|
|
Polyarteritis Nodosa
Periarteritis Nodosa
Submitted by Alexander Trebelev, MD
- Systemic necrotizing inflammation of medium-sized
and small muscular arteries
- More common in adult males
- Spares the arterioles, capillaries, venules and
glomeruli
- Associated with hepatitis B antigenemia
- Signs and symptoms
- Abdominal pain
- Systemic hypertension
- Anorexia and weight loss
- Abdominal distention
- Hematemesis, melena
- Jaundice
- Painless hematuria
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Tender subcutaneous nodules
- Gangrene of fingers and toes
- Kidney (most frequently affected): 85%
- Multiple intrarenal aneurysms
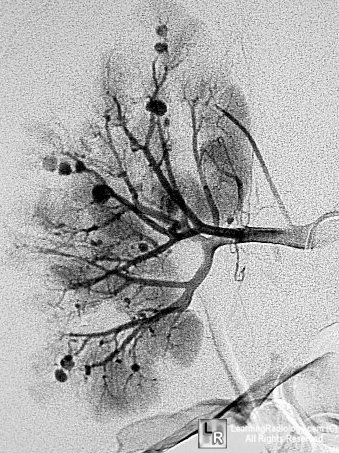
Multiple aneurysms of renal vessels in Polyarteritis
- Aneurysms may thrombose and disappear
- Multiple small cortical infarcts
- Angiographic findings
- 1-5 mm saccular aneurysms of small and
medium-sized arteries in 60-75% of cases
- Secondary to necrosis of internal elastic
lamina
- Luminal irregularities and stenoses
- Arterial occlusions and small tissue infarcts
- Lung (70% of cases)
- Findings are variable and rarely characteristic
enough to allow diagnosis
- Most characteristic pattern is fleeting, patchy
consolidation identical to Loeffler's
- Pericardial effusion
- Pleural effusion
- Discoid atelectasis
- Nodules which may cavitate
- Patchy consolidation
- Liver: affected 66% of cases
- Treatment
- Bockus, Henry L. Gastroenterology, 3rd ed., Vol. 4 Pages 538-541. W. B. Saunders Company, Philadelphia,
London, Toronto, 1976.
- Dahnert, Wolfgang Radiology Review Manual, 4th ed. Page 533, Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia,
Baltimore, etc., 2000.
|
|
|