|
|
Budd-Chiari Syndrome
Hepatic Venous Occlusive Disease
- Obstruction to hepatic venous outflow leads to
increased sinusoidal pressure producing reversed or delayed flow in
portal veins
- Many causes
- Idiopathic most common
- Tumor
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Carcinoma of pancreas
- Carcinoma of kidneys
- Metastatic disease
- Blood dyscrasia
- Leukemia
- Sickle cell disease
- Polycythemia vera
- Birth control pills
- Pregnancy
- Pyrrolizidine alkaloids (senecio) found in
Jamaican tea
- Membranous diaphragm in suprahepatic IVC
- Acutely
- Hepatomegaly and ascites
- Severe symptoms including shock
- Abdominal pain
- Jaundice
- CT
- Hepatomegaly and ascites
- Non-visualization of occluded hepatic veins
- Patchy enhanced appearance with dynamic
imaging
- Inversion of portal blood flow results in
inside-out enhancement of liver
- Caudate lobe is hyperdense early,
decreased later
- Periphery is hypodense early, increased
later
- Then enhancement equilibrates
- Due to reversed portal venous flow
- Enlarged right inferior hepatic vein
- Enlarged portal vein (>12mm in adults)
- Chronically
- Portal hypertension and variceal bleeding
- Enlargement of caudate lobe
- Collateral circulation through azygos and
hemiazygos
- Visualization of paraumbilical vein
- Non-visualization of hepatic veins
- Inversion of portal blood flow results in
inside-out enhancement of liver (see below)
- Periphery is hypodense early
- Then enhancement equilibrates
- Due to reversed portal venous flow
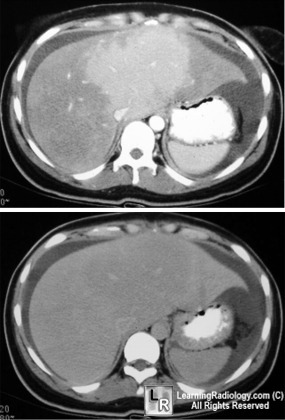
Early and delayed phases of liver enhancement
in Budd-Chiari Syndrome
- Nuclear medicine shows hot caudate lobe with
diminished activity in peripheral zones of liver
- Angiography shows large lakes of sinusoidal
contrast accumulations
- Absence of main hepatic veins
- Diagnosis
- Usually can be made on imaging study
- Treatment
- Anticoagulants
- Surgery
- Balloon dilatation
- TIPS
- Liver transplant
|
|
|