|
Pulmonic Stenosis
•
Pulmonic stenosis without VSD= 8% of all CHD
• Mostly asymptomatic
• When symptomatic, cyanosis and heart failure
• Loud systolic ejection murmur
• Cor
pulmonale
• Rare
calcification of pulmonary valve in older adults
X-ray
• Enlarged main pulmonary artery
• Enlarged left pulmonary artery (jet stream effect)
• Normal to decreased peripheral pulmonary vasculature
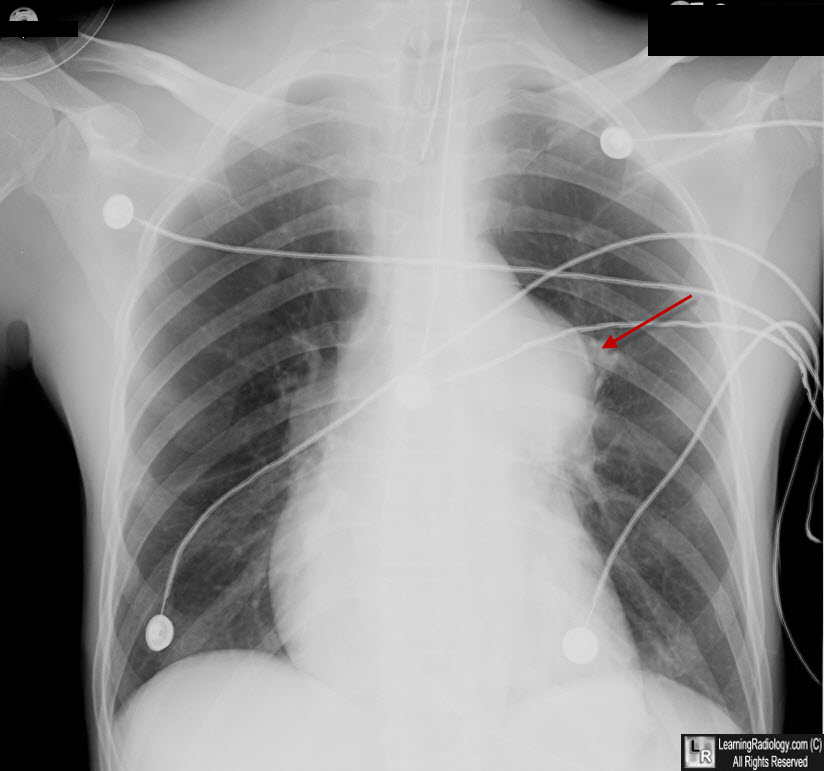
Pulmonic Stenosis. There is post stenotic dilatation of the main pulmonary artery (red arrow) from valvular pulmonic stenosis. This could be presumed to be a mediastinal mass not of vascular origin. A CT scan would be definitive.
Subvalvular pulmonic stenosis
•Infundibular pulmonic stenosis
• Typically in Tetralogy of Fallot
•Subinfundibular pulmonic stenosis
•Associated with VSD (85%)
Valvular Pulmonic Stenosis
• Classic pulmonic stenosis (95%)
• Fusion of pulmonary cusps
• Presents in childhood
• Pulmonic click
• Dome-shaped pulmonic valve
• RX: Balloon valvulo-plasty
Trilogy of Fallot
• Severe pulmonic valvular stenosis
• RV hypertrophy
• ASD with R—L shunt
Supravalvular pulmonic stenosis
•May be either tubular hypoplasia or localized with poststenotic dilatation
•May be associated with:
• Valvular pulmonary stenosis, supravalvular aortic stenosis, VSD, PDA, systemic arterial stenoses
• Williams-Beuren Syndrome: PS, supravalvular AS, peculiar facies
• Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
• Postrubella Syndrome: peripheral pulmonary
stenoses, PDA, low birth weight, deafness, cataracts, mental
retardation
|