|
|
Respiratory Distress Syndrome of the Newborn
Hyaline Membrane Disease
General Considerations
- Acute pulmonary disorder of the newborn characterized by
- Generalized atelectasis
- Intrapulmonary shunting
- Ventilation-perfusion abnormalities
- Reduced lung compliance
- M:F =1.8:1
Cause
- Immature surfactant production (usually begins at 18-20 weeks of gestational age)
- Causes acinar atelectasis
Predispositions
- Premature infants
- Cesarean section
- Infants of diabetic mothers
- Perinatal asphyxia
Clinical findings
- Onset
- Usually less than 2-5 hours after birth
- Increases in severity from 24 to 48 hours
- Then, gradual improvement after 48-72 hours
- Abnormal retraction of chest wall
- Cyanosis
- Expiratory grunting
- Increased respiratory rate
Imaging findings
- Typically, diffuse “ground-glass” opacification of both lungs with air bronchograms and hypoaeration
- Hypoaeration from loss of lung volume (may be counteracted by respiratory therapy)
- Fine granular pattern
- Prominent air bronchograms
- Bilateral and symmetrical distribution
Prognosis
- Spontaneous clearing within 7-10 days (mild course in untreated survivors)
- Death in 18%
Acute complications
- Barotrauma may produce
- Parenchymal pseudocyst
- Pulmonary interstitial emphysema
- Pseudoclearing
- Lungs appear less because of innumerable small pockets of air in the peribronchial interstitial spaces
- Pneumomediastinum
- Pneumothorax
- Pneumopericardium
- Pneumoperitoneum
- Air in the retroperitoneum
- Subcutaneous emphysema
- Diffuse opacity
- Worsening RDS
- Superimposed pneumonia
- Massive aspiration
- Pulmonary hemorrhage
- Congestive heart failure (from PDA or fluid overload)
- Persistent patency of ductus arteriosus
- Oxygen stimulus is missing to close duct
- Hemorrhage
- Pulmonary hemorrhage
- Intracranial hemorrhage
- Necrotizing enterocolitis
- Acute renal failures
Chronic complications
- Lobar emphysema
- Localized interstitial emphysema
- Recurrent inspiratory tract infections
- Retrolental fibroplasia
- Subglottic stenosis from intubation
Treatment
- Supportive
- Exogenous surfactant via trachea
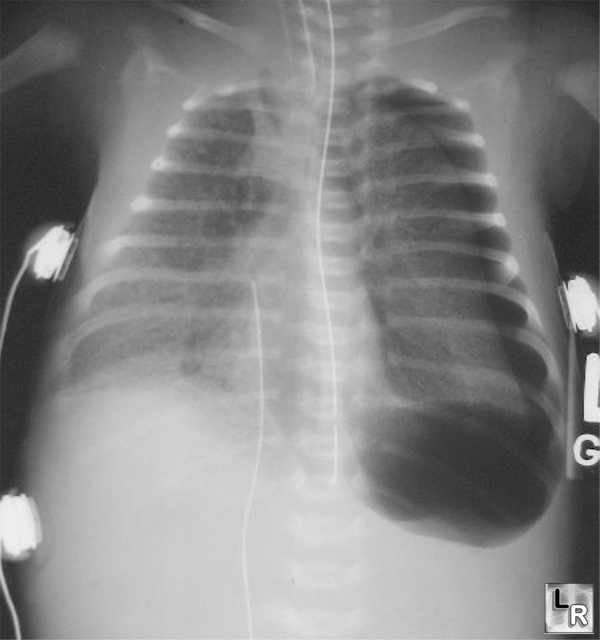
Hyaline Membrane Disease. Diffuse ground-glass appearance to both lungs with a left-sided
tension pneumothorax and pneumomediastinum
(orogastric tube is in distal esophagus)
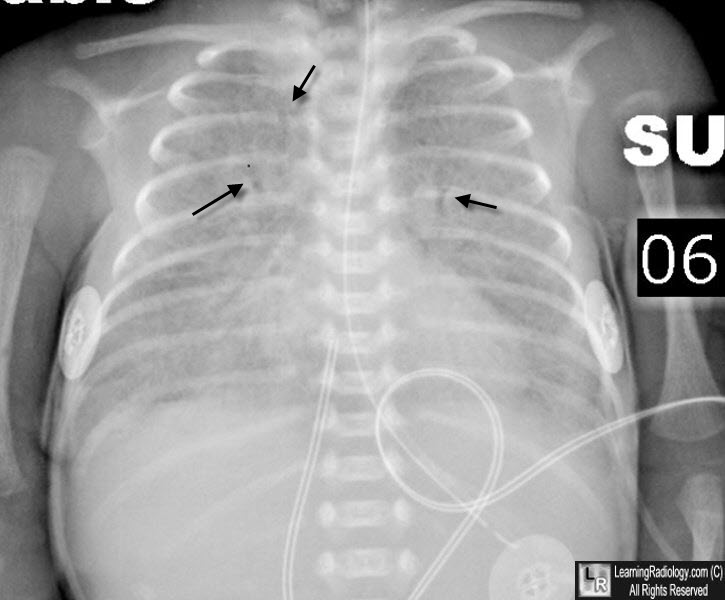
Hyaline Membrane Disease. Diffuse ground-glass appearance to both lungs with multiple air bronchograms (black arrows). An orogastric tube and umbilical venous catheter are present.
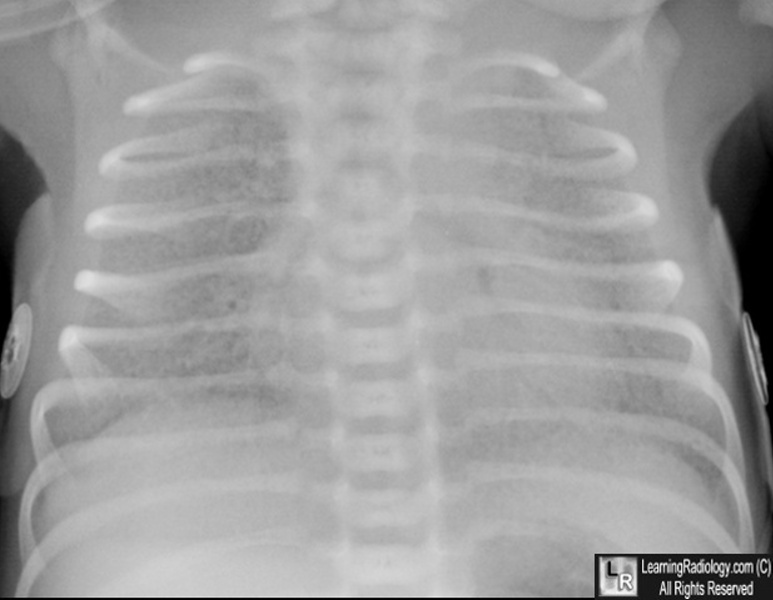
Hyaline Membrane Disease. Diffuse ground-glass appearance to both lungs with hypoaeration and multiple air bronchograms.
|
|
|