|
|
Cystic Fibrosis
Mucovicidosis
General Considerations
- Disease of abnormal exocrine gland function
- Autosomal recessive almost always in Caucasians
- Defect in gene which codes for cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)
- Major clinical manifestations are pulmonary and pancreatic insufficiency
- Elevated concentration of sodium and chloride in sweat
- Most patients are diagnosed by age 1year
Clinical Findings
- Positive sweat chloride test
- Chronic cough
- Recurrent pulmonary infections
- Higher incidence of asthma and allergy
- Diabetes
- Undescended testicles
Imaging Findings
- Atelectasis
- Discoid, segmental, lobar with right upper lobe predominance
- Mucoid impaction
- Nodular and fingerlike densities along bronchovascular bundle
- Cylindrical or cystic bronchiectasis
- Hilar adenopathy
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension and cor pulmonale
- Recurrent pneumonias,
- Particularly Staphylococcus, Pseudomonas and P. cepacia
- Clubbing and hypertrophic osteoarthropathy can occur
- Recurrent pneumothorax is common
Differential Diagnosis
- Asthma
- Bronchiectasis
- Aspergillosis
Associated Findings
- Bulky, fatty stools from lack of pancreatic enzymes
- Rectal prolapse
- Meconium ileus — earliest finding
- Meconium ileus equivalent — due to obstruction from stool in older children
- Fatty infiltration of the liver
- Focal biliary cirrhosis with portal hypertension
- Gallstones
- Pancreatic fibrosis due to recurrent Pancreatitis
- Sinusitis
- Hypoplastic frontal sinuses
Treatment
- Goals are to maintain lung function and nutritional therapy
- Bronchodilators
- Chest physical therapy
- Mucolytic agents
- Pancreatic enzyme supplements
- Multivitamins
Prognosis
- Varies from country to country but highest in the United States
- 80% should reach adulthood

Cystic Fibrosis. White arrow points to mucous-filled bronchus; white circles enclose areas of
peribronchial thickening and nodularity. Yellow arrow points to lingular atelectasis.
For this same photo without arrows, click here
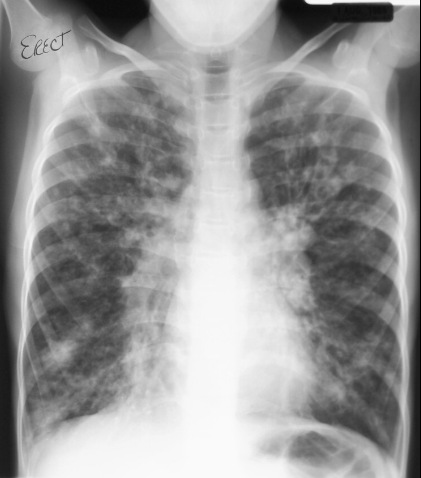
Frontal chest x-ray in cystic fibrosis shows diffuse interstitial
disease
with bronchiectasis and nodular densities of mucoid impaction
For more information, click on the link if you see this icon 
|
|
|