|
Silicosis
· Occupational Exposure
o Free crystalline silica (quartz) or silicon dioxide from
§ Mining
of coal, graphite, iron
§ Tin, Uranium, Gold
§ Silver, Copper
§ Also, sand blasters
§ Iron and steel foundry workers
§ Ceramic workers
§ Tunneling
· Silicosis pathophysiology
o Silica particles ingested by alveolar macrophages
o Breakdown of macrophage releases enzymes which produce fibrogenic
response
· Silicosis natural history
o Requires 10-20 years exposure before x-ray appearance
o Radiographs frequently overestimate degree of symptoms early
o Silicosis has a progressive nature despite cessation of dust exposure
· Imaging findings
o Multiple small rounded opacities 1-10 mm in size
o Usually in upper lobes
§ Mostly in apical and posterior regions of upper lobes
and apical portion of lower lobes
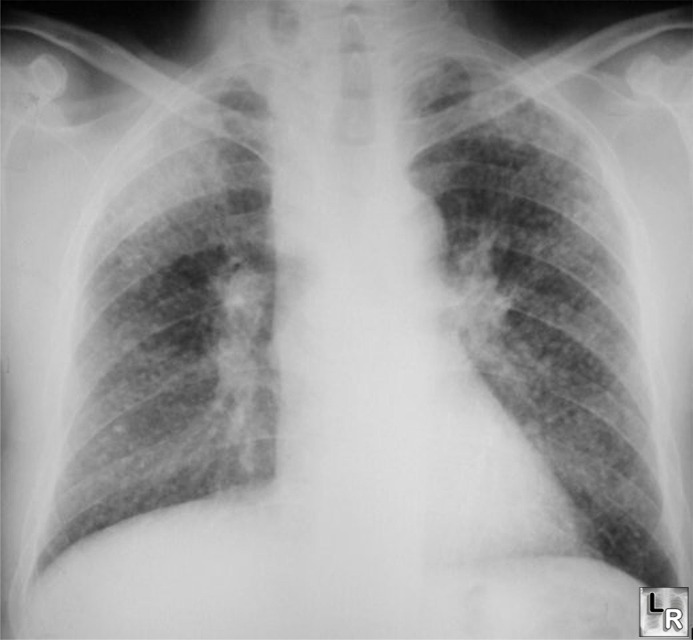
Silicosis features a diffuse micronodular lung disease
with an upper lobe predominance
o May have ground-glass appearance
o May occasionally calcify centrally (20%)
o Lymph node enlargement common
§ Eggshell calcification of hilar nodes (5%)
· DDx:
Sarcoidosis
o Large opacities are conglomerations of small opacities
· Complicated Silicosis (Progressive Massive Fibrosis—PMF)
o Massive fibrosis and conglomerate nodule formation in upper lobes with
scarring and retraction of hila upwards
o Conglomerate nodules are >1 cm in size
§ Usually in mid-zone or periphery of upper lobes
§ Compensatory emphysema occurs in lower lung fields
§ Nodules tend to disappear from rest of lung when PMF
develops
o Progressive Massive Fibrosis (PMF) may cavitate from tuberculosis or
ischemic necrosis
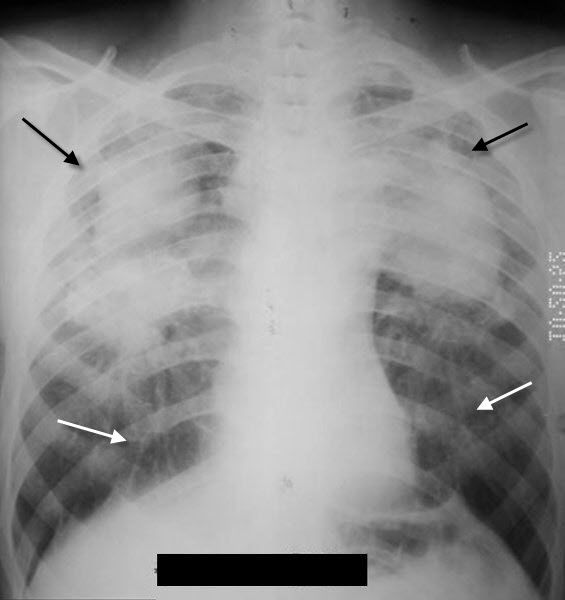
Progressive Massive Fibrosis. There are conglomerate soft-tissue densities in both upper lobes (black arrows) with linear scarring leading from the lower lobes (white arrows).
· Acute silicosis (silicoproteinosis)
o From exposure to high concentrations of silica dust
o Alveoli are filled with lipid-rich, PAS-positive
material
o Bilateral air-space disease with perihilar distribution
§ Imaging findings are similar to alveolar proteinosis
· Caplan’s Syndrome
o Consists of large necrobiotic nodules (rheumatoid nodules)
superimposed on silicosis or coal worker’s pneumoconiosis (CWP)
§ More common with CWP
o Other connective tissue diseases associated with silicosis
§ Scleroderma, RA, SLE
· Silicosis Complications
o Predisposes to TB
o Exhibits “limited” evidence for carcinogenesis in humans
|