|
|
Emphysematous Pyelonephritis
- Acute, fulminant,
necrotizing infection of kidney and perirenal tissues
associated with gas formation which may be life-threatening
- Organism
- E. coli (vast majority of
cases)
- Klebsiella pneumoniae (9%)
- Proteus mirabilis
- Pseudomonas
- Enterobacter
- Candida
- Clostridia (exceptionally
rare)
- Predisposed
- Especially diabetics in
almost all cases
- Immunocompromised patients
- Ureteral obstruction
- Average age
- Mid-fifties
- Twice as common in females
as males
- Clinical findings
- Features of acute severe
pyelonephritis (chills, fever, flank pain, lethargy,
confusion) not responding to treatment
- Positive blood and urine
cultures (in majority)
- Urosepsis
- Shock
- Fever of unknown origin
and no localizing signs in almost 20%
- Frequently have multiple
associated medical problems
- Uncontrolled hyperglycemia
- Acidosis
- Dehydration
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Location
- Most are unilateral
- 5-7% bilateral
- Types
- Type I (33%)
- Streaky or mottled gas
in interstitium of renal parenchyma radiating from
medulla to cortex
- Crescent of subcapsular
or perinephric gas
- No fluid collection (=
no effective immune response)
- Prognosis in this type
is poor (69% mortality)
- Type II (66%)
- Bubbly and/or loculated
intrarenal gas (infers presence of abscess)
- Renal and/or perirenal
fluid collection
- Gas within collecting
system in almost all
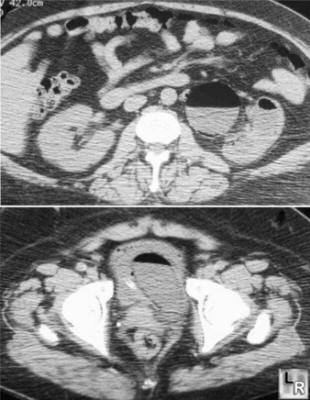
Emphysematous Pyelonephritis. Two axial CT scans of abdomen and pelvis
show air within
collecting system of kidney in top image with air and debris
in bladder lumen and wall in bottom image
- Prognosis in this type is
much better (18% mortality)
- Parenchymal destruction
absent
- Decreased contrast excretion
(due to compromised renal function)
- CT findings
- Most reliable and
sensitive modality
- Mottled areas of low
attenuation extending radially along the pyramids
- Extensive involvement of
kidney and perinephric space
- Air extending through
Gerota’s fascia into retroperitoneal space
- Occasionally gas in renal
veins
- Ultrasound findings
- High-amplitude echoes
within renal sinus and/or renal parenchyma associated with
"dirty" shadowing
- "Comet tail"
reverberations
- Kidney may be completely
obscured by large amount of gas in perinephric space (DDx:
surrounding bowel gas)
- Gas may be confused with
renal calculi
- MR findings
- Signal void on T1WI and
T2WI (DDx: renal calculi, rapidly flowing blood)
- DDx
- Emphysematous pyelitis (gas in collecting
system but not in parenchyma, diabetes in 50%, less grave
prognosis)
- Treatment
- Antibiotic therapy and
nephrectomy
- Drainage procedure with
coexisting obstruction
- Mortality
- 60-75% under antibiotic
treatment
- 21-29% after antibiotic
treatment and nephrectomy
- 80% with extension into
perirenal space
|
|
|