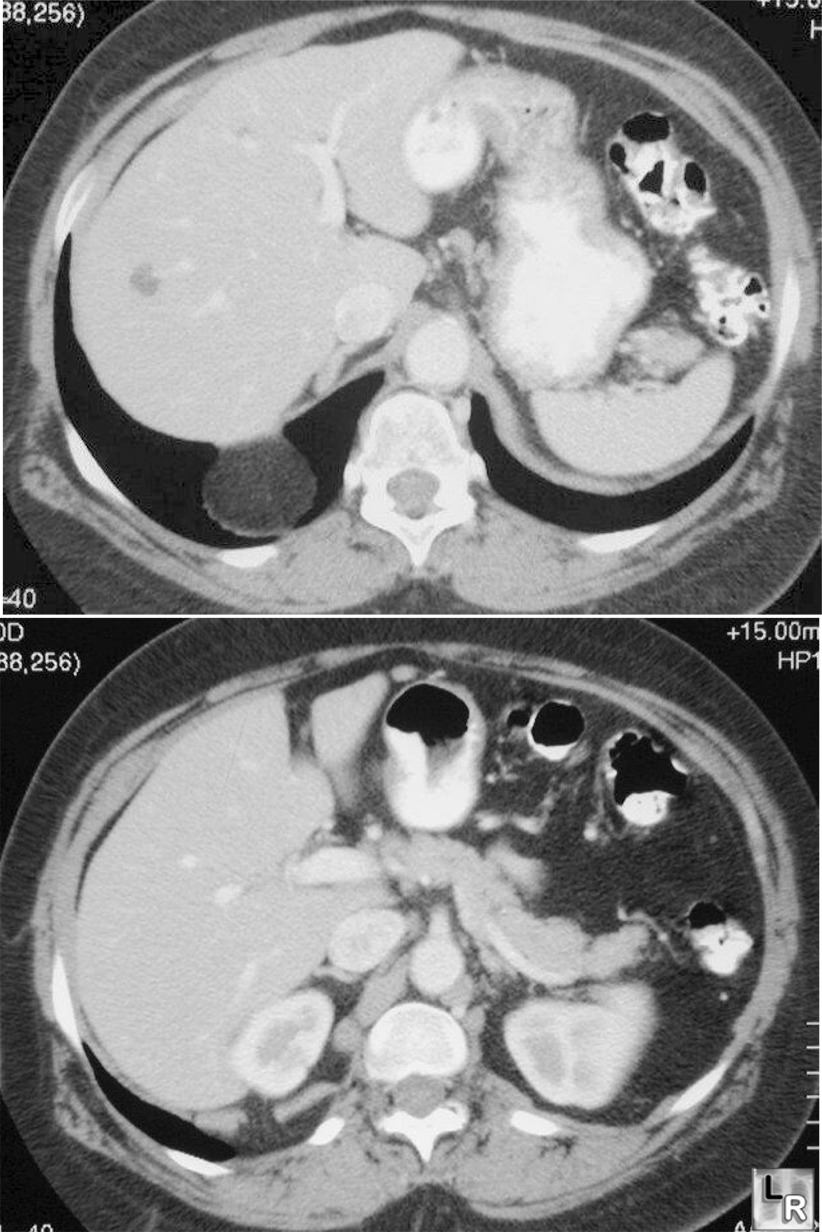
Bochdalek Hernia. Two
axial images from a contrast-enhanced CT of the abdomen reveal a fatty
density protruding through a rent in the posterior aspect of the right
hemidiaphragm. The density represents omental fat which has herniated
through a small Bochdalek hernia.
|
|
|