|
|
Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease
CPPD
- Terminology
- Chondrocalcinosis –
calcification of hyaline (articular) cartilage or fibrocartilage (menisci)
or ligaments
- Usually but not always due to calcium
pyrophosphate
- May also be seen with oxalosis
- Pseudogout is an
older clinical term referring to acute pain (similar to gout) but without
response to the usual treatment for gout
- CPPD – Deposition of
crystals in the joint with or without chondrocalcinosis
- Most common crystalline arthropathy
- Prevalence
- Widespread in older population
- M:F = 3:2
- Clinical findings
- Intermittent attacks
- May be mono-articular or polyarticular (more
often)
- Types
- Frequently occurs in association with osteoarthritis
- Aging process with no known etiology
- In association with metabolic diseases
- Hyperparathyroidism
- Hemochromatosis
- Hypothyroidism
- Hypomagnesemia
- Hypophosphatasia
- Ochronosis
- Calcium pyrophosphate crystals may be recovered from
synovial fluid (most often) or within leukocytes
- Characteristic weakly positive birefringent
diffraction pattern
- Location
- Knee
- Especially meniscus
- Cartilage of patellofemoral joint
- Wrist
- Triangular fibrocartilage in distal radioulnar
joint bilaterally
- Pelvis
- Sacroiliac joint
- Symphysis
- Spine
- Annulus fibrosis of lumbar intervertebral disk
- Never in nucleus pulposus as in ochronosis
- Shoulder
- Glenoid
- Hip
- Elbow
- Ankle
- Acromioclavicular joint
- Imaging Findings
- Pyrophosphate arthropathy resembles osteoarthritis
- Joint space narrowing
- Extensive subchondral sclerosis
- Polyarticular chondrocalcinosis (in fibro- and
hyaline cartilage)
- In knee, disproportionate narrowing of
patellofemoral joint
- Large subchondral cysts are a hallmark
- Numerous intra-articular bodies
- Fragmentation of subchondral bone
- In hand, beaklike projections
from 2nd, 3rd metacarpal heads
- Subchondral cysts (esp.
carpal bones)
- Unusual distribution of
disease (radiocarpal/ulnar joint, patellofemoral joint)
- SLAC - scapholunate advanced
collapse
- Caused by laxness of the
ligaments and malpositioning of the scaphoid and lunate
- May develop in 25% with
CPPD but also occurs for other reasons
- Radio-scaphoid, but not
radio-lunate, joint is narrowed
- Usually have a deep concave
scaphoid fossa in distal radius in CPPD as opposed to SLAC from trauma
- Treatment
- Oral anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and
corticosteroid joint injections successful in shortening the length of
pain and dysfunction of acute attacks of pseudogout
- Treatments to prevent attacks, such as colchicine,
may be effective
- No treatment is available to dissolve the crystal
deposits
- Controlling inflammation helps to halt the
progression of joint degeneration

CPPD Arthropathy. There is chondrocalcinosis in the triangular fibrocartilage of the ulna (white arrow). There is narrowing of the radio-carpal joint and proximal migration of the capitate into the widened space between the scaphoid and the lunate (yellow arrow).
For this same photo without the arrows, click here
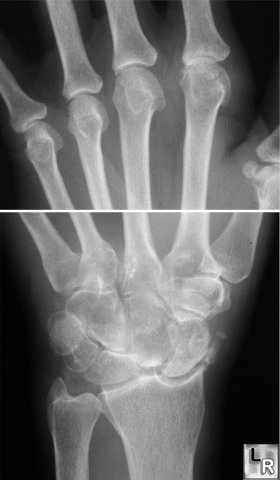
CPPD of hand and wrist - upper photo shows
hook-like projections arising from radial aspect of metacarpal heads;
lower photo shows SLAC-scapholunate advanced collapse with characteristic
indentation in distal radius by scaphoid bone. There is also chondrocalcinosis
of the triangular fibrocartilage of the distal ulna.
For more information, click on the link if you see this icon 
Imaging of the Wrist and Hand: Gilula and Yin, W.B. Saunders, 1996.
|
|
|