|
|
Pigmented Villonodular Synovitis
PVNS
- Benign synovial proliferation primarily
affecting knees with erosions, cysts, soft tissue swelling but with
preservation of the joint space, no osteoporosis or calcification.
Pigment is hemosiderin
- Clinical
- Frequent history of antecedent trauma
- Hemorrhagic "chocolate" effusion
- Insidious onset of swelling
- Pain of long duration
- Decreased range of motion
- Joint locking
- Age
- Mainly 2nd-4th decade; 50% <40 years
- F>M
- Location
- Knee (most common)
- Ankle
- Hip
- Elbow
- Shoulder
- Tarsal or carpal joints
- Predominantly monarticular
- Radiographic findings
- Soft-tissue swelling around joint
- From effusion and synovial proliferation
- Dense soft-tissues from hemosiderin deposits
- Subchondral pressure erosions at margins of
joint from hypertrophied synovium
- Multiple sites of deossification appearing as
cysts
- No calcifications
- No osteoporosis
- No joint space narrowing (until late)
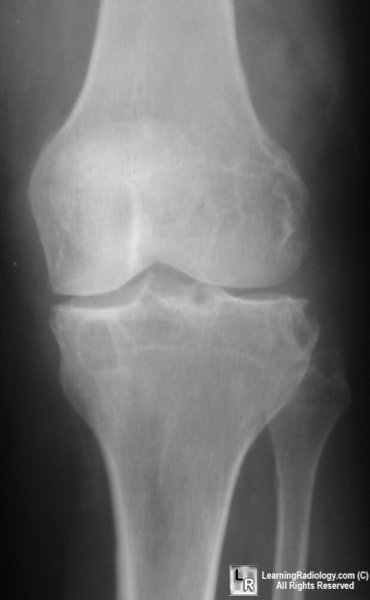 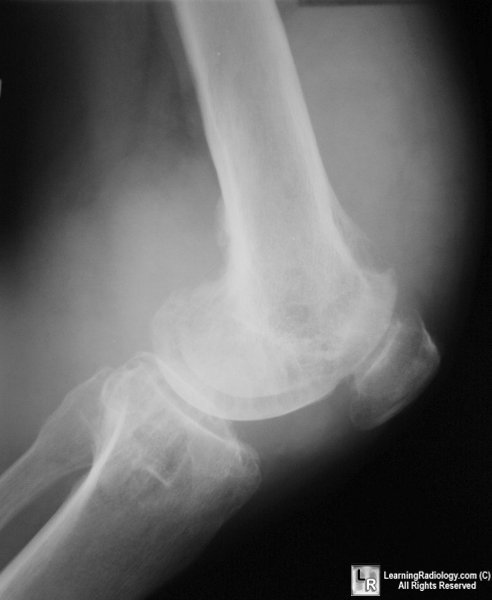
AP and lateral views of the knee demonstrate marked
soft tissue swelling,
cystic changes in both the femur and tibia without significant joint
space narrowing
- MRI findings
- Masses of synovial tissue in a joint with
effusion
- Scalloping / truncation of prefemoral fat pad
- Predominantly low signal intensity on all
sequences (due to presence of iron) (characteristic of this lesion)
- Often heterogeneous low + high signal
intensity on T2WI (hemosiderin deposits in masses + para-articular
fat)
- DDx
- Hemosiderin deposits in other diseases (eg,
rheumatoid arthritis)
- Treatment
- Synovectomy
- Arthrodesis
- Arthroplasty
- Radiation
- DDx
- Synovial sarcoma
- Mass around, but outside of, joint
- Frequently calcify
- Degenerative arthritis
- Joint space narrowing
- Subchondral sclerosis
|
|
|